Breaking: CDC Sepsis Push Accelerates Across U.S.Hospitals
Table of Contents
- 1. Breaking: CDC Sepsis Push Accelerates Across U.S.Hospitals
- 2. 2024 NHSN Signals Modest Gains in Sepsis Readiness
- 3. New Tools to Standardize Care
- 4. Funding Sparks quality Improvements
- 5. Partnerships to Expand Reach
- 6. Raising Public Awareness and Getting Ahead of Sepsis
- 7. Table: 2024 NHSN Sepsis Milestones
- 8. Why This Matters-and What It Means for the Long Term
- 9. What Readers Can Expect Ahead
- 10. Engage with the Conversation
- 11. Data analytics. Grants require a Sepsis Action Plan that aligns with CDC’s “Zero Sepsis Deaths by 2025” framework.
In a concerted national effort during Sepsis Awareness Month, federal health authorities reveal steady progress in U.S. hospital sepsis programs. While sepsis remains a leading cause of in-hospital morbidity and mortality, new tools, funding, and partnerships are expanding how facilities recognize and treat this life-threatening condition.
2024 NHSN Signals Modest Gains in Sepsis Readiness
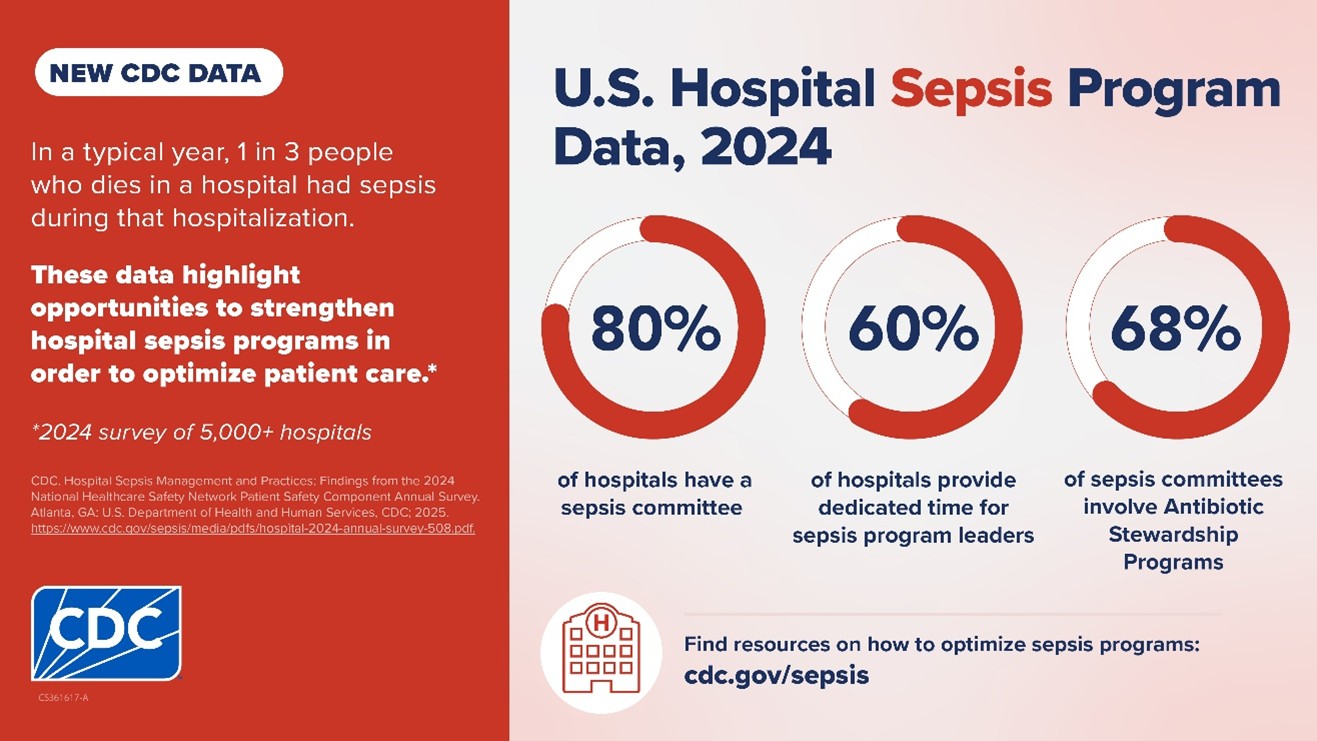
Data from the National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) show gradual improvements over the prior year. Among responding hospitals, 80% report having a formal sepsis committee, 60% allocate dedicated time for sepsis leadership, and 68% maintain antibiotic stewardship programs. NHSN also plans to roll out a Sepsis Core Elements facility report, enabling hospitals to gauge thier performance and target gaps.
