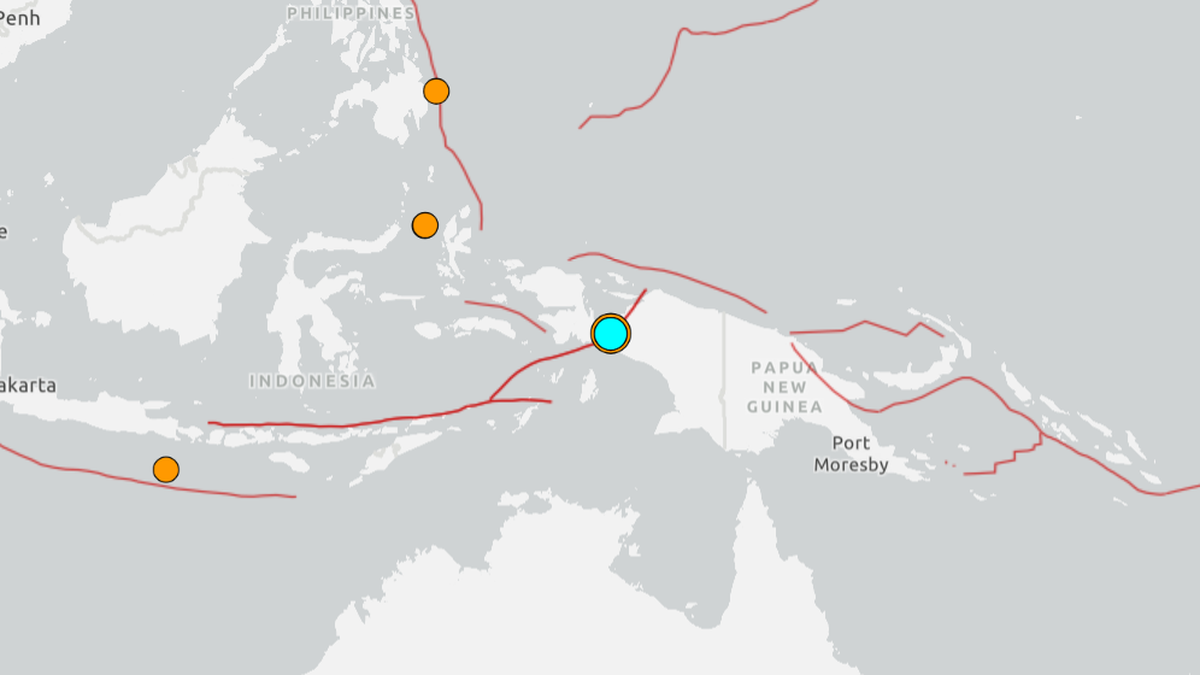
A 6.1 magnitude earthquake rattled Indonesia’s Papua region early Friday, September 19, 2025, triggering structural damage in the coastal town of Nabire. Initial reports indicate no immediate loss of life, though assessments are ongoing.
Damage Assessment in Nabire
Table of Contents
- 1. Damage Assessment in Nabire
- 2. Seismic Details and Tsunami Risk
- 3. Ancient Context and Regional Vulnerability
- 4. Understanding Earthquake Preparedness
- 5. Frequently Asked Questions about Earthquakes in Indonesia
- 6. what are the primary logistical challenges hindering the delivery of humanitarian aid to affected communities in Papua?
- 7. Indonesia’s Papua region Grapples with Scattered Damage Following Magnitude 6.1 Earthquake
- 8. Earthquake Details & Initial Impact
- 9. Damage Assessment & Affected Areas
- 10. Response Efforts & Humanitarian Aid
- 11. Geological Context: Why Papua is Earthquake-Prone
- 12. Earthquake Preparedness in papua: Challenges & Opportunities
- 13. Real-World Example: 2018 Papua Earthquake & tsunami
- 14. Resources & Further Information
According to Suharyanto, head of the National Disaster Mitigation agency, at least two residences and a crucial bridge in Nabire, Central Papua province, have collapsed.A government facility, a place of worship, and the local airport sustained minor damages. The Agency has reported the situation as presently secure and under control.
