“`html
Consumer Confidence Declines Ahead of Autumn Budget Announcement
Table of Contents
- 1. Consumer Confidence Declines Ahead of Autumn Budget Announcement
- 2. Budget Concerns Weigh on Consumer Sentiment
- 3. Retail Sector Echoes Consumer Concerns
- 4. Personal Finances Under Pressure
- 5. Understanding Consumer Confidence
- 6. Frequently Asked Questions
- 7. How might loss aversion influence consumer responses to potential tax increases announced in the upcoming budget?
- 8. Consumer Confidence Declines Prior to Government Budget Announcement: Implications and Analysis
- 9. The Current Dip in Consumer Sentiment
- 10. Impact on Key Economic Sectors
- 11. Government Budget Announcement: What to Watch For
- 12. Past Precedents & Case Studies
- 13. Implications for Investors & Businesses
- 14. Understanding Consumer Psychology & Behavioral Economics
Updated: Thursday, September 18, 2025, 4:34 PM
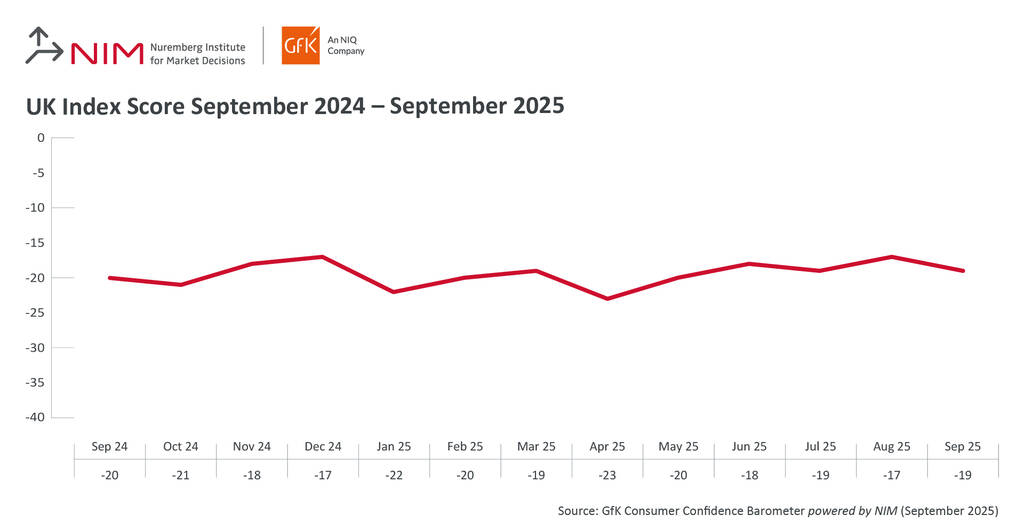
London, UK – A fresh wave of economic uncertainty is sweeping across the united Kingdom, as Consumer Confidence has fallen amid growing anticipation of tax hikes in the upcoming November Budget. New data released by GfK reveals a two-point decrease in the Consumer Confidence Index, landing at -19 for September. Every measure tracked by the Index registered a decline compared to the previous month.
Budget Concerns Weigh on Consumer Sentiment
Economists are projecting that Chancellor Rachel Reeves will be forced to implement approximately £25 billion in tax increases or spending cuts to maintain fiscal stability. Discussions are focusing on potential changes to property taxes, rental income levies, pension taxation, gambling regulations, and inheritance taxes. The Shadow Chancellor faces intense pressure to balance economic responsibility with Labour’s commitment to public services.
“There’s an autumnal chill in the air this month,” noted Neil Bellamy,a leading analyst at GfK. “With tax rises expected in the November Budget, the risk is that confidence inevitably falls, just like the autumn leaves.”
Retail Sector Echoes Consumer Concerns
The british Retail Consortium (BRC) mirrored GfK’s findings, reporting a drop in consumer confidence in September. Expectations regarding the overall economic situation worsened to -36,a notable decline from -32 in August. Personal financial outlooks also weakened, falling to -7 in September.
Helen Dickinson, Chief Executive of the BRC, emphasized that Budget-related anxieties, coupled with persistent cost-of-living pressures, are eroding consumer optimism. She noted that there is little indication of a considerable decrease in inflation in the near future.
Personal Finances Under Pressure
Confidence in personal finances dropped three points to -7 in September, while forward-looking expectations for personal finances over the next year fell by one point, reaching a level of four. Rising food costs are exacerbating these concerns. Core food price inflation reached 5.1 percent over the 12-month period, marking the fifth consecutive increase.
The Bank of England recently maintained its current interest rates, citing ongoing inflationary pressures in the food and services sectors. Governor andrew Bailey cautioned that the UK is not yet out of the woods regarding economic recovery.
Bellamy added, “The August decrease in interest rates does not appear to have provided any obvious boost to the financial mood of consumers or drawn attention away from day-to-day cost issues. Looking at the economy, sentiment is sliding sharply.”
| Indicator | September 2025 | August 2025 |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Confidence Index | -19 | -17 |
| Expectations for Overall Economy | -36 | -32 |
| Personal Financial Situation (Current) | -7 | -4 |
| Personal Financial Situation (Future) | 4 | 5 |
Did You Know? Consumer confidence is a leading economic indicator, often foreshadowing changes in consumer spending patterns.
