New Guidelines Released for Advanced Cardiac PET Imaging
Table of Contents
- 1. New Guidelines Released for Advanced Cardiac PET Imaging
- 2. Enhanced Cardiac Imaging: PET vs. SPECT
- 3. Who Benefits From 18F-flurpiridaz PET MPI?
- 4. Key Technical Considerations for PET MPI
- 5. Mitigating Potential Errors in Imaging
- 6. The Future of Cardiac Diagnostics
- 7. Understanding myocardial Perfusion Imaging
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions about Cardiac PET Imaging
- 9. What are the key changes in updated guidelines regarding patient selection for PET MPI?
- 10. Key Insights from Updated Guidelines on PET Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: Enhancing Diagnostic Precision adn Clinical Applications
- 11. Understanding the Evolution of PET MPI Guidelines
- 12. Advancements in PET MPI Technology & Radiotracers
- 13. Refining Patient Selection for PET MPI
- 14. Standardizing PET MPI Protocols for Optimal Results
- 15. Interpreting PET MPI Results: A Focus on Quantitative MBF
- 16. Clinical Applications: Guiding Treatment Decisions
A collaborative effort by prominent medical organizations has resulted in the release of new clinical guidelines surrounding the use of 18F-flurpiridaz Positron Emission Tomography (PET) for myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI).The guidelines, unveiled Today by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and molecular Imaging (SNMMI) alongside the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM), the American College of Nuclear Medicine (ACNM), and the american Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC), aim to standardize and optimize this increasingly vital cardiac diagnostic tool.
Enhanced Cardiac Imaging: PET vs. SPECT
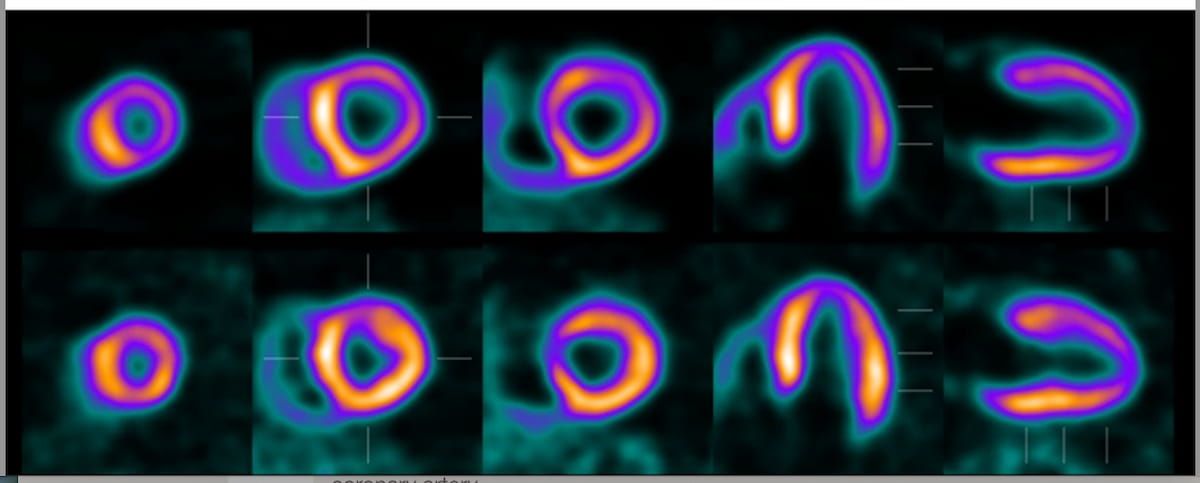
For years, Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) has been the standard for MPI. Though, the new recommendations highlight the benefits of PET imaging, noting its superior spatial resolution, heightened accuracy, and ability to quantitatively assess myocardial blood flow (MBF). This advancement allows for a more detailed and precise evaluation of heart function and potential blockages.
Who Benefits From 18F-flurpiridaz PET MPI?
