Urgent: Polar Vortex Instability Threatens Major Cold Snap Across Europe & Italy
Published: January 2, 2026 – A dramatic shift in atmospheric patterns is brewing over the North Atlantic and Arctic, raising the alarm for a potentially severe and prolonged cold snap across Europe, particularly Italy. Meteorological models are painting a complex picture, but the core message is clear: winter’s bite is about to get significantly sharper. This is a developing story, and archyde.com is providing continuous updates as the situation unfolds. This breaking news impacts travel, infrastructure, and daily life for millions.
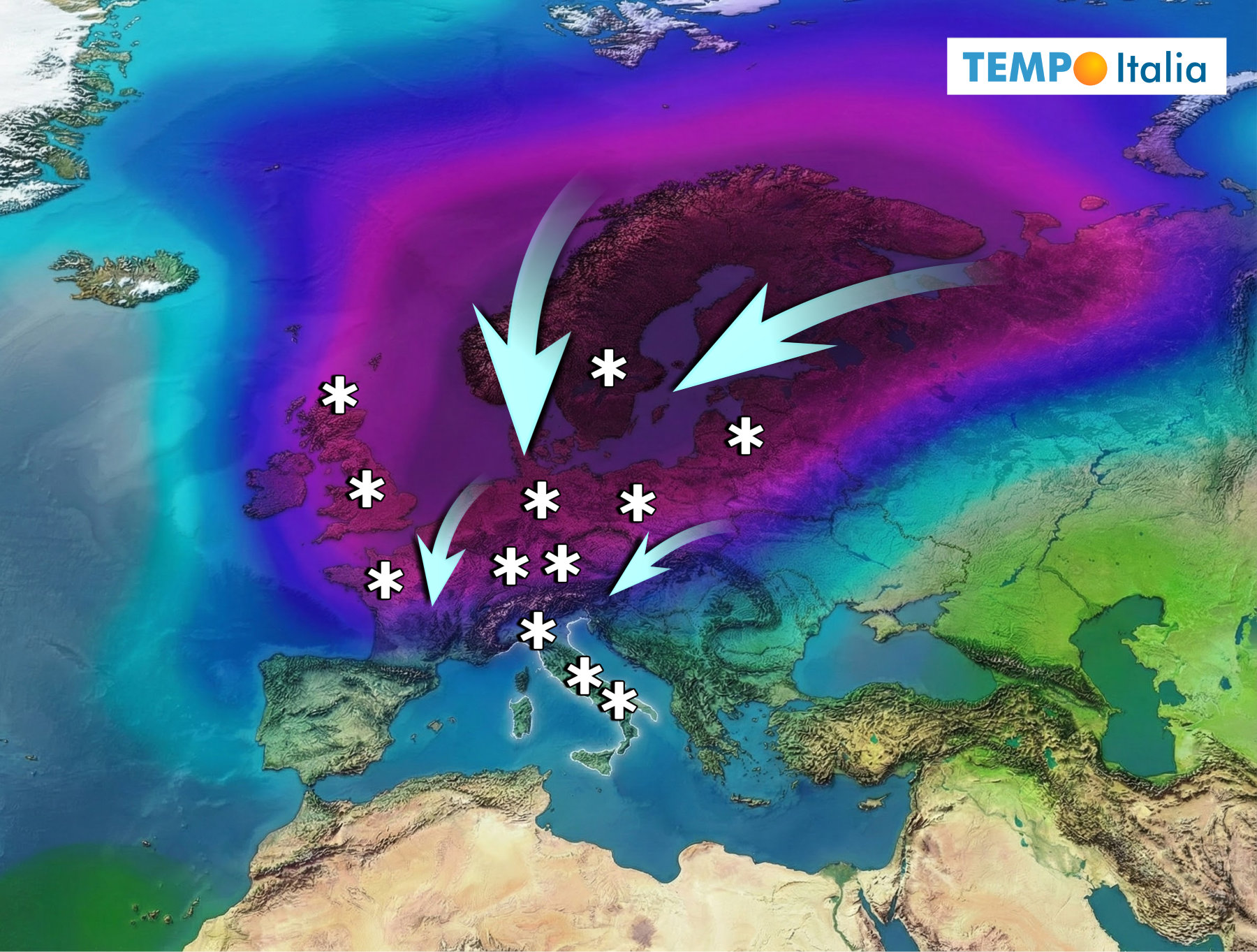
Visualizing the potential impact of a disrupted Polar Vortex.