Pro tip: Track key economic indicators like the Consumer confidence Index and inflation rates to gain insights into potential market trends.
Understanding Consumer Confidence
Consumer confidence is not just about feelings; it’s a vital component of economic health. When people are confident about their finances and the future, they are more likely to spend money, which drives economic growth. Conversely,low consumer confidence can lead to decreased spending and economic slowdowns. Several factors influence consumer confidence, including employment rates, inflation, interest rates, and government policies. Monitoring these factors provides a holistic view of the economic landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is consumer confidence? Consumer confidence measures the degree of optimism that consumers feel about the overall state of the economy and their personal financial situation.
- How is consumer confidence measured? The Consumer Confidence Index is typically calculated through surveys that ask consumers about their views on current economic conditions and future expectations.
- Why is consumer confidence vital? Because it influences spending habits and therefore, economic growth.
- What factors affect consumer confidence? Factors include employment levels, inflation, interest rates, income levels, and government regulations.
- How does the Autumn Budget impact consumer confidence? Tax changes and spending plans announced
How might loss aversion influence consumer responses to potential tax increases announced in the upcoming budget?
Consumer Confidence Declines Prior to Government Budget Announcement: Implications and Analysis
The Current Dip in Consumer Sentiment
Recent data indicates a meaningful decline in consumer confidence leading up to the upcoming government budget announcement.This isn’t simply a fleeting reaction; several key economic indicators point to a growing unease among households. The Conference Board’s Consumer Confidence Index,a widely-tracked metric,fell sharply in September 2025,registering its lowest level in six months. This drop is fueled by concerns surrounding inflation,potential interest rate hikes,and the overall economic outlook.
Several factors are contributing to this downturn:
* rising Cost of Living: Persistent inflation,especially in essential goods like food and energy,is eroding purchasing power.
* Job Market Uncertainty: While unemployment remains relatively low,there are increasing reports of hiring freezes and layoffs in certain sectors.
* Geopolitical Instability: Global events contribute to economic uncertainty, impacting investor and consumer sentiment.
* Housing Market Cool-Down: Rising mortgage rates are slowing down the housing market,impacting both potential buyers and homeowners.
Impact on Key Economic Sectors
The decline in consumer spending – a major driver of economic growth – is already being felt across various sectors.
* Retail Sales: Early September data shows a slowdown in retail sales, particularly in discretionary spending categories like apparel and electronics. Retail sector analysts are bracing for a potentially challenging holiday season.
* Automotive Industry: Car sales are also experiencing a dip, as consumers postpone large purchases due to economic uncertainty and higher financing costs.
* Travel and Leisure: While still relatively robust, the travel and leisure sector is showing signs of softening demand, with consumers becoming more price-sensitive.
* Housing Market: As mentioned, the real estate market is cooling, with declining home sales and a slowdown in price growth. This impacts related industries like construction and home improvement.
Government Budget Announcement: What to Watch For
The upcoming government budget announcement is now under intense scrutiny. The measures outlined in the budget will likely have a significant impact on market sentiment and consumer confidence. Key areas to watch include:
- Fiscal Policy: Will the government prioritize spending on social programs, infrastructure, or tax cuts? The approach taken will signal its commitment to supporting households and stimulating economic growth.
- Inflation Control Measures: What steps will the government take to address persistent inflation? This could include measures to curb government spending, tighten monetary policy, or address supply chain bottlenecks.
- Taxation: Any changes to tax policies will directly impact disposable income and consumer spending.
- Debt Management: The government’s plan for managing its debt will be closely watched by investors and rating agencies.
Past Precedents & Case Studies
Looking back, similar declines in consumer optimism before budget announcements have often foreshadowed significant policy shifts.
* The 2008 Financial Crisis: A sharp drop in consumer confidence in the months leading up to the crisis signaled the impending economic downturn. government intervention,including stimulus packages and bank bailouts,was ultimately required to stabilize the economy.
* Post-Pandemic Recovery (2021-2022): Initial optimism following the pandemic was quickly tempered by rising inflation and supply chain disruptions. Government responses, including targeted relief measures, aimed to mitigate the impact on households.
* Japan’s Lost Decade (1990s): Prolonged economic stagnation in Japan was partly attributed to a lack of decisive government action and a failure to restore consumer confidence.
Implications for Investors & Businesses
The current surroundings presents both challenges and opportunities for investors and businesses.
* defensive Stocks: Investors may shift towards defensive stocks – companies that provide essential goods and services – which tend to be less affected by economic downturns. Examples include utilities,healthcare,and consumer staples.
* Value Investing: Focusing on value stocks – companies that are undervalued by the market – can offer potential upside in a volatile environment.
* Cash Reserves: Businesses should prioritize maintaining healthy cash reserves to weather potential economic headwinds.
* Cost Management: Implementing strict cost management measures is crucial for preserving profitability.
* Innovation & Efficiency: Investing in innovation and improving operational efficiency can definitely help businesses gain a competitive edge.
Understanding Consumer Psychology & Behavioral Economics
The decline in consumer confidence isn’t solely based on rational economic calculations. Behavioral economics plays a significant role.
* Loss Aversion: People tend to feel the pain of a loss more strongly than the pleasure of an equivalent gain. This can lead to increased risk aversion and reduced spending.
* Anchoring Bias: Consumers often rely on initial data (the “anchor”) when making decisions, even if that information is irrelevant. Negative news headlines can serve as an
