GitHub Tightens npm Security Amid Rising Attacks
Table of Contents
- 1. GitHub Tightens npm Security Amid Rising Attacks
- 2. Hundreds of Packages Compromised
- 3. New security Measures on the horizon
- 4. What is Trusted publishing?
- 5. Gradual Rollout and Ongoing Concerns
- 6. Understanding Supply Chain Security
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions about npm Security
- 8. What is the primary reason GitHub is phasing out support for weak security options in the npm registry?
- 9. GitHub to Ban Weak Security Options for npm Registry Users
- 10. Understanding the Shift in npm Security
- 11. What Security Options Are Being targeted?
- 12. Why is GitHub Making This Change?
- 13. Impact on npm Package Publishers
- 14. Benefits of Enhanced npm Security
- 15. Practical Tips for Secure npm Package Management
- 16. Real-World Examples of npm Security Breaches
GitHub,the owner of the widely-used npm registry for JavaScript packages,is implementing heightened security protocols in response to a recent wave of malicious incidents. September has proven notably challenging for the platform, witnessing targeted phishing attacks aimed at package maintainers and the compromise of hundreds of packages through secret-stealing malware.
Hundreds of Packages Compromised
xavier René-Corail,the Security Lab Lead at GitHub,revealed that over 500 compromised packages have been removed from the registry. Additional packages have been blocked from upload pending thorough security scans. This swift action underscores the severity of the threat and GitHub’s commitment to safeguarding the npm ecosystem.
New security Measures on the horizon
René-Corail detailed upcoming changes designed to reinforce security standards. Several legacy authentication methods, including classic tokens and one-time passwords for two-factor authentication (2FA), will be phased out in the near future. Token lifespans will also be shortened, and a transition is underway to prioritize trusted publishing and require 2FA for local publishing by default.
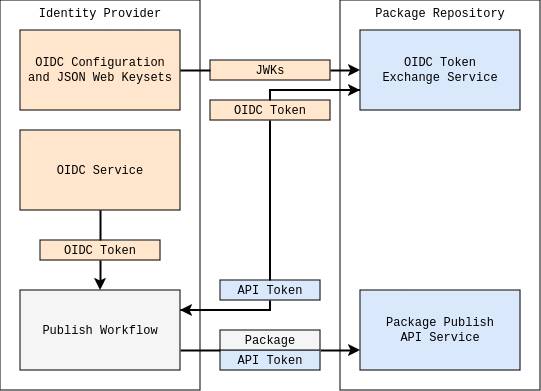
The workflow for trusted publishing
What is Trusted publishing?
Trusted publishing, initially adopted by the PyPI package index, offers an automated security framework. Leveraging OpenID Connect, it verifies the origin of packages, issuing short-lived tokens to mitigate the risks associated with long-lived credentials. Currently, npm’s trusted publishing feature is compatible with GitHub Actions and GitLab CI/CD pipelines. Similar functionality is now being rolled out to other package repositories, including RubyGems, crates.io (rust), and Microsoft’s nuget for.NET,with NuGet’s implementation announced yesterday.
| Package Manager | Trusted publishing Support |
|---|---|
| npm | GitHub Actions, GitLab CI/CD |
| PyPI | Full Support |
| RubyGems | Expanding support |
| crates.io | Expanding Support |
| NuGet | Recently Launched |
Gradual Rollout and Ongoing Concerns
While the team initially planned a phased rollout of trusted publishing, René-Corail acknowledged that the urgency of the situation – “attackers are not waiting” – necessitates accelerating the process. Though, recognizing the potential disruption to existing workflows, the changes will be implemented gradually, with a firm enforcement timeline yet to be announced. A key challenge is accommodating developers who do not utilize GitHub Actions or GitLab CI/CD, with plans to broaden support for additional providers.
Despite the benefits of trusted publishing, some developers have raised concerns. Andrey Sitnik,a maintainer of the popular PostCSS project,expressed doubts about relying solely on OpenID Connect via CI, citing the risk of malware within project dependencies perhaps compromising the publishing process. Other developers have argued that OpenID Connect simply shifts the authentication responsibility and called for additional security layers, such as multi-signature requirements.
Understanding Supply Chain Security
These security enhancements address critical vulnerabilities in the software supply chain. A compromised package can introduce malicious code into countless applications, creating a cascading effect of security breaches. the move to trusted publishing and stronger authentication methods aims to prevent attackers from injecting harmful code into the npm ecosystem. Organizations are increasingly prioritizing supply chain security, implementing robust dependency scanning and vulnerability management practices. The Dependency Track project, such as, offers a free tool for analyzing software components and identifying potential security risks. Staying informed about these developments is essential for all developers and organizations that rely on open-source packages.
Frequently Asked Questions about npm Security
- What is npm?
- npm is the package manager for JavaScript, used to distribute and manage code modules.
- Why is npm security important?
- Compromised npm packages can introduce malware into applications, impacting millions of users.
- What is trusted publishing?
- Trusted publishing verifies the source of packages using OpenID Connect, issuing short-lived tokens for greater security.
- Will these changes affect my existing npm projects?
- GitHub is rolling out changes gradually to minimize disruption to existing workflows.