Communications were disrupted following the quake, with telecommunication networks in Nabire and neighboring towns temporarily offline. Residents reportedly evacuated their homes and sought higher ground as the ground shook.
Seismic Details and Tsunami Risk
The United states Geological Survey pinpointed the epicenter of the 6.1 magnitude quake approximately 28 kilometers (17 miles) south of Nabire, at a depth of 10 kilometers (6 miles). Indonesia’s Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysical Agency swiftly confirmed there was no tsunami threat, as the earthquake’s origin was land-based.
did You Know? Indonesia is located within the ‘Ring of Fire,’ a major area in the Pacific Ocean where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur.
Ancient Context and Regional Vulnerability
Nabire has previously experienced significant seismic events. Deadly earthquakes struck the town in 2004, resulting in 30 fatalities and extensive property damage in February of that year. A subsequent quake in November of the same year caused 32 deaths.
Indonesia, an archipelago comprised of over 280 million people, is particularly susceptible to earthquakes and volcanic activity due to its location along major tectonic plate boundaries. According to the National Disaster Mitigation Agency,Indonesia experiences an average of seven significant earthquakes annually.
| Earthquake Event | Year | Location | fatalities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recent Earthquake | 2025 | Nabire, Papua | 0 (initial reports) |
| Earthquake | 2004 (February) | Nabire | 30 |
| Earthquake | 2004 (November) | Nabire | 32 |
Pro Tip: In the event of an earthquake, drop to your hands and knees, cover your head and neck, and hold on to something stable until the shaking stops.
Understanding Earthquake Preparedness
Earthquake preparedness is crucial for minimizing risk in vulnerable regions. This includes securing heavy objects, developing a family emergency plan, and assembling a disaster supply kit with essentials like water, food, first aid, and a radio.Staying informed about earthquake early warning systems can also provide valuable seconds to prepare.
Indonesia has been actively working to improve its earthquake early warning systems and disaster management infrastructure. Recent efforts include strengthening building codes and conducting regular drills to enhance public awareness and preparedness. UNDRR News
Frequently Asked Questions about Earthquakes in Indonesia
- What causes earthquakes in Indonesia? Indonesia’s location on the Pacific Ring of Fire, where multiple tectonic plates meet and interact, makes it prone to earthquakes.
- Is a tsunami likely after every earthquake in Indonesia? No, a tsunami is only a risk if the earthquake is of sufficient magnitude and occurs underwater, causing displacement of the seafloor.
- How can I prepare for an earthquake? Prepare an emergency kit, secure heavy objects, and have a family evacuation plan.
- What should I do during an earthquake? Drop, cover, and hold on. Protect your head and neck.
- Where can I find reliable information about earthquakes? Reputable sources include the USGS (https://www.usgs.gov/) and Indonesia’s Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysical Agency.
- How frequent are earthquakes in Indonesia? Indonesia experiences an average of seven significant earthquakes annually.
- What is the Ring of Fire? The Ring of Fire is a major area in the basin of the Pacific Ocean where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur.
What are your thoughts on the improvements to disaster preparedness in the region? Share your comments below.
what are the primary logistical challenges hindering the delivery of humanitarian aid to affected communities in Papua?
Indonesia’s Papua region Grapples with Scattered Damage Following Magnitude 6.1 Earthquake
Earthquake Details & Initial Impact
A magnitude 6.1 earthquake struck the Papua region of Indonesia on September 19, 2025, at approximately 03:50 UTC.The epicenter was located approximately 10 kilometers (6.2 miles) southwest of Jayapura,Papua province,at a depth of 10 kilometers (6.2 miles). Initial reports indicate scattered damage across Jayapura city and surrounding areas. This earthquake follows a pattern of seismic activity in the Pacific Ring of Fire, a highly active zone prone to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
* Magnitude: 6.1 Mw
* Date: September 19, 2025
* Time: 03:50 UTC
* Epicenter: 10 km SW of Jayapura, Papua, Indonesia
* depth: 10 km
Damage Assessment & Affected Areas
The earthquake triggered panic among residents, with many fleeing their homes. While a tsunami warning was initially considered, it was quickly lifted by the Indonesian Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysical Agency (BMKG).Damage reports are still emerging,but preliminary assessments reveal:
* Building Damage: Several buildings in Jayapura have sustained cracks and partial collapses. Older structures appear to be the most vulnerable.
