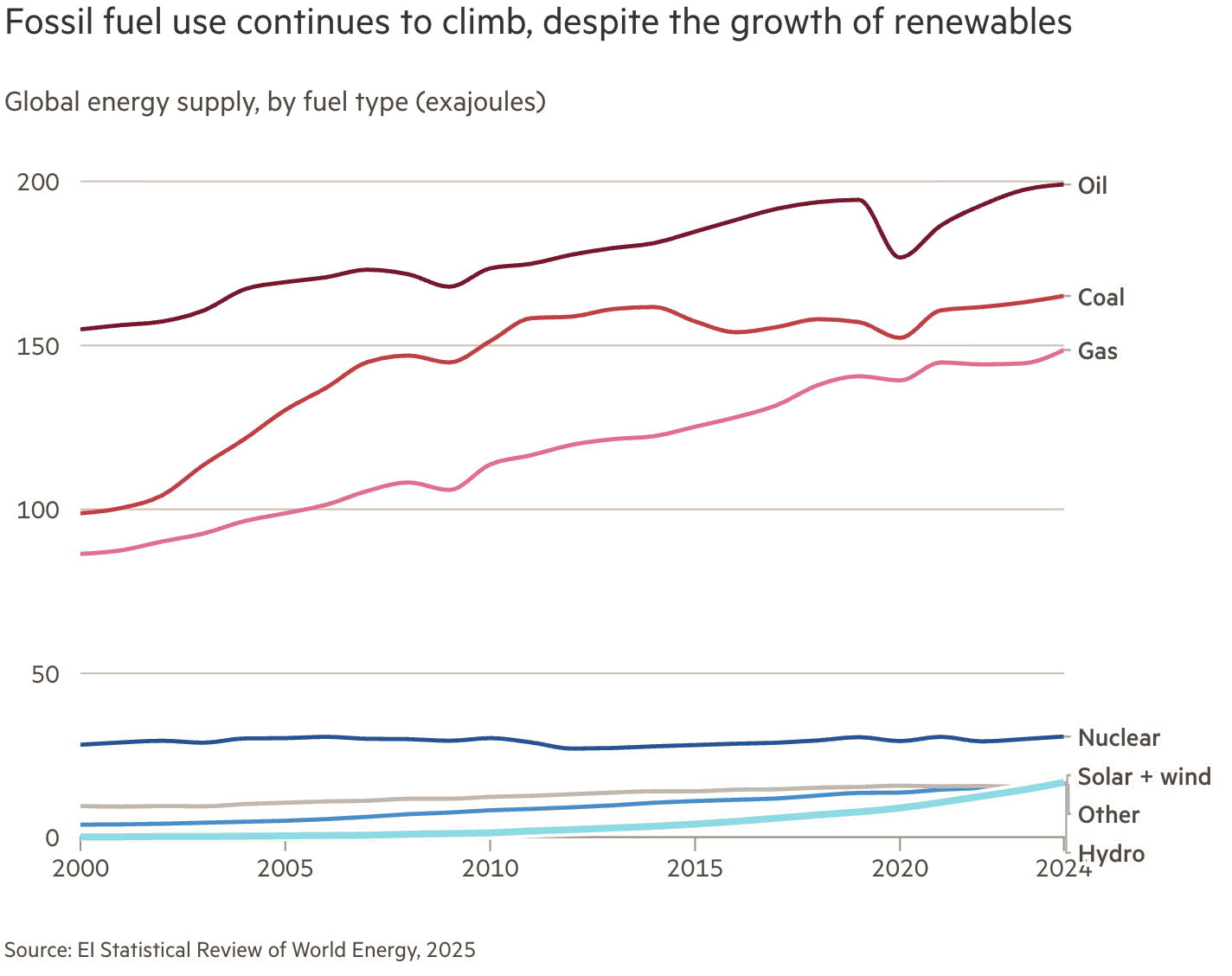
Washington D.C. – The United States is experiencing a dramatic slowdown in the projected growth of renewable energy sources, a trend directly linked to recent policy decisions. The International Energy Agency (IEA) has revised its forecast for renewable energy expansion downwards, now anticipating approximately 250 gigawatts of new capacity by 2030 – a important reduction from previous estimates. Experts predict this shift could lead to a considerable increase in carbon emissions, potentially adding 7 billion metric tons of CO₂ equivalent by the end of the decade.
