Vast Array of Professional Specialties Highlighted in Recent Data Compilation
Table of Contents
- 1. Vast Array of Professional Specialties Highlighted in Recent Data Compilation
- 2. A Deep Dive into Medical Specialties
- 3. Beyond Traditional Medicine: A Spectrum of Expertise
- 4. A Comparative Overview of Select Specialties
- 5. The Importance of Identifying Expertise
- 6. staying Informed on Professional Growth
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions about Professional Specialties
- 8. What are the primary mechanisms by which tranexamic acid exerts its hemostatic effects?
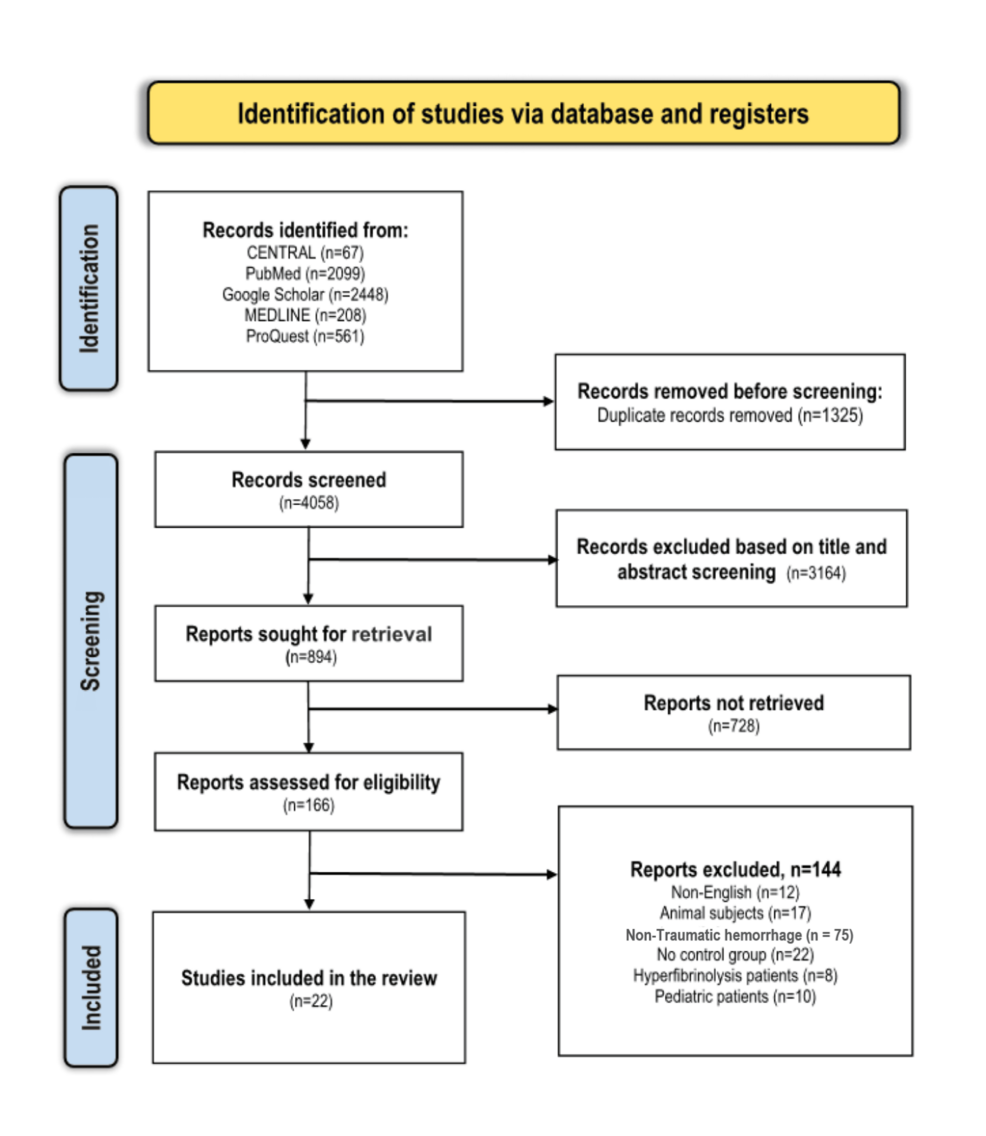
- 9. Efficacy of Tranexamic acid in Traumatic Hemorrhage Management: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 10. Understanding Tranexamic Acid (TXA) & Hemorrhage Control
- 11. Methodology of Recent Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- 12. TXA in Severe Traumatic Injury: Key Findings
- 13. TXA in Specific Trauma scenarios
- 14. Adverse Effects and Safety Considerations
- 15. Practical Implementation & Protocols
New data reveals a remarkably extensive spectrum of professional specialties, encompassing a wide array of fields. The details, recently compiled, underscores the depth and breadth of expertise available across various industries, with a heavy emphasis on medical and healthcare professions.Understanding these specialties is crucial for individuals exploring career paths and for those seeking specialized care.
