Amazon.com at 30: From Books to Everything, a Look Back at Its Humble Beginnings
Table of Contents
- 1. Amazon.com at 30: From Books to Everything, a Look Back at Its Humble Beginnings
- 2. Frequently Asked Questions
- 3. What was the importance of Amazon choosing the name “Amazon” over its initial name “Cadabra”?
- 4. Amazon at 30: A Journey from River Logo to Global Retail Giant
- 5. The Early Days: Books and Beyond (1994-1998)
- 6. Diversification and Expansion: Becoming the everything Store (1998-2005)
- 7. The Rise of Amazon Prime and Mobile (2005-2015)
- 8. Innovation and Global Dominance (2015-Present)
- 9. Amazon’s Impact on Retail and Beyond
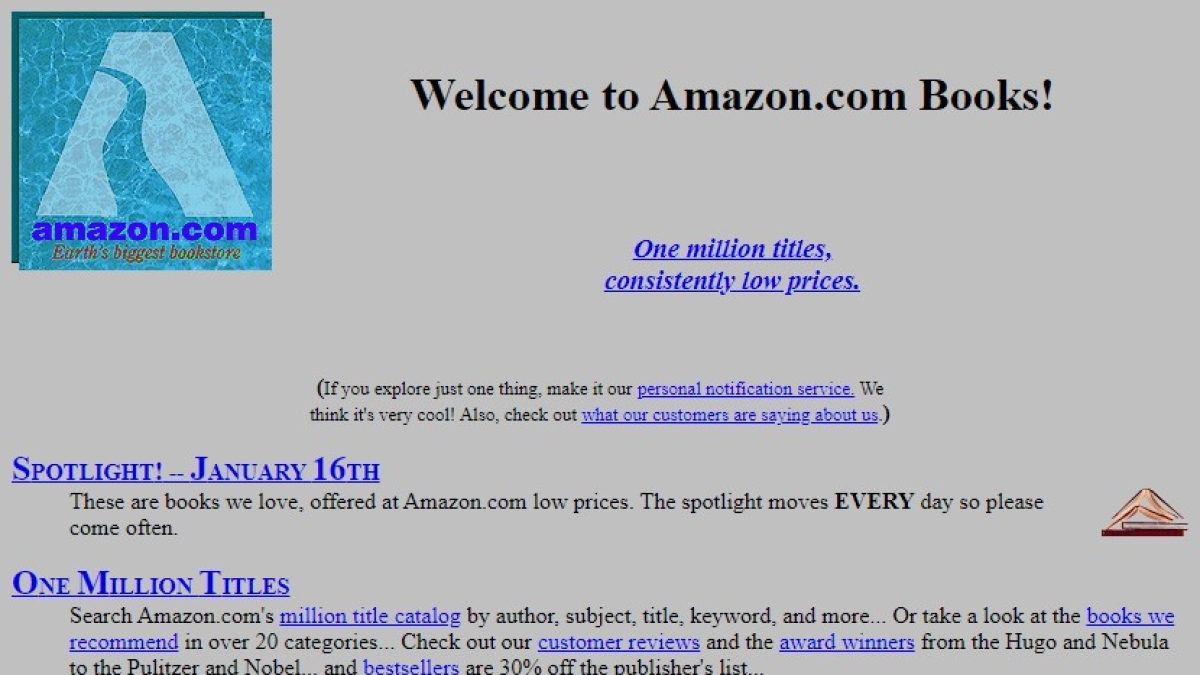
Thirty years ago, the online landscape looked vastly different. If you were to dig through digital archives today, you’d find a relic of what was once Amazon.com, a site almost unrecognizable from the e-commerce giant it is indeed now.
Its early design featured an indefinite gray background, a far cry from the iconic orange arrow logo that now graces its pages. The initial logo evoked the Amazon River, the world’s largest, with a water-like backdrop.
A cheerful, yet standard, black font welcomed visitors with the promise: “A million titles at consistently low prices.” Back then, Amazon sourced its books directly from publishers.
Launched on July 16, 1995, Amazon began its journey selling onyl books. CDs and videotapes arrived three years later, marking the start of its ascent to global success and a business model that would pivot from literature to virtually everything.
A curious anecdote highlights the company’s early days: a bell was rung in the office every time a book was sold.This cherished habit was short-lived; the bell’s frequent ringing soon led to its removal.
Within its first month, Amazon had already sold books across all American states and in 45 countries worldwide. This rapid expansion hinted at the immense potential of online retail.
Reflecting on the site’s conversion from its initial launch,just a year after the brand’s founding on July 5,1994,evokes a sense of nostalgia. Join us as we trace the evolution of the book e-commerce leader over three decades.
Frequently Asked Questions
- When was Amazon.com launched?
-
Amazon.com was launched on July 16, 1995, selling only books.
- What was Amazon’s initial product offering?
-
Initially, Amazon.com exclusively sold books, supplied directly by publishers.
- When did Amazon start selling CDs and videotapes?
-
Amazon began selling CDs and videotapes three years after its launch, in 1998.