Rising Electricity Demand Fuels Fossil Fuel Reliance
Table of Contents
- 1. Rising Electricity Demand Fuels Fossil Fuel Reliance
- 2. Energy Costs on the Rise
- 3. US Loses Ground in Global Energy Transition
- 4. The Long-Term Implications of Energy Policy
- 5. Frequently Asked Questions About renewable Energy
- 6. What are the primary impacts of supply chain disruptions on U.S.solar energy companies?
- 7. The United States’ Solar Energy Downturn: Understanding Why U.S. Lags Behind the Global Boom
- 8. the Shifting Landscape of U.S. Solar Power
- 9. Key Factors Driving the U.S.Solar Slowdown
- 10. U.S. vs. global Solar Growth: A Comparative Look
- 11. The Impact on Consumers & Homeowners
- 12. Navigating the Current Market: Tips for Consumers
- 13. The Future of U.S. Solar: Opportunities for Growth
This deceleration in renewable adoption coincides with a surge in national electricity demand, largely driven by the proliferation of data centers. These energy-intensive facilities frequently enough require a consistent and unwavering power supply, increasingly turning to gas-fired power plants and nuclear energy as solutions. Turbine manufacturers specializing in gas technology are currently facing substantial order backlogs, while the development of new nuclear plants is consistently plagued by delays.
Energy Costs on the Rise
The Energy Information Governance reports that retail electricity prices have already climbed by 5 percent as July, and analysts caution that further increases are likely if supply fails to keep pace with demand. Pol Lezcano, Director of Energy and Renewables at CBRE, cautions, “The writing is on the wall,” suggesting that consumers shoudl brace for potentially higher energy bills. While renewable energy sources offer lower wholesale costs due to free resources such as sunlight and wind, developers require financial returns on their investments, and grid operators must maintain a stable supply when renewable output is limited.
“Even as the cost of producing electricity from renewables falls, consumers may not see immediate or proportional reductions in their bills, raising questions over the impact of renewables on power affordability,” stated the IEA in its most recent analysis.
US Loses Ground in Global Energy Transition
Beyond domestic impacts, the US’s diminished commitment to renewable energy is ceding global leadership in the energy transition to China. The nation is actively pursuing trade agreements that prioritize the sale of American fossil fuels – including oil, natural gas, and nuclear technologies – to countries like those within the European Union, potentially undermining international efforts to decarbonize industries like shipping. Despite this, the decreasing cost of solar technology in other parts of the world presents a compelling counter-narrative.
experts warn that the current policies could inflict lasting damage on the US’s competitiveness against China in the renewable energy sector.Antonio Cammisecra,Chief Executive of ContourGlobal,asserts,”China has run far away in terms of competitiveness,” and rebuilding US capabilities will require a considerable investment of time and resources.
| Metric | Previous Forecast (2030) | current Forecast (2030) | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Capacity (GW) | 500 | 250 | -50% |
| Projected CO₂ Emissions Increase (by 2030) | N/A | 7 billion tonnes equivalent | N/A |
| Retail Electricity Price Increase (Since July) | N/A | 5% | N/A |
Did You Know? The US Department of energy’s Loan Programs Office has over $100 billion in funding available to support innovative clean energy projects.
Pro Tip: Businesses and homeowners can explore federal and state tax incentives to offset the cost of installing renewable energy systems.
What role should government play in incentivizing renewable energy development? And how can the U.S. regain its competitive edge in the global clean energy market?
The Long-Term Implications of Energy Policy
The decisions made today regarding energy policy will have far-reaching consequences for future generations. A sustained commitment to renewable energy sources is not only crucial for mitigating climate change but also for fostering economic innovation, creating jobs, and enhancing energy security.The transition to a cleaner energy future requires a comprehensive strategy that incorporates investments in research and development, infrastructure upgrades, and supportive regulatory frameworks.
Frequently Asked Questions About renewable Energy
- What is the primary driver of the slowdown in US renewable energy growth? Policy shifts and increased demand for consistent power from data centers are key factors.
- How will reduced renewable energy growth impact carbon emissions? Experts estimate a potential increase of 7 billion tonnes of CO₂ equivalent by 2030.
- Are renewable energy sources always cheaper than fossil fuels? While wholesale costs are lower, developers need returns on investment, and grid stability can add expenses.
- What is China’s role in the global energy transition? China is rapidly gaining a competitive advantage in renewable energy technologies.
- What can be done to revitalize renewable energy growth in the US? Investments in research,infrastructure,and supportive policies are essential.