The Dance of the Arctic: NAO, AO, and a Weakening Vortex
The focus of meteorological attention is currently fixed on two key atmospheric oscillators: the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) and the Arctic Oscillation (AO). Both are currently exhibiting strongly negative phases, a condition that historically precedes significant cold air outbreaks. A negative NAO/AO essentially weakens the ‘dam’ that usually keeps frigid Arctic air contained, allowing it to spill southward. This isn’t just about a few chilly days; the current projections suggest this pattern could persist for a significant portion of January.
While the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) suggests a possible stabilization around January 10th, the American Global Forecast System (GFS) model paints a more concerning picture – a prolonged disturbance of the Polar Vortex. This divergence highlights the inherent uncertainty in long-range forecasting, but the consensus is leaning towards a more active and potentially harsher winter than previously anticipated. Understanding these models is crucial for anyone following weather patterns; the ECMWF is often favored for its longer-range accuracy, while the GFS excels at short-term predictions.
Italy in the Crosshairs: Mediterranean Cyclogenesis and Snow Potential
For Italy, the situation is particularly intriguing. The combination of a negative AO and NAO dramatically increases the risk of Mediterranean cyclogenesis – the formation of low-pressure systems over the Mediterranean Sea. These systems are notorious for bringing widespread, often intense, weather events, including heavy snowfall at surprisingly low altitudes, especially in northern and central Italy. However, it’s a delicate balance. A poorly positioned Atlantic block could steer these storms away, or worse, draw warm, moist air from North Africa, resulting in rain instead of snow.
Evergreen Insight: Mediterranean cyclogenesis is a recurring phenomenon, but its intensity and frequency are being influenced by climate change. Warmer sea surface temperatures provide more energy for these storms, potentially leading to more extreme precipitation events. Historically, Italy has experienced devastating floods linked to these types of systems, underscoring the importance of preparedness and accurate forecasting.
The Pacific Connection: EPO and Hemispheric Circulation
The influence isn’t limited to the Atlantic. What’s happening thousands of miles away in the Pacific Ocean, specifically the East Pacific Oscillation (EPO), is also playing a critical role. A strong positive EPO currently favors high pressure over North America, which, in turn, influences the jet stream and the flow of cold air towards Europe. However, models predict a rapid collapse of the EPO towards negative values in the second half of January. This shift could trigger a radical change in hemispheric circulation, potentially prolonging the cold spell.
Stratospheric Warming: The Wild Card
Adding another layer of complexity is the potential for a stratospheric warming event. Anomalous heating in the stratosphere can disrupt the Polar Vortex, even splitting it in two. While not all stratospheric warmings translate into surface-level impacts, the current conditions – combined with the negative AO and NAO – significantly increase the risk. The GFS model suggests disturbances that could prevent the vortex from reconsolidating, opening the door for further cold incursions even after Epiphany (January 6th).
SEO Tip: Searching for “Polar Vortex updates” or “European winter forecast” on Google News will yield the latest information. Archyde.com is committed to providing timely and accurate reporting on these evolving conditions.
The atmosphere isn’t a predictable machine; it’s a chaotic system prone to last-minute surprises. The current situation is a stark reminder that even in an era of advanced modeling, uncertainty remains. However, the convergence of multiple negative indices signals a heightened risk of a significant and potentially prolonged cold snap across Europe and Italy. Stay tuned to archyde.com for the latest updates and expert analysis as this story develops. We’ll continue to monitor the data from international centers, providing you with the information you need to stay informed and prepared.