These guidelines specify a range of patients who would benefit from 18F-flurpiridaz PET MPI. These include individuals experiencing chest pain with an intermediate to high probability of coronary artery disease (CAD), and also those without symptoms but who are at a important risk-greater than 20 percent-of developing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) within the next decade. Moreover, the technique is valuable for quantifying blood flow to the heart muscle during both rest and stress.
Key Technical Considerations for PET MPI
Accomplished implementation of 18F-flurpiridaz PET MPI requires specific technical protocols. Facilities must have access to a 12-lead electrocardiograph and a sphygmomanometer to monitor patients during stress testing. Crucially, the PET/CT scanner should be equipped with cardiac electrocardiogram (ECG) gating.The intravenous injection of 18F-flurpiridaz should occur at peak exercise-defined as exceeding 85 percent of an age-adjusted maximum heart rate or the point of maximal exertion.
Image acquisition should follow a 10-minute list-mode protocol, with imaging performed 15 to 25 minutes post-injection. Researchers emphasize that conventional modeling techniques are inadequate for calculating myocardial blood flow and myocardial flow reserve instantly following exercise, as the tracer has already distributed throughout the heart muscle.
Mitigating Potential Errors in Imaging
The guidelines address the importance of minimizing misalignment artifacts, recommending the use of low-dose CT scans for attenuation correction during both rest and stress imaging. Careful inspection of the fused PET and CT data is also essential to prevent misregistration, wich can lead to inaccurate readings of myocardial blood flow, particularly in the lateral, anterior, and anterolateral regions of the heart.
Did You Know? According to the American Heart Association, heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States, accounting for nearly 805,000 deaths in 2022.
The Future of Cardiac Diagnostics
Initial studies suggest that assessing stress MBF may provide a more refined diagnostic evaluation of coronary lesions with 50 to 69 percent stenosis compared to traditional relative perfusion assessments. Additionally, stress MBF may offer improved detection of epicardial CAD when compared to myocardial flow reserve (MFR). The ability to quantify resting and stress end-diastolic volume,ejection fraction,and end-systolic volume with 18F-flurpiridaz PET allows for thorough evaluation of left ventricular function.
| Imaging Technique | Spatial Resolution | Quantitative Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| SPECT | Lower | limited |
| PET (18F-flurpiridaz) | Higher | Enhanced |
Pro Tip: Early and accurate diagnosis of coronary artery disease is crucial for implementing preventative measures and improving patient outcomes.
Understanding myocardial Perfusion Imaging
Myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) is a non-invasive diagnostic test that assesses blood flow to the heart muscle. It helps identify areas of reduced blood flow, which may indicate coronary artery disease.Different imaging techniques, like SPECT and PET, capture images of the heart at rest and during stress to reveal potential blockages or abnormalities.
The choice between SPECT and PET MPI depends on various factors, including patient characteristics, available resources, and the clinical question being addressed. As technology advances, PET imaging is becoming increasingly favored due to its superior capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cardiac PET Imaging
- What is 18F-flurpiridaz PET MPI? It’s an advanced imaging technique used to assess blood flow to the heart muscle,offering higher accuracy than traditional methods.
- Who is a good candidate for PET MPI? Individuals with chest pain, risk factors for heart disease, or those needing a more detailed assessment of heart function.
- How dose PET MPI differ from SPECT? PET MPI provides higher resolution images and allows for quantitative assessment of blood flow, leading to a more precise diagnosis.
- What preparation is needed for a PET MPI scan? Your doctor will provide specific instructions, which may include fasting and avoiding caffeine before the test.
- Are there any risks associated with PET MPI? PET MPI is generally safe, but it involves exposure to a small amount of radiation.
- How long does a PET MPI scan take? The entire process typically takes several hours, including preparation, exercise/stress testing, and imaging.
- What does the future hold for cardiac PET imaging? Expect further refinements in imaging protocols, improved diagnostic accuracy, and expanded clinical applications.
What are your thoughts on the increasing role of advanced imaging in diagnosing heart disease? Share your comments below!
What are the key changes in updated guidelines regarding patient selection for PET MPI?
