New Strategies Offer Hope in the Fight Against Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Table of Contents
- 1. New Strategies Offer Hope in the Fight Against Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- 2. Beyond “War”: A New Metaphor for Lymphoma Treatment
- 3. Understanding Non-hodgkin Lymphoma: Types and Challenges
- 4. Key Lymphoma Statistics
- 5. Advancements in Treatment: Bispecific Antibodies and Beyond
- 6. The Vital Role of Support Networks and Nursing Care
- 7. What are the latest breakthroughs in CAR T‑cell therapy for lymphoma?
- 8. The Chessboard of Lymphoma: Patients, Doctors, and New Treatment Paths
- 9. Understanding the Lymphoma Landscape: Types and Subtypes
- 10. the Diagnostic Journey: From Suspicion to confirmation
- 11. Conventional Treatment Approaches: Chemotherapy, Radiation, and Stem Cell Transplant
- 12. The Rise of Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapies: A New Era in Lymphoma Care
- 13. Managing Side Effects: A Holistic Approach
- 14. The Patient-Doctor Partnership: Shared Decision-Making
- 15. Real-World Example: The Impact of CAR T-cell Therapy
- 16. Benefits of Early Diagnosis and Advanced Treatment
A shift in perspective and innovative treatments are reshaping the landscape for patients battling these complex blood cancers.
Beyond “War”: A New Metaphor for Lymphoma Treatment
The conventional “war on cancer” metaphor is being re-evaluated, as healthcare professionals emphasize the nuanced journey of living with and treating Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. A new campaign employs the analogy of chess – a game of strategy, setbacks, and restarts – to better represent the patient experience and the evolving approaches to care. this shift aims to move away from framing treatment as a simple win or lose battle, acknowledging the long-term challenges and complexities faced by patients and their families.
This initiative, “Check Lymphoma,” highlights the potential of emerging therapies like bispecific antibodies, designed to improve both treatment outcomes and quality of life for individuals with lymphoma.The campaign is a collaborative effort involving Abbvie, the Italian Association against Leukemia, lymphoma and Myeloma (AIL), the Italian Lymphoma Federation (FIL), and the Italian Group of Lymphoma Nurses (GFIL), offering resources and patient stories on www.scaccoallinfoma.it.
Understanding Non-hodgkin Lymphoma: Types and Challenges
Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas encompass over 50 distinct subtypes, broadly categorized as indolent (slow-growing) or aggressive (fast-growing).Approximately 45% of cases are indolent, often allowing patients to live with the condition for years, while aggressive forms, though rapidly progressing, frequently respond well to treatment, with over half achieving recovery. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is the most prevalent aggressive type, impacting lymph nodes and potentially other organs, and accounts for roughly 150,000 new cases globally each year, with around 4,400 diagnoses in Italy alone.
follicular lymphoma, the most common indolent form, is often assessed using the FLIPI index and carries a risk of recurrence and diminishing effectiveness of conventional therapies over time. According to Marco Ladetto, a Professor of Hematology at the University of Eastern Piedmont, recurrence signifies the return of lymphoma even after initial prosperous treatment, while refractory lymphoma indicates a lack of response despite therapeutic intervention. Recurrences in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma tend to appear within months or years, while follicular lymphoma can relapse after decades.
Key Lymphoma Statistics
| Lymphoma Type | Global New Cases (Annual) | Italian New Cases (Annual) | Typical Progression |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma | ~150,000 | ~4,400 | Rapid; Early Recurrence |
| Follicular Lymphoma | not Specified | Not Specified | Slow; Potential for Late Recurrence |
Advancements in Treatment: Bispecific Antibodies and Beyond
Despite complexities, treatment success rates are increasing, particularly with innovative therapies. While CAR-T cell therapy offers potential cures for around 40% of patients,challenges remain regarding resistance and manufacturing timelines. Bispecific antibodies represent a critically important advancement, redesigning treatment protocols for both follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Currently approved in Italy following at least two prior treatment lines, these antibodies redirect the body’s T lymphocytes to target and destroy cancerous cells.
Clinical trials demonstrate complete remission rates of approximately 40% for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and over 60% for follicular lymphoma, with sustained responses observed for years. Experts anticipate a future where these treatments are integrated earlier in the treatment process, combined with chemotherapy and other immunomodulatory agents.
