International Recognition of palestinian Statehood Draws Mixed Reactions
Table of Contents
- 1. International Recognition of palestinian Statehood Draws Mixed Reactions
- 2. Growing Momentum for Recognition
- 3. The Critical Role of a Two-State Solution
- 4. US and Israeli Responses
- 5. The Path Forward: Dependence on US Involvement
- 6. Past Context of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict
- 7. frequently Asked Questions
- 8. How might the South Sudan case study inform strategies for mitigating potential security vulnerabilities in a newly formed Palestinian state?
- 9. Understanding the Implications of Recognizing a Palestinian State: Insights from CNA Experts
- 10. Geopolitical Ramifications of Palestinian Statehood
- 11. Security Considerations: A CNA Outlook
- 12. Economic Viability and Development
- 13. political Challenges and Governance
- 14. Case Study: the South Sudan Experience (2011)
- 15. The Role of International Mediation & Guarantors
- 16. Potential
Published: September 22, 2025
Growing Momentum for Recognition
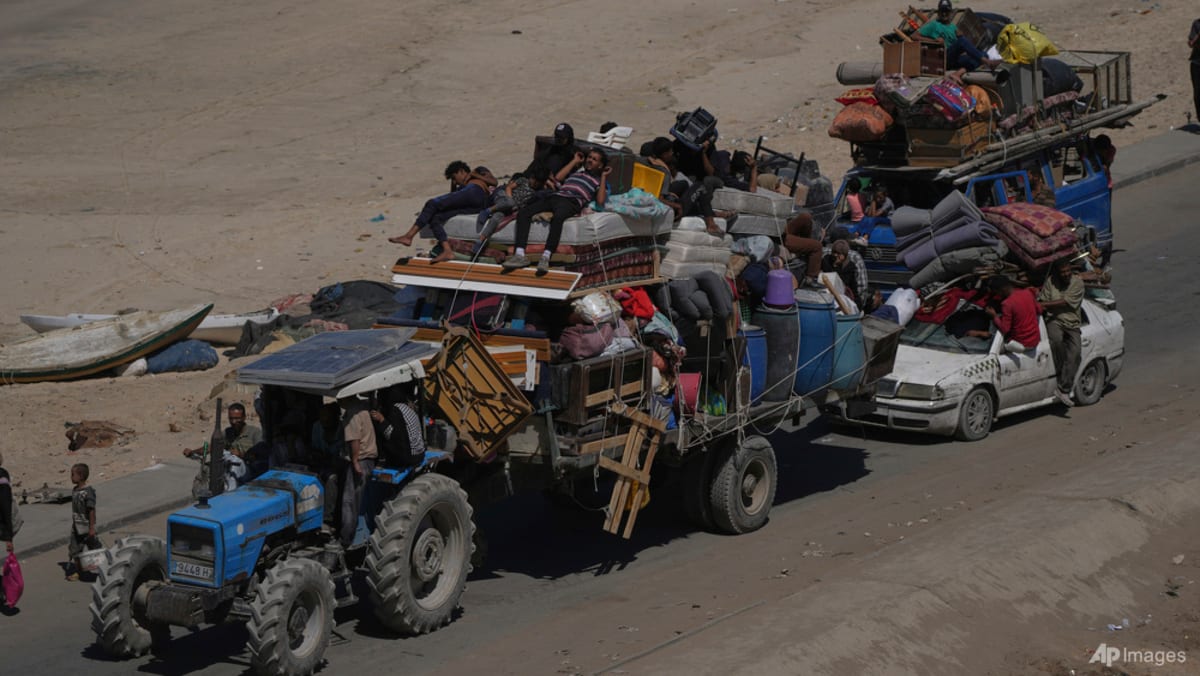
Recent declarations of intent to acknowledge Palestinian statehood by multiple countries have ignited a complex international discussion. Experts suggest this shift, while largely symbolic in the immediate context of the Gaza conflict, represents a possibly notable turning point in diplomatic efforts.