- How do data centers impact energy demand? Data centers require a constant and reliable power supply, often opting for fossil fuels or nuclear energy.
- What impact are current energy policies having on consumers? Electricity prices are already rising,and further increases are anticipated.
Share this article with your network and join the conversation in the comments below!
What are the primary impacts of supply chain disruptions on U.S.solar energy companies?
The United States’ Solar Energy Downturn: Understanding Why U.S. Lags Behind the Global Boom
the Shifting Landscape of U.S. Solar Power
Recent months have seen a noticeable slowdown in the U.S. solar energy sector. While global solar installations continue to surge, the United States is experiencing a downturn, prompting questions about its competitiveness and future in the renewable energy market. This isn’t necessarily a sign of failure, but rather a “necessary reset” as highlighted by industry analysts, signaling unsustainable practices catching up. Understanding the factors contributing to this shift is crucial for both investors and consumers interested in solar panel installation, renewable energy investment, and the broader clean energy transition.
Key Factors Driving the U.S.Solar Slowdown
Several interconnected issues are contributing to the current state of the U.S. solar industry. These extend beyond simple market fluctuations and point to systemic challenges.
* Supply Chain Disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions have substantially disrupted global supply chains, impacting the availability and cost of key components like solar panels, inverters, and battery storage systems. This has led to project delays and increased costs for solar energy companies.
* Trade Policies & Tariffs: U.S. trade policies, including tariffs on imported solar components, have added to the cost of solar power systems. While intended to protect domestic manufacturing, these tariffs have, in some cases, hindered growth and competitiveness. The Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention act (UFLPA) has also created notable hurdles for sourcing materials.
* Interest Rate Hikes: Rising interest rates have made financing solar projects more expensive, impacting both utility-scale developments and residential solar financing options. This affects the return on investment for developers and increases the upfront cost for homeowners.
* Net Metering Policy Changes: Changes to net metering policies in several states have reduced the financial incentives for homeowners to install residential solar panels. Net metering allows homeowners to receive credit for excess energy sent back to the grid, and reductions in these credits diminish the economic benefits of solar energy.
* Labor Shortages: A skilled labor shortage in the solar installation industry is hindering project completion and driving up labor costs. This impacts the speed and efficiency of renewable energy projects across the country.
* Grid Interconnection Challenges: Connecting solar energy systems to the existing power grid can be a lengthy and complex process, often involving significant costs and delays. Grid modernization is crucial for accommodating the increasing influx of renewable energy sources.
U.S. vs. global Solar Growth: A Comparative Look
While the U.S. faces these challenges, othre countries are experiencing robust solar growth.
* China: Remains the global leader in solar manufacturing and installation,benefiting from government support,economies of scale,and a streamlined regulatory environment.
* Europe: Driven by ambitious climate goals and energy security concerns, Europe is rapidly expanding its solar capacity, notably in countries like Germany, Spain, and Italy.
* India: Is experiencing significant growth in solar energy, fueled by declining costs and government incentives.
* australia: Has a high rate of residential solar adoption due to favorable policies and abundant sunshine.
These regions have often prioritized long-term planning, consistent policy support, and investment in grid infrastructure – areas where the U.S. has lagged.
The Impact on Consumers & Homeowners
The U.S. solar downturn directly impacts consumers considering solar panel installation.
* increased Costs: Higher component prices and financing costs translate to more expensive solar systems.
* Longer Wait Times: Supply chain issues and labor shortages can lead to longer installation timelines.
* Reduced Incentives: Changes to net metering and other incentives may decrease the financial benefits of going solar.
* Company Instability: Some solar companies are facing financial difficulties,potentially leading to project cancellations or warranty issues.
Despite the challenges, going solar can still be a smart investment. Here’s how to navigate the current market:
- Shop Around: Get quotes from multiple solar installers and compare pricing, warranties, and financing options.
- Research Company Stability: Choose a financially stable solar company with a proven track record.
- Understand Net Metering: Familiarize yourself with your state’s net metering policies and how they will impact your savings.
- Explore Financing Options: Consider various solar financing options, including loans, leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs).
- Factor in tax Credits: Take advantage of federal and state solar tax credits to reduce the overall cost of your system. The Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is a significant benefit.
- Consider Battery Storage: Solar battery storage can increase energy independence and provide backup power during outages.
The Future of U.S. Solar: Opportunities for Growth
Despite the current downturn, the long
