Unusual Cerebral Event Unfolds After Successful Thrombectomy: A Case Report
Table of Contents
- 1. Unusual Cerebral Event Unfolds After Successful Thrombectomy: A Case Report
- 2. The procedure and Immediate Outcomes
- 3. The Unforeseen Complication
- 4. understanding the Broader Implications
- 5. Long-Term Perspectives
- 6. Frequently Asked Questions
- 7. How does the interplay between infective endocarditis, cerebral embolism, and subarachnoid hemorrhage complicate the decision-making process for thrombectomy?
- 8. Rescue Thrombectomy for Infective Endocarditis-Related Cerebral Embolism and Subsequent Subarachnoid hemorrhage: A Case Report
- 9. Introduction to the Complexities of IE and Stroke
- 10. Case presentation: A Multidisciplinary challenge
- 11. Understanding Cerebral Embolism in Infective Endocarditis
- 12. The Role of Rescue Thrombectomy in IE-Related stroke
- 13. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and its Implications
- 14. Outcomes and Lessons learned
- 15. Benefits of Timely Intervention
- 16. Practical Tips
A remarkable medical case has come to light, detailing a patient’s experience with a cerebral embolism. The patient underwent a successful early thrombectomy but later showed signs of complications.
The term “infective” refers to something that is capable of spreading disease, in this case, possibly highlighting the complexity of the situation. This breaking news describes an intricate medical case that has brought attention to the potential after-effects of a thrombectomy procedure. The incident involved a patient experiencing a cerebral embolism. Doctors were able to successfully perform an early thrombectomy. However, within six hours of the treatment, the patient developed a subarachnoid hemorrhage.This chain of events underscores the unpredictability of medical conditions and the importance of vigilant post-operative care.
The procedure and Immediate Outcomes
The initial procedure, a thrombectomy, which aims to remove a blood clot from a blood vessel in the brain, was deemed successful. This procedure is crucial in restoring blood flow and preventing further damage. Though, the subsequent hemorrhage highlights the challenges physicians face in treating complex cases. Successful early intervention doesn’t always ensure a smooth recovery.
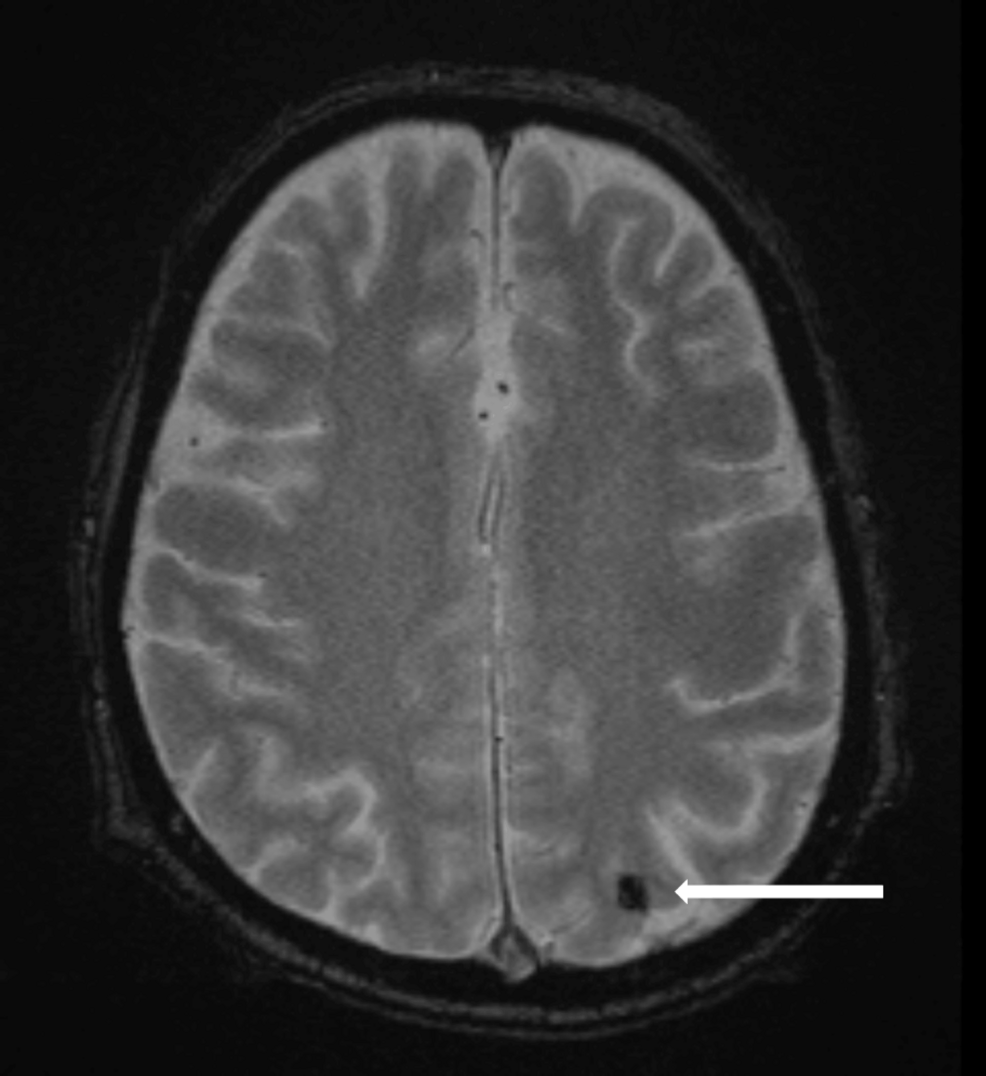
The Unforeseen Complication
The advancement of a subarachnoid hemorrhage,a bleeding into the space around the brain,just hours after the thrombectomy,adds layers of complexity to the patient’s situation. This complication, while rare, demonstrates the need for continuous monitoring of the patient after any surgical intervention. Timely diagnosis and intervention are vital for optimizing patient outcomes.
understanding the Broader Implications
This case report has a number of implications regarding patient care. The rapid onset of the hemorrhage after a successful procedure suggests that factors beyond the initial intervention may have played a role. It’s a good illustration of how a patient’s individual health factors can affect treatment.