Key Insights from Updated Guidelines on PET Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: Enhancing Diagnostic Precision adn Clinical Applications
Understanding the Evolution of PET MPI Guidelines
Recent updates too guidelines surrounding PET myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) represent a meaningful step forward in cardiovascular diagnostics. These revisions, largely driven by advancements in technology and a growing body of clinical evidence, aim to optimize the use of cardiac PET scans for improved patient care. The focus is on refining patient selection, standardizing protocols, and enhancing the interpretation of results.Key organizations like the American society of nuclear Cardiology (ASNC) and the American Heart Association (AHA) have contributed to these updated recommendations.
Advancements in PET MPI Technology & Radiotracers
The landscape of PET imaging for heart disease has been transformed by several technological innovations:
* Improved PET/CT scanners: Newer generation scanners offer higher resolution, faster acquisition times, and reduced radiation exposure. This is exemplified by systems like the Discovery LS mentioned in Shandong Province hospitals (as noted in recent reports),showcasing advanced capabilities in PET-CT imaging.
* Novel Radiotracers: Beyond customary Rubidium-82,we’re seeing increased utilization of Nitrogen-13 ammonia and Oxygen-15 water. These tracers offer distinct pharmacokinetic properties and can be tailored to specific clinical scenarios.
* Quantitative PET MPI: A major shift is towards quantitative myocardial perfusion assessment. This involves using software to calculate absolute myocardial blood flow (MBF) values, providing a more objective and reproducible measure of ischemia than visual interpretation alone.
Refining Patient Selection for PET MPI
Updated guidelines emphasize a more targeted approach to patient selection. PET myocardial perfusion scans are particularly valuable in:
- Patients with Intermediate Risk of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Individuals with atypical chest pain or inconclusive stress tests benefit significantly from the higher accuracy of PET MPI.
- Evaluating Known CAD: PET MPI can assess the extent and severity of ischemia in patients already diagnosed with CAD, guiding decisions regarding revascularization.
- Risk Stratification After Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS): Determining the presence and extent of viable myocardium after a heart attack is crucial for prognosis and treatment planning.PET scans after heart attack provide valuable insights.
- Assessment of Microvascular Dysfunction: PET MPI is uniquely suited to detect coronary microvascular disease, a common cause of chest pain, especially in women.
Standardizing PET MPI Protocols for Optimal Results
Consistency in protocol is paramount for reliable results. Key recommendations include:
* Standardized Rest and Stress Protocols: Defined protocols for both pharmacological stress (using agents like adenosine or regadenoson) and exercise stress are essential.
* Image Acquisition Parameters: Specific guidelines for scan duration, attenuation correction, and reconstruction algorithms are crucial for minimizing variability.
* Quantitative Analysis software: Utilizing validated software for MBF quantification is now considered standard practice.
* Radiation Dose Optimization: Employing techniques to minimize radiation exposure while maintaining image quality is a priority.
Interpreting PET MPI Results: A Focus on Quantitative MBF
The move towards quantitative PET MPI necessitates a shift in interpretation.Instead of relying solely on visual assessment of perfusion defects, clinicians should focus on:
* Absolute MBF Values: Defining thresholds for ischemia based on absolute MBF values (ml/min/g) provides a more objective assessment.
* Coronary Flow Reserve (CFR): Calculating CFR (the ratio of stress MBF to rest MBF) offers a complete measure of coronary artery function. A CFR < 2.0 generally indicates significant ischemia.
* Regional MBF Distribution: Identifying areas of reduced MBF can pinpoint the location and extent of ischemia.
* Integration with Other Imaging Modalities: Combining PET MPI findings with data from coronary CT angiography (CCTA) or invasive coronary angiography can provide a more complete picture of CAD.
Clinical Applications: Guiding Treatment Decisions
Updated guidelines highlight the impact of PET MPI on clinical decision-making:
* Revascularization Guidance: PET MPI can identify patients who are most likely to benefit from coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
* **Prognostic Assessment