Image source, LLOYDS BANK
-
- Author, Writing
- Author’s title, BBC News World
Many of the world’s largest websites and applications are experiencing problems due to an outage that has affected Amazon Web Services.
Among the apps that showed intermittency this Monday are Snapchat, Duolingo, Zoom and Roblox.
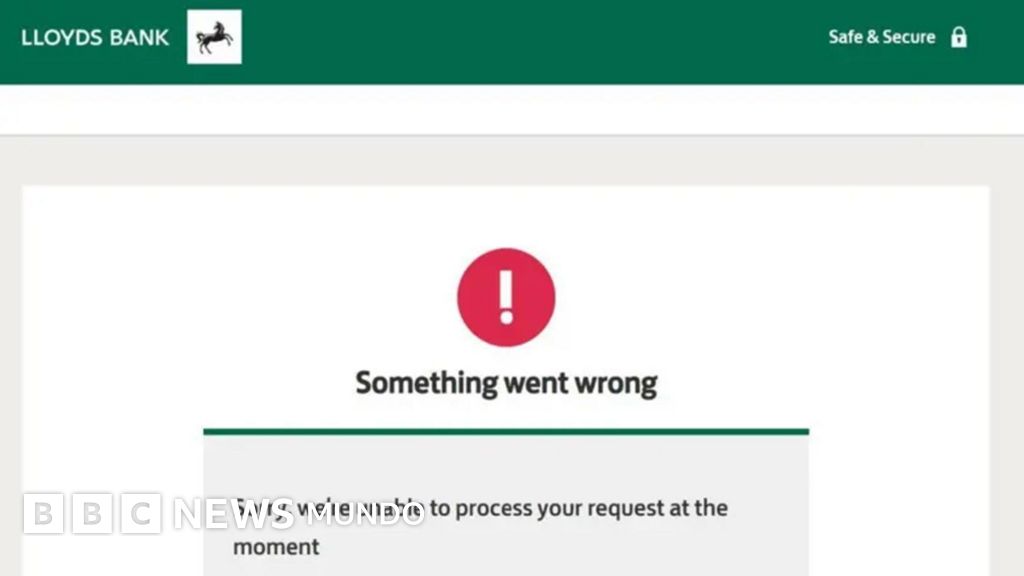
Also banks such as Lloyds and Halifax, which announced that their online services are available again.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the cloud computing division of Amazon and powers the infrastructure for millions of websites and applications.
In the most recent report on the situation, AWS noted that the issue that caused the outage has now been fixed and that most services should work correctly.
However, issues will continue to arise while all processes return to normal speed.
Likewise, other services may take some time to resume because requests were made before and during the outage on local devices that now need to be submitted and processed.
Imagine many people trying to send messages and suddenly they are all sent at once. That causes a delay while the system processes them all.
Amazon also reported that there is an issue with the launch of what it calls “new EC2 instances.” These are virtual computers hosted on the technology company’s servers, with their own hard drive space and operating systems.
Previously, Downdetector – the outage monitoring platform owned by Ookla – told the BBC that it received more than four million problem reports globally this morning alone, more than double the 1.8 million it normally records in a full business day.
a hypothesis
Table of Contents
- 1. a hypothesis
- 2. What potential financial losses could major banks experience due to disrupted transaction processing during the AWS outage?
- 3. Global Amazon Cloud Outage Disrupts Hundreds of Apps Including Snapchat, Zoom, and Major Banks
- 4. The Scope of the AWS Outage – October 20th, 2025
- 5. Affected Services: A Detailed Breakdown
- 6. Root Cause & AWS Response – What We know So Far
- 7. The Ripple Effect: Understanding Cloud Dependency
- 8. Past Context: Past AWS Outages
- 9. Mitigating Cloud Outage Risks: Best Practices
- 10. The Future of Cloud Resilience
“We don’t know the details of what has caused several crucial Amazon Web Services services to go down, says BBC technology reporter Liv McMahon. “And we may not know for some time.”
However, Amazon stated in one of its updates on the situation that the issue “appears to be related to the DNS resolution of the DynamoDB API endpoint on US-EAST-1.”
DNS, which stands for Domain Name System (DNS): Domain Name System), is often compared to an internet phone book.
McMahon explains that this system effectively converts the names of websites that users use into numerical equivalents of IP addresses that computers can read and understand.
This process fundamentally underpins the way we use the Internet, and interruptions can prevent web browsers from finding the content they are looking for.
But interruptions are not something new.
“There have been several massive internet outages in the last five years, where problems with a single company have had huge repercussions,” says BBC technology journalist Joe Tidy.
“More often than not, these issues are resolved within hours as engineers scramble to reverse errors or fix issues on the fly.”
The reporter explains that experts have long pointed to the growing dependence on a small number of internet giants as a factor, “as more eggs are put in fewer baskets: when a large company fails, much of modern life and business comes to a standstill.”