A Deep Dive into Medical Specialties
The compilation showcases an impressive list of medical fields, ranging from highly specialized areas like Allergy and Immunology and Cardiac/Thoracic/Vascular Surgery, to more general disciplines such as Family Medicine and Internal Medicine. Several subspecialties are also represented, reflecting the ever-evolving nature of medical practice. The detailed breakdown provides a valuable resource for prospective medical students and healthcare professionals evaluating their options.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, healthcare occupations are projected to grow 13 percent from 2021 to 2031, much faster than the average for all occupations. (Bureau of Labor Statistics) This growth is driven by an aging population and advancements in medical technology.
Beyond Traditional Medicine: A Spectrum of Expertise
The data extends beyond conventional medical fields, including specialties such as Anatomy, Biostatistics, and Medical Physics. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of emerging areas like health Policy and Integrative/Complementary Medicine. The inclusion of these fields demonstrates a growing recognition of the interconnectedness of healthcare with broader societal and scientific advancements.
A Comparative Overview of Select Specialties
to illustrate the diversity, here’s a comparative look at a few highlighted specialties:
| Specialty | Focus | Typical Work Environment |
|---|---|---|
| cardiology | Heart and blood vessel health | Hospitals, clinics, private practice |
| Neurology | nervous system disorders | Hospitals, clinics, research institutions |
| Psychiatry | Mental health and emotional well-being | Hospitals, clinics, private practice |
| Radiology | Medical imaging for diagnosis | Hospitals, imaging centers |
Did You Know? The field of Biostatistics is increasingly crucial in analyzing medical data and improving healthcare outcomes.
The Importance of Identifying Expertise
The comprehensive list underlines the need for clear identification of professional expertise, notably within the healthcare sector. Accurate categorization of specialties ensures patients can access the care they need from qualified professionals.Furthermore, it facilitates effective dialog and collaboration among healthcare providers.
Pro Tip: When seeking a specialist, always verify their credentials and ensure they are board-certified in their respective field.
The data also reveals a notable number of individuals identifying as ‘not a medical professional’, highlighting the broad range of backgrounds accessing and utilizing this information.This underscores the importance of accessible and understandable resources for all.
staying Informed on Professional Growth
The landscape of professional specialties is constantly evolving. Continuous education and professional development are essential for maintaining expertise and adapting to new advancements. Resources like the American Medical Association (AMA) and various specialty-specific organizations offer valuable information and training opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions about Professional Specialties
what are your thoughts on the growing number of specialized fields? Do you believe this trend benefits patients and professionals alike?
Share this article with your network and join the conversation below!
What are the primary mechanisms by which tranexamic acid exerts its hemostatic effects?
Efficacy of Tranexamic acid in Traumatic Hemorrhage Management: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Understanding Tranexamic Acid (TXA) & Hemorrhage Control
Tranexamic acid (TXA), an antifibrinolytic medication, has become increasingly central to the management of traumatic hemorrhage. Its mechanism centers around inhibiting the breakdown of blood clots, thereby promoting hemostasis. This article delves into a systematic review and meta-analysis of current evidence regarding TXAS efficacy in diverse traumatic scenarios. We’ll explore its use in both civilian and military settings, focusing on key outcomes like mortality, transfusion requirements, and complications. Keywords: tranexamic acid, traumatic hemorrhage, hemorrhage control, antifibrinolytic, TXA, bleeding management, trauma care.
