Korean Hair Care Brand Dr. Groot Offers Solution For damaged Hair
Table of Contents
- 1. Korean Hair Care Brand Dr. Groot Offers Solution For damaged Hair
- 2. What Sets Dr. groot Apart?
- 3. Key Dr.Groot Products & Benefits
- 4. Limited-Time Offer
- 5. what are the most effective ways to thicken thinning hair with dr. Groot’s top hair thickening treatments?
- 6. Revitalize Your Hair: 20% Off Dr. Groot’s Top Hair Thickening Treatments
- 7. Understanding Hair Thinning: Causes & Types
- 8. Dr. Groot’s Featured Hair Thickening Treatments – Now 20% Off!
- 9. Beyond Products: Lifestyle Factors for Hair Health
- 10. Real Results: Patient Experiences
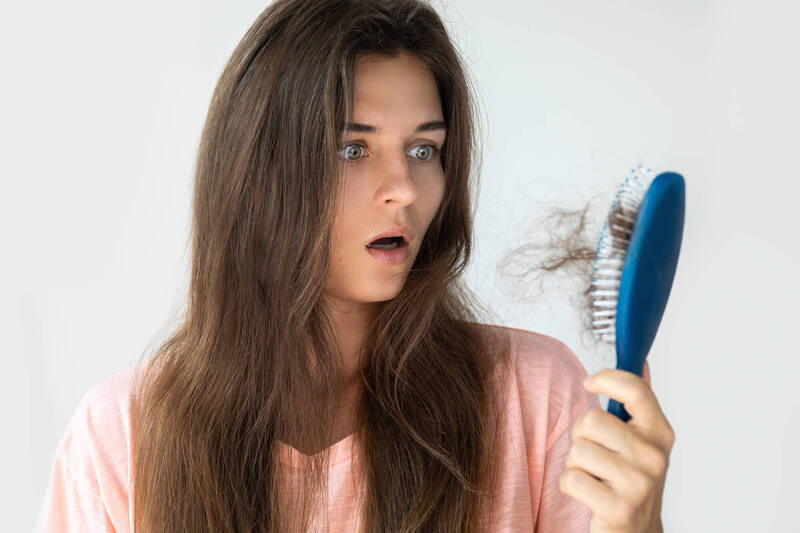
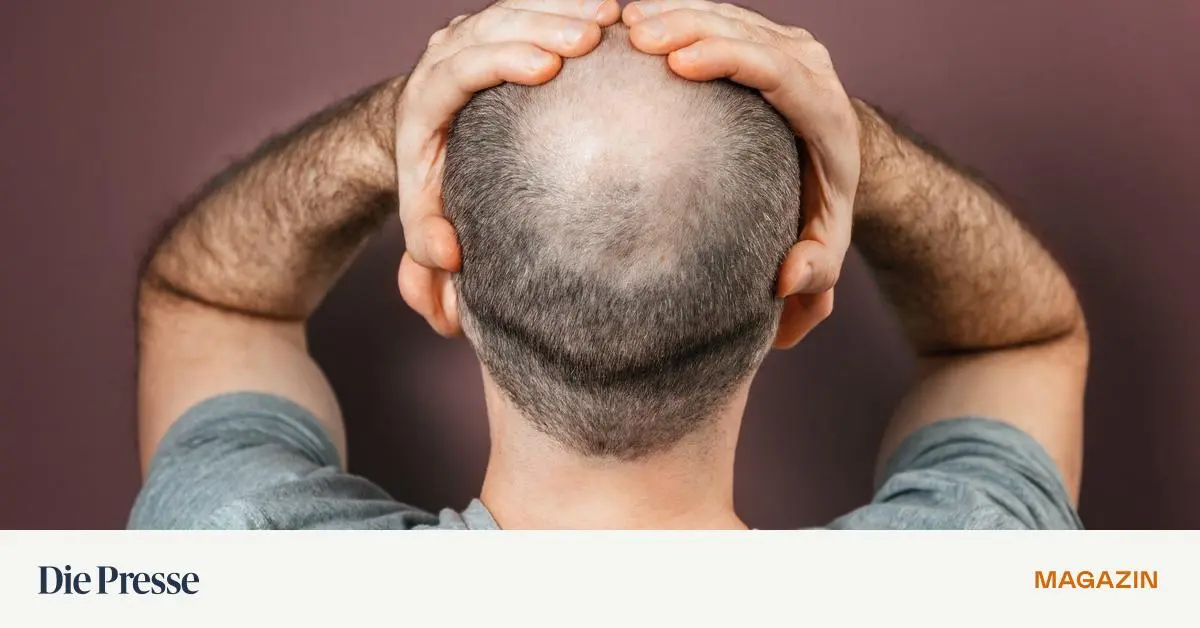
For Individuals Battling Brittle, Damaged Hair, A New Approach To Revitalization Is Emerging From The Korean Beauty Industry. Dr. Groot, A Leading Brand In Hair Care, Positions Itself As A Solution For Those Seeking To Restore Health And Thickness To Their Mane.