Subscribe here to our new newsletter to receive a selection of our best content of the week every Friday.
And remember that you can receive notifications in our app. Download the latest version and activate them.
What potential financial losses could major banks experience due to disrupted transaction processing during the AWS outage?
Global Amazon Cloud Outage Disrupts Hundreds of Apps Including Snapchat, Zoom, and Major Banks
The Scope of the AWS Outage – October 20th, 2025
A widespread outage impacting Amazon Web Services (AWS) has crippled numerous popular applications and critical financial services today, October 20th, 2025. The disruption, beginning around 09:15 UTC, has affected services like Snapchat, Zoom, and a significant number of major banking institutions globally. This isn’t a localized issue; reports indicate impacts across North America, Europe, and Asia, highlighting the pervasive reliance on Amazon’s cloud infrastructure. The outage underscores the risks associated with centralized cloud services and the potential for cascading failures.
Affected Services: A Detailed Breakdown
The impact of the AWS outage is far-reaching. Here’s a breakdown of key services experiencing disruptions:
* Social Media: Snapchat users are reporting complete inability to send snaps or refresh their feeds.
* Communication Platforms: Zoom meetings are frequently disconnecting, and users are experiencing difficulties joining calls.
* Financial Institutions: Several major banks, including Capital One and HSBC, have reported intermittent issues with online banking and mobile app access. Transaction processing has also been affected in some cases.
* Streaming Services: While not universally impacted, some streaming platforms are experiencing buffering issues and playback errors.
* Gaming: Popular online games relying on AWS servers are experiencing connectivity problems and server downtime.
* Other Applications: A wide range of other applications, from productivity tools to e-commerce platforms, are also affected, demonstrating the breadth of AWS’s client base.
Root Cause & AWS Response – What We know So Far
Amazon has acknowledged the outage and is currently investigating the root cause. Initial reports suggest the issue stems from a problem with AWS’s Kinesis Data Streams service, a fully managed, scalable, and durable real-time data streaming service. This service is fundamental to many applications’ backend operations.
AWS’s official status page indicates they are experiencing “increased error rates” and are working to restore service. The company has not yet provided a specific timeline for full resolution, but updates are being posted regularly. The incident is categorized as a “service disruption,” indicating a significant impact on multiple AWS services.
The Ripple Effect: Understanding Cloud Dependency
This outage serves as a stark reminder of the inherent risks of relying heavily on a single cloud provider.Many organizations, even large ones, have adopted a “cloud-first” strategy, migrating critical infrastructure and applications to AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. While cloud services offer scalability, cost-effectiveness, and convenience, they also introduce a single point of failure.
* Vendor Lock-in: Organizations can become heavily reliant on a specific cloud provider’s services,making it difficult and costly to switch.
* Shared Responsibility Model: While cloud providers are responsible for the security of the cloud, customers are responsible for security in the cloud. Outages highlight the need for robust disaster recovery planning on the customer side.
* Cascading Failures: A failure in a core cloud service, like Kinesis, can have a cascading effect, impacting numerous dependent applications and services.
Past Context: Past AWS Outages
AWS has experienced several significant outages in the past.
* November 2020: A widespread outage affected the US-East-1 region, impacting services like Netflix, TikTok, and Airbnb.
* December 2021: Issues with S3 (Simple Storage Service) caused disruptions for numerous applications.
* April 2022: An outage in the US-West-2 region impacted services like Disney+ and Twitch.
These past incidents demonstrate a pattern of vulnerabilities within AWS’s infrastructure and the potential for recurring disruptions. Each outage prompts renewed scrutiny of cloud resilience and disaster recovery strategies.
Mitigating Cloud Outage Risks: Best Practices
Organizations can take several steps to mitigate the risks associated with cloud outages:
- Multi-Cloud Strategy: Distribute applications and data across multiple cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) to reduce reliance on a single vendor.
- Hybrid Cloud Approach: Combine public cloud services with on-premises infrastructure for greater control and resilience.
- Robust Disaster Recovery Plan: Develop and regularly test a thorough disaster recovery plan that includes failover procedures and data backups.
- Redundancy and Load Balancing: Implement redundancy and load balancing across multiple availability zones and regions.
- Monitoring and Alerting: Utilize robust monitoring and alerting tools to detect and respond to potential issues proactively.
- Independent Data Backups: Regularly back up critical data to a separate, independent location – not solely relying on cloud provider backups.
The Future of Cloud Resilience
The current AWS outage is likely to accelerate the trend towards more resilient cloud architectures. Expect to see increased adoption of multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, as well as a greater emphasis on disaster recovery planning and proactive monitoring. The incident also highlights the need for improved clarity and communication from cloud providers during outages. The demand for cloud outage insurance and risk mitigation services will likely increase as businesses seek to protect themselves from the financial and reputational consequences of future disruptions.