The Vital Role of Support Networks and Nursing Care
Effective lymphoma care requires a strong support system. nurses and caregivers play a crucial role,bridging interaction gaps and providing emotional support. Giuliana Nepoti, head of the GIFIL Commission, emphasizes the nurse’s ability to translate medical jargon and empower patients to understand their condition and treatment. AIL national president Giuseppe Toro highlights the evolving expectations for patients, emphasizing the possibility of healing or maintaining a high quality of life, even with chronic lymphoma, and the importance of patient and caregiver emotional support.
Patient support groups, like those facilitated by AIL and FIL, offer a space to share anxieties, hopes, and practical advice for navigating the challenges of diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management.
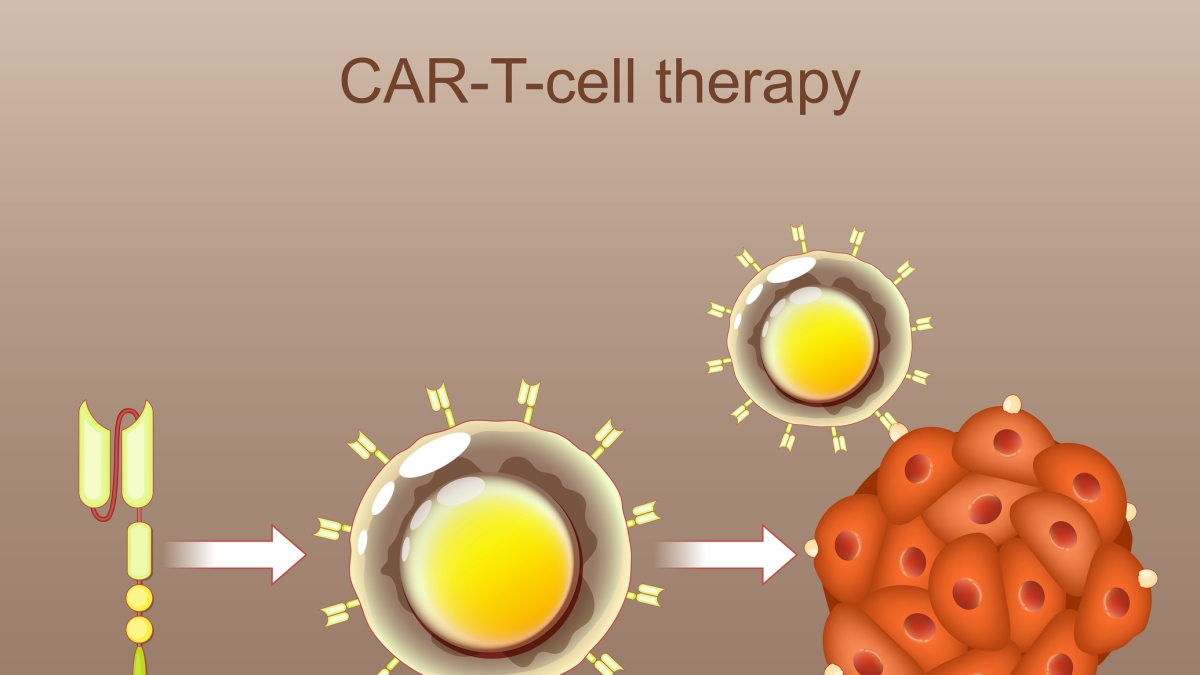
What are the latest breakthroughs in CAR T‑cell therapy for lymphoma?
The Chessboard of Lymphoma: Patients, Doctors, and New Treatment Paths
Lymphoma, a cancer originating in the lymphatic system, presents a complex challenge for both patients and healthcare professionals. Understanding the nuances of this disease – its various subtypes, diagnostic approaches, and evolving treatment landscape – is crucial. Think of navigating lymphoma as a game of chess; each piece (treatment option, diagnostic test, patient characteristic) has a specific role, and strategic moves are essential for a positive outcome.
Understanding the Lymphoma Landscape: Types and Subtypes
Lymphoma isn’t a single disease. It encompasses over 80 different subtypes, broadly categorized into two main types: Hodgkin lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).