Methodology of Recent Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
Recent comprehensive analyses, including those published in leading trauma journals, have employed rigorous methodologies. These typically involve:
* Search Strategy: Utilizing databases like PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library with predefined search terms (e.g., “tranexamic acid,” “trauma,” “hemorrhage,” “bleeding”).
* Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria: Studies are selected based on specific criteria – often randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating TXA administration in trauma patients with significant bleeding. Exclusion criteria commonly involve studies with poor methodological quality or irrelevant patient populations.
* Data Extraction: Standardized data extraction forms are used to collect facts on patient demographics, injury severity, TXA dosage, timing of administration, and key outcomes.
* Statistical Analysis: Meta-analysis is performed using appropriate statistical models (e.g., random-effects models) to pool data from multiple studies and estimate overall treatment effects. Heterogeneity is assessed using I² statistics.
TXA in Severe Traumatic Injury: Key Findings
The evidence base regarding TXA in severe traumatic injury is substantial, though nuanced.
* CRASH-2 Trial Impact: The landmark CRASH-2 trial demonstrated a significant reduction in mortality in trauma patients receiving TXA within three hours of injury. This trial, involving over 20,000 patients, remains a cornerstone of TXA recommendations.
* Subgroup Analyses: Subsequent analyses have identified potential subgroups that may benefit most from TXA. These include patients with:
* Blunt Trauma: Evidence suggests a more pronounced benefit in blunt trauma compared to penetrating trauma.
* Significant Hypotension: Patients presenting with hypotension (systolic blood pressure <90 mmHg) appear to derive greater benefit.
* Head Injury: The role of TXA in traumatic brain injury (TBI) remains controversial, with some studies suggesting potential harm. Ongoing research is crucial.
* Timing of Administration: Early administration of TXA (within the first hour of injury, often termed “prehospital TXA”) is increasingly advocated. Delays in administration appear to diminish its effectiveness. Prehospital TXA is a growing area of focus.
TXA in Specific Trauma scenarios
The efficacy of TXA varies depending on the specific type of trauma.
* Penetrating Trauma: While the CRASH-2 trial included penetrating trauma patients, the benefit appears less consistent than in blunt trauma. Some studies have even suggested a potential increase in adverse events (e.g., thromboembolic complications) in this population.
* Military Trauma: TXA has been widely adopted in military settings due to the high incidence of severe hemorrhage. Studies from combat zones have generally shown a positive impact on mortality and transfusion requirements.
* Orthopedic Trauma: TXA is routinely used in major orthopedic surgeries (e.g., hip and knee arthroplasty) to reduce blood loss and transfusion needs. its use in fracture-related hemorrhage is also gaining traction.
* Pelvic Fracture Hemorrhage: Pelvic fractures are a significant cause of traumatic hemorrhage. TXA, combined with pelvic binding techniques, can be a life-saving intervention.
Adverse Effects and Safety Considerations
While generally considered safe, TXA is not without potential adverse effects.
* Thromboembolic Events: The primary concern is an increased risk of thromboembolic complications (e.g.,deep vein thrombosis,pulmonary embolism). This risk appears to be relatively low,but should be considered,especially in patients with pre-existing risk factors.
* Visual Disturbances: TXA can cause transient visual disturbances, especially with high doses or prolonged use.
* Seizures: Rarely, TXA has been associated with seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment.
* Cardiac Events: Some studies have raised concerns about a potential association between TXA and increased risk of cardiac events,but this remains controversial. TXA side effects require careful monitoring.
Practical Implementation & Protocols
Successful implementation of TXA protocols requires a coordinated approach.
- Education & Training: Healthcare providers (paramedics, emergency physicians, surgeons) must be thoroughly trained on TXA administration, indications, and potential adverse effects.
- Standardized Protocols: Clear, evidence-based protocols should be established for TXA use in different trauma scenarios.
- Early Administration: Prioritize early administration of TXA,ideally within the first hour of injury. *Rapid