Analysts like dr. Ozcelik emphasize that while Recognition itself won’t instantly alleviate hardships faced by those in Gaza, it offers a crucial “glimmer of hope.” Though, questions remain regarding tangible improvements in circumstances and the necessary follow-up actions this recognition demands.
The Critical Role of a Two-State Solution
The prevailing consensus among international relations specialists points to a two-state solution as the only viable path toward a lasting resolution. Kupchan asserts that a single-state solution is improbable,citing the unlikelihood of a jewish state willingly relinquishing power.
Palestinian self-determination, weather as a fully sovereign state or an entity with defined, though limited, powers, is seen as essential. such a solution would not only address Palestinian aspirations but also contribute to IsraelS long-term security as a democratic nation.
Did You Know? The concept of a two-state solution dates back to the 1947 United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine.
US and Israeli Responses
The United States, a long-standing ally of Israel, has characterized the recognition moves as “performative,” prioritizing a diplomatic resolution to the ongoing Israel-Hamas conflict. A State Department spokesperson, speaking on background, underscored the US focus on hostage release, Israeli security, and regional stability.
Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu vehemently condemned the recognition efforts, labeling them as a reward for terrorism in reference to the October 7th attacks by Hamas. He firmly stated his opposition to the establishment of a palestinian state west of the Jordan River and vowed to expand Jewish settlements in the West Bank – a move widely considered illegal under international law.
| Country/Entity | position on Palestinian Statehood |
|---|---|
| United States | Critical of recognition; prioritizes diplomatic solution. |
| Israel | Strongly opposes recognition; vows continued settlement expansion. |
| Various European Nations | Increasingly supportive of recognition as part of a two-state solution. |
The Path Forward: Dependence on US Involvement
Experts suggest that considerable changes on the ground are unlikely without the United States’ support for a Palestinian state. Dr. Ozcelik contends that the impact of European recognition will be limited in the absence of US participation.The intricate and sensitive nature of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict necessitates a broader international consensus, with the US playing a pivotal role.
Pro Tip: Stay informed about ongoing developments in the region by consulting reputable news sources and international organizations like the United Nations.
Past Context of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a decades-long dispute with roots in competing claims over the same territory. The conflict has evolved through various stages, including the British Mandate, the 1948 arab-Israeli War, the Six-Day War of 1967, and the Oslo Accords of the 1990s. These events have shaped the political landscape and continue to influence the search for a peaceful resolution.
The issue of Palestinian statehood has been a central element of the conflict, with Palestinians seeking an autonomous state in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. Israel has concerns over security, borders, and the status of Jerusalem, which both sides claim as their capital.International efforts to mediate a solution have faced numerous challenges,highlighting the complexity of the conflict.
frequently Asked Questions
- What is a two-state solution? A two-state solution proposes the creation of an independent palestinian state alongside Israel, allowing both peoples to exercise self-determination.
- Why is US involvement crucial to Palestinian statehood? The United States holds significant diplomatic and economic influence in the region, making its support vital for any lasting peace agreement.
- What are the main obstacles to a Palestinian state? Key obstacles include Israeli settlement expansion, disagreements over borders, the status of Jerusalem, and security concerns.
- What impact will recognizing a Palestinian state have on gaza? While largely symbolic currently, recognition could offer a glimmer of hope and create momentum for future negotiations.
- Is a one-state solution considered a viable choice? Experts generally agree that a single state is unlikely due to fundamental disagreements and competing national aspirations.
How might the South Sudan case study inform strategies for mitigating potential security vulnerabilities in a newly formed Palestinian state?
Understanding the Implications of Recognizing a Palestinian State: Insights from CNA Experts
Geopolitical Ramifications of Palestinian Statehood
The potential recognition of a Palestinian state is a complex issue with far-reaching geopolitical consequences. Experts at the Center for Naval Analyses (CNA) have consistently analyzed the security, political, adn economic dimensions of this debate. A key consideration is the impact on regional stability. recognizing Palestinian statehood could alter the existing power dynamics in the Middle East, perhaps leading to both opportunities and challenges.