- what can I do to improve the security of my npm projects?
- Enable two-factor authentication,use trusted publishing when possible,and regularly scan dependencies for vulnerabilities.
- What is 2FA?
- Two-Factor Authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method, such as a code from your phone, in addition to your password.
- How dose OpenID Connect help with security?
- OpenID Connect provides a standardized way to verify the identity of a package publisher, preventing unauthorized uploads.
What are your thoughts on the new security measures? How do you ensure the security of your JavaScript projects? Share your insights in the comments below!
What is the primary reason GitHub is phasing out support for weak security options in the npm registry?
GitHub to Ban Weak Security Options for npm Registry Users
Understanding the Shift in npm Security
GitHub, the leading AI-powered developer platform (https://github.com/), is taking a significant step towards bolstering the security of the npm registry.Starting late 2025, the platform will begin phasing out support for weak or outdated security options commonly used by npm package publishers. This move directly addresses the growing concerns surrounding supply chain security and aims to protect developers and end-users from malicious packages. This isn’t just about github; it’s a broader industry trend towards software supply chain security.
What Security Options Are Being targeted?
The primary focus of this change revolves around authentication methods. Specifically,GitHub is targeting:
* Password-based authentication: Relying solely on passwords for npm account access is increasingly vulnerable to breaches.
* Weak or compromised API tokens: Tokens that haven’t been rotated or are exposed in public repositories pose a substantial risk.
* Lack of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Accounts without 2FA are significantly easier to compromise.
GitHub is pushing for stronger authentication methods like:
* SSH Keys: A more secure alternative to passwords.
* Personal Access Tokens (PATs) with granular scopes: Limiting the permissions of tokens reduces the potential damage from a compromise.
* GitHub Actions and CI/CD integration: Automating package publishing with secure workflows.
* Mandatory Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security to account access.
Why is GitHub Making This Change?
The decision stems from a surge in npm package security incidents and a growing awareness of the risks associated with vulnerable dependencies. Several high-profile attacks have demonstrated the potential for malicious actors to inject harmful code into widely used packages, impacting countless applications.
Here’s a breakdown of the key drivers:
- Supply Chain Attacks: The npm registry is a critical part of the software supply chain. compromising a single package can have cascading effects.
- Increased Sophistication of Attacks: Attackers are employing increasingly refined techniques to bypass existing security measures.
- Industry Best Practices: The move aligns with broader industry efforts to improve software security, such as the SLSA (Supply-chain Levels for Software Artifacts) framework.
- Developer Protection: Protecting developers from unknowingly integrating malicious code into their projects is paramount.
Impact on npm Package Publishers
The changes will require npm package publishers to update their authentication methods. Here’s a timeline and what to expect:
* Phase 1 (Late 2025): Notifications will be sent to publishers using vulnerable authentication methods.
* Phase 2 (Early 2026): Publishing with weak security options will be temporarily blocked, with clear instructions on how to upgrade.
* Phase 3 (Mid 2026): Full enforcement of the new security requirements. Publishing with unsupported methods will be permanently disabled.
Actionable Steps for Publishers:
- Review Your Authentication Methods: Log into your npm account and check your authentication settings.
- Enable 2FA: If you haven’t already, enable Two-Factor Authentication instantly.
- Generate and Use PATs: Create Personal Access Tokens with the minimum necessary scopes.
- Rotate API Tokens Regularly: Regularly rotate your API tokens to minimize the impact of a potential compromise.
- Consider SSH Key Authentication: Explore using SSH keys for a more secure publishing workflow.
Benefits of Enhanced npm Security
The transition to stronger security measures offers several benefits:
* Reduced Risk of Supply chain attacks: Minimizing vulnerabilities in the npm registry significantly reduces the risk of malicious code entering your projects.
* Improved Trust and Confidence: A more secure npm ecosystem fosters greater trust and confidence among developers.
* Enhanced Software Integrity: Stronger security measures help ensure the integrity of the software you build and deploy.
* Compliance with Security Standards: Adopting these practices can help you comply with industry security standards and regulations.
* Protection of User Data: Ultimately, a more secure npm registry protects the data of your users.
Practical Tips for Secure npm Package Management
Beyond updating authentication methods, consider these best practices:
* use a Package Lockfile: package-lock.json or yarn.lock ensures consistent dependency versions across environments.
* Regularly Audit Dependencies: Use tools like npm audit or yarn audit to identify and address known vulnerabilities in your dependencies.
* Keep dependencies Updated: Regularly update your dependencies to benefit from security patches and bug fixes.
* Implement Subresource Integrity (SRI): SRI helps verify the integrity of files downloaded from CDNs.
* Utilize Dependency Scanning Tools: Integrate dependency scanning tools into your CI/CD pipeline to automatically detect vulnerabilities.
* Monitor npm Advisory Database: Stay informed about new vulnerabilities by monitoring the npm advisory database.
Real-World Examples of npm Security Breaches
Several incidents highlight the importance of npm security:
* The event-stream Incident (2018): A malicious actor compromised the event-stream package, injecting code that stole cryptocurrency from users.
* **The coa Incident (20
