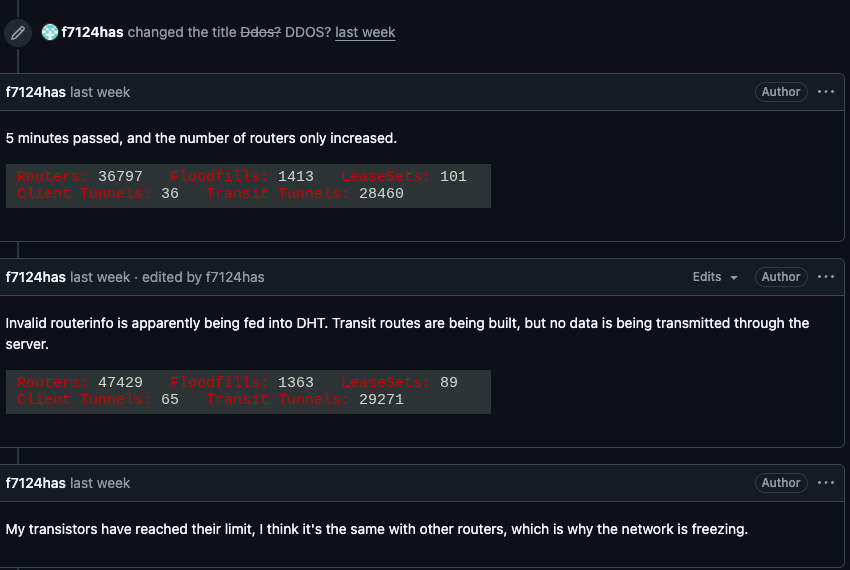
Stay ahead with breaking tech news, gadget reviews, AI & software innovations, cybersecurity tips, start‑up trends, and step‑by‑step how‑tos.
Netflix is experimenting with a novel approach to live event engagement, transforming a theatrical performance of “Stranger Things: The First Shadow” into an interactive experience for audiences. A recent performance saw Netflix recording the show, culminating in a surprise element at the end designed to engage viewers beyond the traditional screen.
The initiative marks a continued push by Netflix to blend live entertainment with interactive features, building on the platform’s recent rollout of real-time voting capabilities. This move aims to deepen audience involvement and create a more immersive experience, particularly for highly anticipated productions like the “Stranger Things” prequel. The company first tested live voting in August 2025 with “Dinner Time Live with David Chang,” and has since expanded the feature to shows like “Star Search,” allowing viewers to influence outcomes directly through their devices or TV remotes.
Attendees at a showing on February 16, 2026, witnessed the recording process, with a unique surprise incorporated at the conclusion of the performance. While details of the surprise remain largely undisclosed, the event signals Netflix’s intention to leverage live performances as opportunities for interactive storytelling. This approach aligns with the company’s broader strategy of integrating content and technology, as highlighted by Netflix CTO Elizabeth Stone, who previously stated the goal is to allow viewers to “feel like they’re part of the story, influence the storyline, and feel immersed” (TechCrunch).
How Netflix is Expanding Interactive Features
Netflix’s foray into interactive live events isn’t limited to voting. The platform has also been exploring interactive games on smart TVs and live broadcasts of sporting events, including NFL Christmas specials and WWE shows. The integration of these elements suggests a broader vision for Netflix as not just a streaming service, but as a dynamic entertainment hub. The real-time voting feature, available globally, allows viewers to cast votes using their TV remote or the Netflix mobile app during specific moments within a live event (Netflix Help Center). Votes are tallied in real-time, and viewers receive immediate feedback on the results (TechCrunch).
The “Stranger Things” initiative builds on Netflix’s January 20, 2026, announcement that viewers could play a role in live events with real-time voting (Netflix About). “Star Search” was identified as the first event to utilize this feature, paving the way for further interactive experiences across the platform. Viewers participating in real-time voting agree to the Star Search At-Home Audience Voting Rules, available at netflix.com/votingrules.
Implications for Live Entertainment
This move towards interactive live events could significantly alter the landscape of entertainment consumption. By empowering viewers to actively participate in the unfolding narrative, Netflix is attempting to foster a stronger sense of community and engagement. The success of this approach will likely depend on the seamless integration of the interactive elements and the ability to maintain a compelling viewing experience. The limited voting window and the inability to change votes once submitted are designed to ensure the integrity of the process and encourage real-time participation (Netflix Help Center).
As Netflix continues to experiment with these features, it will be crucial to monitor audience response and refine the interactive elements to maximize their impact. The platform’s ability to successfully blend live entertainment with technology could set a new standard for audience engagement and pave the way for a more immersive and participatory future of streaming.
The integration of interactive elements into “Stranger Things: The First Shadow” represents a significant step in Netflix’s ongoing efforts to innovate the streaming experience. The company’s continued investment in live content and interactive features suggests a long-term commitment to creating more engaging and immersive entertainment for its subscribers. What comes next for Netflix’s interactive initiatives remains to be seen, but the platform’s recent moves indicate a clear direction towards a more participatory and dynamic future of streaming.
What are your thoughts on Netflix’s interactive approach to live events? Share your opinions in the comments below!