The report urges medical professionals to remain vigilant and prioritize thorough post-operative care. It should inform strategies to identify and manage potential complications early on.
Did You Know? The term “infective” is frequently enough used in epidemiology to describe a person capable of spreading an illness.
Pro Tip: Always discuss potential risks and complications with your doctor before undergoing any medical procedure.
This case report is a good reminder of the importance of constant medical evaluation. Continuous study and careful observation are crucial to improving patient results. We can learn a lot by analyzing rare occurrences.
Do you think that this case highlights the need for more comprehensive patient monitoring after neurosurgical procedures? Share your thoughts below!
How might advancements in imaging technology affect the early detection of post-operative complications? we invite you to comment!
Long-Term Perspectives
This medical case underscores the need for ongoing research to improve diagnostic tools and therapeutic approaches. The goal is to refine medical protocols to prevent or mitigate such complications. Research into patient-specific risk factors is also essential.
As medical technologies advance, such as improved imaging and minimally invasive procedures, early detection and management of post-operative complications are expected to increase. These advancements may lead to better patient outcomes in the future.
for additional insights,consider consulting reputable medical journals and resources like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the World Health Organization (WHO). They supply current data and details on health topics.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the interplay between infective endocarditis, cerebral embolism, and subarachnoid hemorrhage complicate the decision-making process for thrombectomy?
Introduction to the Complexities of IE and Stroke
Infective endocarditis (IE), a life-threatening infection of the heart’s inner lining or valves, can led to devastating neurological complications. Cerebral embolism, a common manifestation of IE, occurs when infected vegetations break loose and travel to the brain, causing stroke. This can lead to severe disability and even death. Furthermore,these emboli can result in subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH),further complicating the clinical picture. This case report highlights the challenges and potential benefits of rescue thrombectomy in such a complex scenario.
Case presentation: A Multidisciplinary challenge
Patient Profile: A [Age] year-old [Gender] presented with [Chief Complaint] and a history of [Relevant Medical History, e.g., intravenous drug use, pre-existing heart condition].
Initial Assessment: The patient’s clinical presentation demonstrated a acute stroke symptoms including [Symptoms].
Diagnostic Imaging: Initial CT scan revealed [Findings]. Further imaging, including CTA and MRI/MRA, confirmed [Findings].
etiology: [Specific IE causative organism identified through blood cultures and echocardiogram].
Management:
Initial Treatment: The patient received [Initial medical management, including antibiotics, supportive care].
Neurological Deterioration: Despite initial interventions, the patient experienced [Specific neurological decline or complications].
Intervention: Considering the clinical decline and imaging findings, rescue thrombectomy was performed using [Technique].
surgical Findings: [Describe findings during the thrombectomy].
Post-Procedure Care: The patient underwent close neurological monitoring and post-operative management, which included [Specifics of the aftercare provided].
Understanding Cerebral Embolism in Infective Endocarditis
Pathogenesis: IE can lead to the formation of vegetations on the heart valves, containing bacteria and platelets. These vegetations can embolize, causing blockage of cerebral arteries leading to ischemic stroke.
Common Locations: Middle cerebral artery (MCA) is the most frequently affected.
Associated Risks: The friable nature of the vegetations increases the risk of hemorrhagic transformation and subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).
Early Recognition: Early detection through prompt imaging (CT, MRI) is essential for guiding treatment strategies.
Rationale: Rescue thrombectomy aims to restore blood flow to the ischemic area of the brain, preventing further neurological damage.
Selection Criteria: Patients with acute ischemic stroke caused by large vessel occlusion (LVO) may be candidates.
Procedure Technique: Endovascular thrombectomy utilizes a catheter system introduced through a peripheral artery (e.g.,femoral artery) to the blocked cerebral vessel and retrieve the blood clot.
Timing Matters: Early intervention enhances the chances of good outcome in appropriate patient selection.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and its Implications
Mechanism: Cerebral emboli can lead to weakened blood vessels and subsequent SAH.
Neurological Impact: the presence of SAH can significantly worsen patient outcomes.
Management: Managing the SAH involves controlling intracranial pressure (ICP), and preventing aneurysmal rupture if applicable is important.
Outcomes and Lessons learned
Clinical Enhancement: The patient in this case study experienced [Specific results], including [neurological improvements].
Limitations: The presence of SAH posed a critical challenge and may require additional interventions to improve outcomes.
multidisciplinary Approach: Accomplished management requires the coordination of cardiologists, neurologists, neurosurgeons, interventional neuroradiologists, and intensivists.
Further research: additional studies are needed to validate the efficacy of rescue thrombectomy in patients with IE related cerebral embolism with subsequent subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Benefits of Timely Intervention
Improved neurological outcomes.
Reduced risk of long-term disability.
Potential for faster recovery.
Increased likelihood of returning to a good quality of life.
Practical Tips
Early diagnosis using advanced imaging is pivotal
Appropriate selection of patients for thrombectomy.
Aggressive medical management, including prompt initiation of antibiotics.
Close neurological monitoring and management of ICP.
* Multidisciplinary approach of care.