Malicious Microsoft Teams Installers Spread ‘Oyster‘ Backdoor Via SEO-Poisoned Ads
Table of Contents
- 1. Malicious Microsoft Teams Installers Spread ‘Oyster’ Backdoor Via SEO-Poisoned Ads
- 2. How The Attack Works
- 3. A Growing Trend
- 4. Staying Protected Against Malware Downloads
- 5. What indicators of compromise (IOCs) could be used to identify systems infected wiht Oyster malware?
- 6. Malvertising Campaign Uses Fake Microsoft Teams Installers to Spread Oyster malware
- 7. Understanding the Threat: Oyster Malware & Malvertising
- 8. How the Campaign Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
- 9. Oyster Malware: Capabilities and Impact
- 10. Identifying Fake Microsoft Teams Installers
- 11. Mitigation Strategies: Protecting Your Systems
- 12. Real-World Examples & Case Studies
- 13. Staying Informed: Threat Intelligence & Resources
New York, NY – A sophisticated cyberattack campaign is underway, utilizing Search Engine Optimization (SEO) poisoning and deceptive online advertisements to distribute malware disguised as the legitimate Microsoft Teams installer. Security researchers have identified that these fraudulent downloads contain the ‘oyster’ backdoor,providing threat actors with a stealthy entry point into corporate networks.
The ‘Oyster’ malware, also identified as Broomstick and CleanUpLoader, initially emerged in the middle of 2023. As then, it has been associated with numerous malicious operations. This backdoor grants attackers remote control over compromised systems, enabling them to execute arbitrary commands, deploy further malicious software, and exfiltrate sensitive data.
How The Attack Works
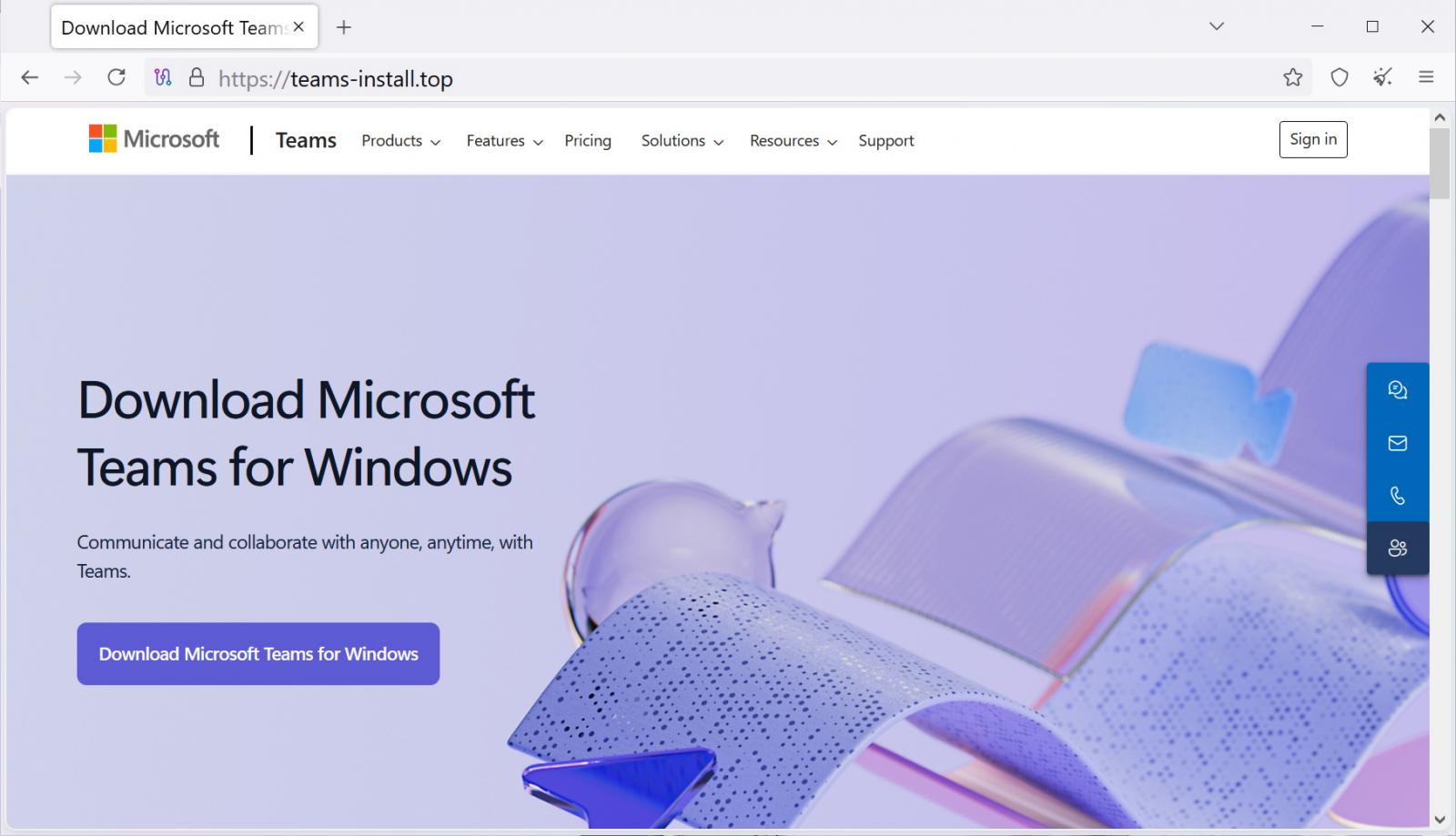
The attack unfolds through a tactic known as malvertising, were malicious advertisements are used to redirect users to fake websites. Threat actors are targeting individuals searching for “Teams download,” presenting a convincing, yet fraudulent, website that mimics the official Microsoft download page at teams-install[.]top.

Despite not directly imitating Microsoft’s official domain, the fraudulent website presents a nearly identical interface, enticing users to download “MSTeamsSetup.exe,” using the same filename as the genuine Microsoft installer.The malicious file is digitally signed with valid certificates from “4th State Oy” and “NRM NETWORK RISK MANAGEMENT INC”, bolstering its apparent legitimacy.
Upon execution,the fake installer silently drops a malicious Dynamic Link Library (DLL) file named CaptureService.dll into the %APPDATA%Roaming folder. To maintain persistence – ensuring the malware remains active even after a system reboot – a scheduled task named “CaptureService” is created, running the malicious DLL every 11 minutes.