* Hodgkin Lymphoma: Often characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, this type generally has a high cure rate, particularly in early stages.
* Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: A more diverse group,NHL includes various subtypes like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL),follicular lymphoma,mantle cell lymphoma,and Burkitt lymphoma. Each subtype behaves differently and requires a tailored approach.
Accurate subtyping is paramount. Modern diagnostic techniques, including flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and genetic testing, are vital for precise classification. This precision guides treatment decisions and helps predict prognosis.
the Diagnostic Journey: From Suspicion to confirmation
Recognizing the early signs of lymphoma is the first step. Symptoms can be vague – swollen lymph nodes (frequently enough painless), fatigue, fever, night sweats, unexplained weight loss, and itchy skin. Though, these symptoms can also indicate other conditions, making accurate diagnosis challenging.
The diagnostic process typically involves:
- Physical Examination: assessing for enlarged lymph nodes and other physical signs.
- Biopsy: Removing a sample of affected lymph node tissue for microscopic examination. This is the gold standard for diagnosis.
- imaging Scans: CT scans, PET scans, and MRI help determine the extent of the disease (staging).
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: Assessing whether lymphoma has spread to the bone marrow.
- Blood Tests: Evaluating overall health and identifying specific markers associated with lymphoma.
Conventional Treatment Approaches: Chemotherapy, Radiation, and Stem Cell Transplant
for decades, chemotherapy has been the cornerstone of lymphoma treatment. Different chemotherapy regimens are used depending on the subtype and stage of the disease. Radiation therapy is often used in combination with chemotherapy, particularly for localized lymphoma.
* chemotherapy: Uses drugs to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. Common regimens include CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone) for aggressive lymphomas.
* Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells.Effective for localized disease and palliative care.
* Stem Cell Transplant: Used for relapsed or refractory lymphoma.Involves high-dose chemotherapy followed by infusion of healthy stem cells to rebuild the bone marrow. Can be autologous (using the patient’s own stem cells) or allogeneic (using stem cells from a donor).
The Rise of Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapies: A New Era in Lymphoma Care
The past decade has witnessed a revolution in lymphoma treatment with the advent of targeted therapies and immunotherapies. These approaches offer more precise and less toxic options for many patients.
* Targeted Therapies: These drugs specifically target vulnerabilities within lymphoma cells. Examples include:
* BTK Inhibitors: (e.g., ibrutinib) block a protein crucial for B-cell survival, effective in mantle cell lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma.
* BCL-2 Inhibitors: (e.g., venetoclax) induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in lymphoma cells.
* Immunotherapies: Harness the power of the patient’s own immune system to fight cancer.
* Monoclonal Antibodies: (e.g., rituximab) target specific proteins on lymphoma cells, marking them for destruction by the immune system.
* CAR T-cell Therapy: A groundbreaking therapy where a patient’s T cells are genetically engineered to recognize and attack lymphoma cells. Highly effective for certain aggressive lymphomas that have failed other treatments.
* Checkpoint Inhibitors: Release the brakes on the immune system, allowing it to more effectively target cancer cells.
Managing Side Effects: A Holistic Approach
Treatment for lymphoma, while frequently enough effective, can cause significant side effects. managing these side effects is crucial for maintaining quality of life.
* Common Side Effects: Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, mouth sores, increased risk of infection.
* Supportive Care: Medications to manage nausea, pain, and infection. Nutritional counseling. psychological support.
* Integrative Therapies: Acupuncture, massage, and mindfulness can help alleviate symptoms and improve well-being.
Effective lymphoma care requires a strong partnership between patients and their healthcare team. Open interaction, shared decision-making, and a focus on patient preferences are essential. Patients should actively participate in discussions about their treatment options, potential benefits, and risks.
Real-World Example: The Impact of CAR T-cell Therapy
Consider a 55-year-old patient with aggressive DLBCL who had relapsed after multiple lines of chemotherapy. Traditional treatment options were limited. CAR T-cell therapy offered a new hope. After undergoing the therapy, the patient achieved complete remission and remains cancer-free two years later. This exemplifies the transformative potential of these innovative treatments.
Benefits of Early Diagnosis and Advanced Treatment
*