Many People Experience Hair Damage Due To Frequent Use Of Heat Styling Tools And Chemical Treatments. This Can Lead To Weakened Strands, Split Ends, and Overall Lackluster Appearance. Now,A Focus On Natural Ingredients And Gentle Formulations May Offer A Path To Repair And Renewal.
What Sets Dr. groot Apart?
Dr. Groot Has Quickly Gained recognition As A Top-Rated Korean Hair Care Brand, specializing In Solutions For Hair Thickening And Scalp Health. The Brand’s Ideology Centers around Utilizing The Power Of Natural Ingredients, Such As Biotin And Prebiotics, To Nourish Hair From The Root.
Unlike Many Customary Hair Care Products, dr. Groot Formulations Are Notably Free From Sulfates And Other Harsh Chemicals. This Makes Them Suitable For A Wide Range Of Hair Types And Textures, Minimizing The Risk Of Irritation Or Further Damage. The Brand Offers A Comprehensive Lineup Including Shampoos, Serums, and conditioners Designed To Address Various Hair Concerns.
Key Dr.Groot Products & Benefits
Dr. Groot’s Product Range Is designed To Target Multiple aspects Of Hair Health, From Strengthening The Scalp To Promoting Hair Growth.Here’s A Brief Overview Of Some Key Offerings:
| Product Type | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Hair Thickening Shampoos | Cleanses While Adding Volume And Strength. |
| Revitalizing Shower Treatments | Deeply Conditions And Nourishes The Scalp. |
| Hair Serums | Targets Specific Concerns Like Dryness And Damage. |
According To The National institutes Of health, Biotin—A Key Ingredient In Many Dr. Groot Products—Plays A Crucial Role In Hair Health By Strengthening Keratin, The Protein That Makes Up Hair. Learn more about Biotin’s benefits here.
Limited-Time Offer
For A Limited Time, consumers Can Save 20% On Dr. Groot Best-Selling Products By Using The Code LOOT20 At Checkout. This Presents An Chance To Invest In High-Quality Hair Care at A Reduced Cost.
Are You Ready To Explore The Potential Of Korean Hair Care to Transform Your hair? What are Your Biggest Hair Concerns, And How Do You Think natural Ingredients Could help?
what are the most effective ways to thicken thinning hair with dr. Groot’s top hair thickening treatments?
Revitalize Your Hair: 20% Off Dr. Groot’s Top Hair Thickening Treatments
As a dermatologist specializing in hair health, I frequently encounter patients concerned about thinning hair and a lack of volume. It’s a common issue, impacting both men and women, and often linked to factors like genetics, stress, diet, and hormonal changes. Fortunately, advancements in hair care offer effective solutions. At Dr. Groot, we’ve dedicated years to researching and formulating treatments designed to address these concerns, and right now, you can experience the benefits with 20% off our top hair thickening treatments!