A Growing Trend
This latest campaign echoes previously observed attacks involving fake Google Chrome and Microsoft Teams installers distributing the Oyster malware. This demonstrates that SEO poisoning and malvertising continue to be favored methods employed by cybercriminals to infiltrate corporate networks. According to a recent report by Check Point, malvertising increased by 188% in the first quarter of 2024, posing an ever-growing threat to organizations globally.
“the consistent exploitation of user trust in search results and established brands is a hallmark of these attacks,” explains a representative from Blackpoint SOC. “IT professionals, frequently targeted for their access to critical systems, must exercise extreme caution when downloading software.”
here’s a breakdown of the key components of this attack:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Malware | Oyster (Broomstick, CleanUpLoader) Backdoor |
| Attack Vector | SEO Poisoning & Malvertising |
| Targeted Software | Microsoft Teams |
| Malicious Filename | MSTeamsSetup.exe |
| Persistence Mechanism | Scheduled Task: CaptureService |
Did You Know? Approximately 30% of all malware infections originate from compromised advertising networks, a figure that has been steadily climbing over the past year.
Pro Tip: Always verify the authenticity of software downloads by directly visiting the official vendor’s website, and avoid clicking on links from search engine advertisements whenever possible.
Staying Protected Against Malware Downloads
Protecting your organization from SEO-poisoned malware requires a multi-layered security approach. regularly update all software, implement robust endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems, and educate employees about the dangers of phishing and malvertising. A strong email security gateway can also block malicious attachments and links before they even reach users. Consider using a reputable antivirus solution that incorporates machine learning to identify and neutralize emerging threats. encourage a culture of cybersecurity awareness, where employees are empowered to report suspicious activity and question unfamiliar downloads.
Are you concerned about the rising threat of malvertising? What steps is your organization taking to protect itself from these attacks? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
What indicators of compromise (IOCs) could be used to identify systems infected wiht Oyster malware?