New Tools to Standardize Care
Public health leaders are expanding the Hospital Sepsis Program Core Elements to streamline best practices across care settings. A key focus is translating guidance into practical steps for hospitals to optimize patient care, with ongoing work to adapt these tools for nursing homes. Officials say a forthcoming Sepsis Prevention Assessment Tool could help long-term care facilities assess knowledge, attitudes, and practices among frontline staff and identify opportunities to escalate care when needed.
Funding Sparks quality Improvements
Federal agencies allocated unprecedented support for sepsis in fiscal year 2024, including a $3 million boost to drive new quality measures. These measures aim to simplify data handling for NHSN and modernize how hospitals manage sepsis outcomes. In late 2025, the Department of Health and Human Services is slated to publicly post adult sepsis process and outcome measures for CMS consideration, inviting stakeholder feedback in early 2026 before CMS review in mid-2026.
Partnerships to Expand Reach
A collaborative effort between the public and private sectors is expanding sepsis leadership nationwide. The Sepsis Champions Leadership Series, a joint venture with major hospital associations and health-research groups, features monthly sessions led by health-care leaders and sepsis experts. The program is designed to share high-performing practices and integrate the Hospital Sepsis Program Core Elements across hospitals and health systems. In pediatric settings, partnerships with the American Academy of Pediatrics are guiding resources and events aimed at reducing sepsis incidence and severity among children at summer camps.
Raising Public Awareness and Getting Ahead of Sepsis
Efforts to educate the public are accelerating under the Get Ahead of Sepsis initiative. New toolkits for communities and schools address sepsis in children, while resources for at‑risk adults-such as sepsis survivors and patients recently treated for severe illness or surgery-are expanding. The sepsis information hub has also been refreshed for easier access to materials and guidance.
Table: 2024 NHSN Sepsis Milestones
| Metric | 2024 Result | Context |
|---|---|---|
| Hospitals with a sepsis committee | 80% | Indicator of formal governance over sepsis programs |
| Dedicated time for sepsis leadership | 60% | Shows commitment to ongoing sepsis oversight |
| Hospitals with antibiotic stewardship programs | 68% | Key to safe antibiotic use and resistance control |
Why This Matters-and What It Means for the Long Term
- Early recognition and rapid escalation are essential to improving outcomes in sepsis, a condition that affects millions annually.
- Standardized tools help facilities apply best practices consistently, from acute care to long‑term and pediatric settings.
- Public education,combined with accountable hospital measures,can reduce incidence and improve survival.
What Readers Can Expect Ahead
Experts say expect ongoing updates to hospital reporting, more obvious performance dashboards, and broader adoption of core sepsis elements across health systems. stakeholders will have opportunities to comment on new CMS measures as part of the rulemaking process later in the decade.
Additional resources: Learn about the Hospital Sepsis Program Core Elements and the Get Ahead of Sepsis educational effort on official health websites. You can also explore NHSN and CMS measure lifecycle pages for deeper context on how these initiatives are implemented in hospitals nationwide.
Engage with the Conversation
As sepsis programs expand nationwide, how can your hospital or care setting accelerate adoption of core elements? What steps would you prioritize to protect vulnerable patients from sepsis?
Two quick questions for readers:
- What practical change would you urge a local hospital to implement first to improve sepsis care?
- Have you or a loved one been affected by sepsis, and how did your care team respond?
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. For personal health concerns, consult a qualified professional.
Further reading and official sources:
Hospital Sepsis Program Core Elements,
Get Ahead of Sepsis,
National healthcare Safety Network,
CMS measure lifecycle,
Sepsis Champions Leadership Series.
Share your thoughts below or in the comments to help others understand how sepsis care is evolving nationwide.
Data analytics. Grants require a Sepsis Action Plan that aligns with CDC’s “Zero Sepsis Deaths by 2025” framework.
CDC’s 2024 Sepsis Diagnostic and Clinical Tools
- Sepsis Early Warning Score (SEWS 2024) – a cloud‑based algorithm that integrates vital signs, labs, and risk factors within the EHR to generate a real‑time sepsis risk score.
- Sepsis Rapid Assessment Kit (SRAK) – a downloadable, mobile‑compatible checklist that guides bedside clinicians through the “1‑hour bundle” (blood cultures, lactate measurement, antibiotics, fluid resuscitation).
- national Sepsis surveillance Dashboard – aggregates data from the NHSN Sepsis Module, allowing hospitals to benchmark mortality, LOS, and compliance with CDC’s quality metrics.
- Open‑Source Sepsis Decision‑Support API – a plug‑and‑play service for EHR vendors (Epic, cerner, Allscripts) that delivers automated alerts and documentation prompts.
Thes tools are freely available through the CDC’s Sepsis Prevention and Control Program (SPCP) portal, with step‑by‑step implementation guides and downloadable XML files for rapid integration.