Understanding Hair Thinning: Causes & Types
Before diving into solutions, it’s crucial to understand why hair thinning occurs. Several factors contribute:
* Androgenetic Alopecia: Commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, this is a genetic condition.
* Telogen Effluvium: Temporary hair shedding frequently enough triggered by stress, illness, or childbirth.
* Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential vitamins and minerals (iron, zinc, biotin) can impact hair growth.
* Scalp Conditions: Dermatitis, psoriasis, and fungal infections can contribute to hair loss.
* Styling Practices: Tight hairstyles and harsh chemical treatments can damage hair follicles.
identifying the root cause is the first step towards effective treatment. A consultation with a dermatologist can definitely help pinpoint the specific type of hair loss you’re experiencing.
Dr. Groot’s Featured Hair Thickening Treatments – Now 20% Off!
We’ve curated a selection of our most effective treatments, now available at a special discount. Here’s a closer look:
1. Dr. Groot’s DHT Blocker Shampoo:
This isn’t your average shampoo. Formulated with saw palmetto, biotin, and ketoconazole, it actively combats dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to androgenetic alopecia. DHT shrinks hair follicles, leading to thinner strands. By blocking DHT, this shampoo helps promote thicker, fuller-looking hair.
* Key Benefits: Reduces DHT levels, strengthens hair follicles, improves scalp health.
* Usage: Use daily or as directed by your dermatologist.
2. Dr. Groot’s Scalp Serum with Minoxidil & Redensyl:
Our potent scalp serum combines the proven effectiveness of minoxidil with the innovative power of Redensyl.Minoxidil widens blood vessels in the scalp, improving blood flow to hair follicles. Redensyl stimulates stem cells to reactivate dormant follicles, promoting new hair growth.
* key Benefits: Stimulates hair growth, increases hair density, revitalizes the scalp.
* Usage: Apply directly to the scalp twice daily. consistent use is key for optimal results.
3. Dr. Groot’s Hair Growth Vitamins:
Nourishing your hair from within is just as significant as topical treatments. Our Hair Growth Vitamins contain a complete blend of essential vitamins and minerals, including biotin, zinc, iron, vitamin D, and vitamin C. These nutrients support healthy hair growth and strengthen existing strands.
* key Benefits: supports healthy hair growth, strengthens hair, improves overall hair health.
* Usage: Take two capsules daily with a meal.
4. dr. Groot’s Peptide Complex Conditioner:
This luxurious conditioner utilizes a blend of powerful peptides to strengthen and repair damaged hair. Peptides are the building blocks of protein, and they help to rebuild the hair shaft, making it stronger and more resilient.
* Key Benefits: Repairs damaged hair, strengthens hair shaft, adds shine and manageability.
* Usage: Apply after shampooing, leave on for 2-3 minutes, and rinse thoroughly.
Beyond Products: Lifestyle Factors for Hair Health
While Dr. Groot’s treatments offer targeted solutions, adopting a hair-healthy lifestyle can significantly enhance results. Consider these tips:
* Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in protein, iron, zinc, and vitamins.
* Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
* Gentle Hair Care: Avoid harsh chemical treatments, excessive heat styling, and tight hairstyles.
* Scalp Massage: Regular scalp massage can improve blood circulation and stimulate hair growth.
* Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep your hair and scalp hydrated.
Real Results: Patient Experiences
We’ve seen incredible transformations with Dr. Groot’s treatments. One patient, Sarah M. (age 35), experienced significant hair thinning after pregnancy. After using our DHT Blocker Shampoo and Scalp Serum for six months, she reported a noticeable increase in hair density and volume. “I was so worried about losing my hair permanently,” she shared. “Dr. Groot’s products gave me my confidence back.” (Patient testimonial used with permission).
Another patient, David L. (age 52), struggled with male pattern baldness for years. He found relief with our Scalp Serum and Hair Growth Vitamins. “I’ve tried everything, and nothing seemed to work,” he said. “Dr. Groot’s products actually made a difference. I’m seeing new hair growth in areas where I had previously lost all hope.” (Patient testimonial used with permission).