* Infrastructure Disruptions: Power outages were reported instantly following the quake, impacting communication networks and essential services. Road access to some remote villages has been hampered by landslides triggered by the shaking.
* Landslides: The mountainous terrain of Papua makes it particularly susceptible to landslides during earthquakes. Several landslides have been reported, blocking roads and potentially damaging homes.
* Hospital Strain: Local hospitals are reporting an influx of patients with minor injuries sustained during the earthquake.
Specific areas reporting damage include:
* Abepura District
* Heram District
* Waena District
Response Efforts & Humanitarian Aid
The Indonesian National Board for Disaster Management (BNPB) has mobilized teams to assess the full extent of the damage and coordinate relief efforts. The military and police are assisting in evacuation and search and rescue operations.
* Search and Rescue: Teams are actively searching for individuals potentially trapped under collapsed structures.
* Medical Assistance: Medical personnel and supplies are being deployed to affected areas to provide treatment to the injured.
* Emergency Shelter: Temporary shelters are being established for those displaced from their homes.
* Food & Water Distribution: BNPB is coordinating the distribution of food, clean water, and other essential supplies to affected communities.
* Logistical Challenges: Delivering aid to remote areas of Papua remains a notable challenge due to limited infrastructure and difficult terrain. Helicopters are being utilized to reach isolated communities.
Geological Context: Why Papua is Earthquake-Prone
Papua,located within the complex tectonic boundaries of the Pacific Ring of Fire,experiences frequent seismic activity. The region is situated where several major tectonic plates – including the Pacific, Australian, and Eurasian plates – interact.
* Subduction Zones: The collision and subduction of these plates generate immense pressure, leading to frequent earthquakes.
* Fault Lines: Numerous fault lines crisscross the Papua region,further increasing the risk of seismic events.
* Historical earthquakes: Papua has a history of significant earthquakes,including devastating events in the past. Understanding this history is crucial for preparedness and mitigation efforts.
* Volcanic Activity: The region also features active volcanoes, which contribute to the geological instability.
Earthquake Preparedness in papua: Challenges & Opportunities
Improving earthquake preparedness in Papua is critical to minimizing the impact of future events. Several challenges hinder these efforts:
* Remote Location: The remoteness and rugged terrain of many Papuan communities make it difficult to deliver aid and implement preparedness programs.
* Limited Infrastructure: Poor infrastructure, including roads, communication networks, and healthcare facilities, exacerbates the impact of earthquakes.
* Awareness Gaps: Public awareness of earthquake safety measures is often limited, particularly in remote areas.
* Building Codes: Enforcement of building codes designed to withstand seismic activity is inconsistent.
Opportunities for Improvement:
- Strengthening Infrastructure: Investing in earthquake-resistant infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings.
- Early Warning Systems: Developing and implementing effective earthquake early warning systems.
- Community Education: Conducting comprehensive community education programs on earthquake preparedness and response.
- Disaster Risk Reduction: Integrating disaster risk reduction measures into development planning.
- Improved Communication: Enhancing communication networks to facilitate rapid details dissemination during emergencies.
Real-World Example: 2018 Papua Earthquake & tsunami
The 2018 Papua earthquake and subsequent tsunami serve as a stark reminder of the region’s vulnerability.A magnitude 7.0 earthquake triggered a tsunami that devastated coastal areas, resulting in significant loss of life and widespread destruction. The event highlighted the importance of:
* Rapid Response: The need for a swift and coordinated response to minimize casualties.
* Effective Evacuation: The critical role of effective evacuation procedures.
* Community Resilience: The importance of building community resilience to withstand and recover from disasters.
* Infrastructure Investment: The necessity of investing in resilient infrastructure.
Resources & Further Information
* BMKG (Indonesian Meteorology, climatology, and Geophysical Agency): [https[https