Malvertising Campaign Uses Fake Microsoft Teams Installers to Spread Oyster malware
Understanding the Threat: Oyster Malware & Malvertising
A recent and concerning malvertising campaign is leveraging deceptive tactics to distribute Oyster malware. This campaign specifically targets users seeking to download Microsoft Teams, a widely used collaboration platform. Malvertising, the practise of using legitimate online advertising networks to spread malicious content, poses a notable threat because it bypasses traditional security measures. Users often trust the platforms displaying the ads, making them more susceptible to clicking on malicious links.The core of this attack relies on distributing fake Microsoft Teams installers that, instead of the legitimate application, deliver the Oyster malware payload. This is a prime example of software supply chain attacks and adware distribution.
How the Campaign Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The attack unfolds in several stages:
- Compromised Ad Networks: Attackers inject malicious advertisements into legitimate ad networks. These ads often appear on popular websites, increasing their reach.
- Deceptive Advertising: The ads are designed to mimic official Microsoft Teams advertising, using similar branding and messaging. Keywords like “Download Teams,” “Microsoft Teams Free,” and “Teams Collaboration” are frequently used to attract clicks.
- Fake Download Pages: Clicking the ad redirects users to a convincing, but fraudulent, download page. This page closely resembles the official Microsoft Teams website.
- Malicious Installer: The download link on the fake page offers a malicious installer disguised as the genuine Microsoft Teams setup file. This installer contains the Oyster malware.
- Malware Installation: When executed, the installer silently installs Oyster malware on the victim’s system.
Oyster Malware: Capabilities and Impact
Oyster malware is a sophisticated threat with a range of malicious capabilities.While specific functionalities can vary, common characteristics include:
* Data Stealing: Oyster is designed to steal sensitive information, including login credentials, financial data, and personal details.
* Remote Access: The malware can establish a backdoor, granting attackers remote access to the compromised system.
* Credential Harvesting: It actively searches for and exfiltrates stored credentials from browsers and other applications.
* Persistence Mechanisms: oyster employs techniques to ensure it remains active on the system even after reboots.
* Lateral Movement: In some cases, Oyster can be used to move laterally within a network, compromising additional systems.
This makes Oyster a especially dangerous threat for both individual users and organizations. The potential for data breaches and financial loss is substantial.
Identifying Fake Microsoft Teams Installers
Protecting yourself requires vigilance. Here’s how to spot a fake Microsoft Teams installer:
* Download Source: Always download Microsoft Teams directly from the official Microsoft website (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-teams/download-app). Avoid downloading from third-party websites or suspicious links.
* URL Inspection: Carefully examine the URL of the download page. Look for subtle misspellings or variations of the official Microsoft domain.
* File Hash Verification: After downloading, verify the file hash (SHA256) of the installer against the official hash provided by Microsoft. This ensures the file hasn’t been tampered with.
* Security Software: Ensure your antivirus software and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions are up-to-date and actively scanning for threats.
* Browser Security: Utilize browser extensions designed to block malicious websites and advertisements.
Mitigation Strategies: Protecting Your Systems
Beyond identifying fake installers, proactive measures are crucial:
* Employee training: Educate employees about the risks of malvertising and phishing attacks. Emphasize the importance of downloading software only from official sources.
* Ad Blocker Implementation: Deploy ad blockers on company networks to reduce exposure to malicious advertisements.
* network segmentation: Segment your network to limit the potential impact of a triumphant malware infection.
* Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in your systems.
* Endpoint Protection: Implement robust endpoint protection solutions, including antivirus, firewall, and intrusion detection systems.
* Zero Trust Architecture: Consider adopting a Zero Trust security model, which assumes that no user or device is inherently trustworthy.
Real-World Examples & Case Studies
While specific details of impacted organizations are often confidential,security researchers have documented numerous instances of this malvertising campaign targeting a wide range of industries,including healthcare,finance,and education. One notable case involved a small business that experienced a significant data breach after an employee unknowingly downloaded the malicious Teams installer. The attackers gained access to sensitive customer data, resulting in financial losses and reputational damage. This highlights the importance of proactive security measures and employee awareness training.
Staying Informed: Threat Intelligence & Resources
Keeping abreast of the latest threats is essential. Here are some valuable resources:
* Microsoft Security Blog: (https://msrc.microsoft.com/blog)
* Security Industry News Websites: (e.g., KrebsOnSecurity, the Hacker News, BleepingComputer)
* Threat Intelligence Platforms: (e.g., VirusTotal, AlienVault OTX)
* **CERT/CC