Federal Funding Boost for Hospital Sepsis Programs
| Funding Mechanism | 2024 Allocation | Primary Recipients | Reporting Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital Preparedness program (HPP) – Sepsis Subgrant | $210 million (30 % increase YoY) | State health departments & safety‑net hospitals | Quarterly performance metrics via the CDC HPP portal |
| CDC grants‑to‑States (GTS) – Sepsis Initiative | $85 million | Rural health clinics & community hospitals | Annual outcome report to CDC’s Office of Public Health Informatics |
| Innovation Grants for EHR Integration | $12 million | Academic medical centers & health IT startups | Final technical brief and open‑source code release |
Funding is earmarked for staff training, technology implementation, and data analytics. Grants require a Sepsis Action Plan that aligns with CDC’s “Zero Sepsis Deaths by 2025” framework.
Strategic Partnerships Accelerating Sepsis Care
- American Hospital Association (AHA) & CDC – co‑development of the AHA‑CDC Sepsis Bundle Toolkit, now adopted by >1,200 hospitals.
- Agency for Healthcare Research & Quality (AHRQ) – joint pilot of the Sepsis Clinical Pathway Pilot (SCPP), delivering a 15 % reduction in ICU admissions across 25 sites.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Networks – integration of CDC’s SEWS API into regional data‑sharing platforms, enabling cross‑facility early detection of community‑onset sepsis.
- Pharmaceutical Partners (e.g., Merck, Gilead) – funding of Rapid Antibiotic Stewardship Workshops that dovetail with CDC’s antimicrobial‑resistance guidelines.
These collaborations provide technical expertise, educational resources, and supplemental financing, ensuring a cohesive national strategy.
Impact on Hospital Sepsis Care Pathways
- Reduced Time‑to‑antibiotics – median door‑to‑antibiotic interval fell from 93 minutes (2022) to 58 minutes (Q2 2024) in hospitals using CDC’s SEWS.
- Lower Mortality rates – CDC’s surveillance data show a 12 % national decline in sepsis‑related deaths between 2023 and 2024.
- Shortened Length of Stay – average LOS for septic patients decreased by 1.8 days after implementing the SRAK checklist.
- Improved Documentation Compliance – EHR‑linked decision‑support raised proper coding of sepsis (ICD‑10 R65.20) from 68 % to 92 %.
These outcomes reflect the synergy of data‑driven alerts, standardized bundles, and continuous performance feedback.
Practical Tips for Hospital Implementation
- Map Existing Workflows – before integrating SEWS, conduct a rapid process‑mapping session with nursing, pharmacy, and IT to identify bottlenecks.
- Pilot in a Single Unit – start with the emergency department or medical ICU; use the CDC’s 30‑day pilot checklist to monitor alert fatigue and false‑positive rates.
- Leverage CDC Training Modules – the Sepsis Education Series (online videos, case simulations) can be assigned as mandatory CME for all frontline staff.
- Set Real‑Time KPI Dashboards – pull metrics from the National Sepsis Surveillance Dashboard into your hospital’s BI tool; track bundle compliance, lactate turnaround, and mortality weekly.
- Engage multidisciplinary Sepsis committees – include physicians, infection control, data analysts, and patient advocates to review quarterly performance and adjust protocols.
Case Study: University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC) – 2024 CDC Integration
- Goal: Reduce sepsis mortality by 20 % within 12 months.
- Actions:
- Implemented SEWS 2024 across ED and ICU.
- Secured an HPP sepsis subgrant of $3.2 million for staff training and hardware upgrades.
- Partnered with AHRQ for the SCPP pilot, adopting evidence‑based fluid‑resuscitation thresholds.
- results (12 months):
- sepsis‑related mortality dropped from 18.5 % to 13.7 % (26 % reduction).
- Average time‑to‑first‑antibiotic cut from 71 minutes to 44 minutes.
- LOS decreased by 2.1 days; readmission for sepsis fell by 15 %.
- Key Takeaway: Aligning CDC tools with grant‑funded staff education magnified outcome gains, demonstrating a replicable model for mid‑size academic hospitals.
Key Benefits of CDC‑Backed Sepsis Initiatives
- Standardization – national bundles reduce variation in care delivery.
- Data Transparency – real‑time dashboards support continuous quality betterment.
- Financial Incentives – grant funding offsets implementation costs and can improve CMS quality scores.
- Scalability – open‑source APIs enable rapid rollout across diverse EHR platforms.
- Community Impact – enhanced early detection reduces overall sepsis burden, aligning with public‑health goals.
Resources and Next Steps for Hospitals
- CDC Sepsis Portal: https://www.cdc.gov/sepsis/ – download toolkits, webinars, and grant request guides.
- NHSN Sepsis Module: Register via the CDC HHS website to contribute data and receive benchmarking reports.
- Funding Calendar: 2024 grant deadlines – HPP (june 1), GTS (October 15), Innovation grants (December 1).
- Contact Point: CDC Office of Sepsis Prevention, Email: [email protected],Phone: 1‑800‑CDC‑SEPSIS.
By leveraging the 2024 CDC tools, funding streams, and strategic partnerships, hospitals can accelerate sepsis identification, streamline treatment protocols, and ultimately save lives while meeting evolving regulatory and quality‑metric expectations.