* Impact on Israeli Security: CNA research highlights concerns regarding the security implications for Israel. A newly formed Palestinian state’s ability to control its territory and prevent terrorist activity is a primary concern. This necessitates robust security cooperation agreements and international monitoring mechanisms.
* Regional Power Shifts: Recognition could empower non-state actors and potentially embolden groups opposed to existing regional alliances. Conversely, it could also foster a more inclusive political landscape, encouraging dialog and cooperation.
* International Law & Norms: The move would considerably impact international law concerning self-determination and territorial disputes. It sets a precedent for future claims of statehood and could influence conflict resolution efforts globally.
Security Considerations: A CNA Outlook
CNA’s analysis emphasizes the critical need for a comprehensive security framework accompanying any recognition of a Palestinian state. This framework must address several key areas:
- border Security: Establishing secure and internationally recognized borders is paramount. This includes preventing the smuggling of weapons and materials that could be used for hostile activities.
- Counterterrorism Efforts: A robust counterterrorism strategy,developed in collaboration with international partners,is essential to prevent the emergence of terrorist safe havens within the Palestinian state.
- Security Sector Reform: Building a professional and accountable Palestinian security force capable of maintaining law and order is crucial.CNA experts advocate for sustained training and capacity-building programs.
- Intelligence Sharing: Effective intelligence sharing between Israel, Palestine, and international partners is vital for preempting and responding to security threats.
Economic Viability and Development
The economic sustainability of a Palestinian state is a significant challenge. CNA studies indicate that a viable Palestinian economy is essential for long-term stability and peace.
* Dependency Reduction: currently, the Palestinian economy is heavily reliant on foreign aid. Reducing this dependency through lasting economic development is a key priority.
* investment & Trade: Attracting foreign investment and fostering trade relationships with regional and international partners are crucial for economic growth.
* Resource Management: Effective management of natural resources, including water and land, is essential for sustainable development.
* Infrastructure Development: Investing in infrastructure projects, such as transportation networks and energy systems, is vital for supporting economic activity. The World Bank and IMF have published reports detailing the economic challenges and potential pathways for growth.
political Challenges and Governance
Establishing effective governance within a Palestinian state presents numerous political challenges. CNA research identifies several key areas of concern:
* Internal Divisions: The political divide between Fatah and Hamas remains a significant obstacle to establishing a unified and stable government. Reconciliation efforts are essential.
* Rule of Law: Strengthening the rule of law and ensuring an independent judiciary are crucial for promoting accountability and protecting human rights.
* Corruption: Addressing corruption and promoting clarity are essential for building public trust and attracting investment.
* Democratic Institutions: Developing robust democratic institutions, including a free press and civil society organizations, is vital for ensuring citizen participation and accountability.
Case Study: the South Sudan Experience (2011)
The 2011 independence of South Sudan offers a cautionary tale. While initially greeted with international optimism, South Sudan quickly descended into civil war due to weak governance, ethnic tensions, and a lack of economic diversification. CNA experts point to this example as a reminder of the importance of addressing underlying political and economic vulnerabilities before recognizing statehood. The failure to establish strong institutions and a sustainable economy contributed to the conflict, highlighting the need for a long-term commitment to state-building.
The Role of International Mediation & Guarantors
Successful recognition and establishment of a Palestinian state will require sustained international mediation and the involvement of credible guarantors.
* The Quartet: The role of the Middle East Quartet (United States, Russia, European Union, and United Nations) is crucial in facilitating negotiations and ensuring compliance with agreements.
* Regional actors: Engaging regional actors, such as Egypt, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia, is essential for building consensus and fostering regional stability.
* Security Guarantees: Providing security guarantees to both Israel and Palestine can help build trust and prevent future conflicts.
* Monitoring Mechanisms: Establishing independent monitoring mechanisms to oversee the implementation of agreements and address violations is vital.