- What was notable about early Amazon sales tracking?
-
In its early days, a bell was rung in the office each time a book was sold.
- How widespread was Amazon’s reach in its first month?
-
Within its first month, Amazon sold books in all American states and 45 countries.
Amazon at 30: A Journey from River Logo to Global Retail Giant
The Early Days: Books and Beyond (1994-1998)
Founded by jeff Bezos in 1994, Amazon began as an online bookstore, operating out of his garage in Bellevue, Washington. The initial name, “Cadabra,” was quickly scrapped for the more globally recognizable “Amazon,” inspired by the Amazon river – symbolizing vastness and scale. This early focus on e-commerce and a customer-centric approach were foundational.
July 5, 1994: Amazon.com officially launches.
1995: First order is placed – a copy of “Fluid Concepts and Creative Analogies.”
1997: Amazon goes public, raising $54 million.
Key Strategy: Bezos famously prioritized long-term growth over short-term profits, a strategy that would define Amazon’s trajectory. This involved aggressive investment in technology, infrastructure, and customer acquisition.
The initial success wasn’t just about selling books online. It was about offering a superior customer experience: personalized recommendations, easy ordering, and reliable delivery. This focus on customer experience became a core tenet of the Amazon philosophy.
Diversification and Expansion: Becoming the everything Store (1998-2005)
The late 90s and early 2000s saw Amazon aggressively diversify its product offerings. This period marked the conversion from an online bookstore to the “Everything Store.”
1998: Expansion into music and video sales.
1999: Launch of Amazon Auctions (later spun off as eBay). Introduction of Amazon Marketplace, allowing third-party sellers to list products. This was a pivotal moment, expanding selection exponentially.
2000: Introduction of Amazon Web Services (AWS), initially offering storage and computing power to developers. This seemingly unrelated venture would become a massive revenue driver.
2002: Launch of Amazon Fulfillment, offering warehousing and shipping services to third-party sellers.
2005: Introduction of Amazon Prime, a subscription service offering free two-day shipping and other benefits. Amazon Prime fundamentally changed consumer expectations around delivery speed and convenience.
This period was characterized by significant investment and,at times,skepticism from Wall Street. However,Bezos’s long-term vision continued to guide the company. The expansion into cloud computing with AWS proved particularly prescient.
The Rise of Amazon Prime and Mobile (2005-2015)
The introduction of Amazon Prime in 2005 was a game-changer. It fostered customer loyalty and encouraged more frequent purchases. Together,the rise of mobile technology presented new opportunities.
2007: Launch of the Kindle e-reader, disrupting the publishing industry.
2008: Amazon Appstore launches, entering the mobile app market.
2010: Introduction of Amazon Instant Video (now Prime Video), expanding into digital content streaming.
2011: Amazon achieves greater sales than Barnes & Noble for the first time.
2014: Amazon acquires Twitch, a live streaming platform for gamers.
The focus shifted towards creating an ecosystem of products and services, seamlessly integrated to enhance the customer experience. Digital transformation was in full swing. The Kindle demonstrated Amazon’s willingness to disrupt established industries.
Innovation and Global Dominance (2015-Present)
The last decade has seen Amazon continue to innovate at a rapid pace,expanding into new markets and technologies.
2015: Amazon surpasses Walmart as the most valuable retailer in the US.
2017: Acquisition of Whole Foods Market, marking a significant entry into the grocery industry.
2018: Amazon reaches a market capitalization of $1 trillion.
2020: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerates e-commerce growth, benefiting Amazon considerably.
2023: Amazon invests heavily in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
current Focus: artificial intelligence (AI),logistics innovation (drones,robotics),and expansion into healthcare.
amazon’s dominance extends beyond retail. AWS is now a leading provider of cloud services, powering countless businesses worldwide. the company’s influence spans logistics, artificial intelligence, digital advertising, and entertainment.
Amazon’s Impact on Retail and Beyond
Amazon’s impact on the retail landscape is undeniable. It has forced conventional retailers to adapt to the demands of the digital age.
Price Transparency: Amazon’s competitive pricing has driven down prices across the board.
convenience: amazon Prime and fast shipping have raised consumer expectations for convenience
Breaking News: Tax Credit for Newspaper Printing Expenses Approved for 2024
The Department for Information and Publishing has just announced the approval of a tax credit for expenses incurred by publishing companies in 2023 for the purchase of cards used in newspaper printing. This move is expected to provide significant relief to the publishing industry and support the continued production of newspapers.
Key Details of the Tax Credit Approval
The decree, issued by the head of the Department for Information and Publishing, approves the list of subjects eligible for the tax credit for the year 2024. This decision is in accordance with Article 1, Paragraph 319 of the Law of December 30, 2023, No. 213. The tax credit can be used as compensation by submitting the F24 model through the telematic services of the Revenue Agency starting from the fifth working day following this publication.
Eligibility and Amount
A total of 226 requests were deemed admissible for the contribution, with the total amount of the requested tax credit standing at 49,421,156.24 euros. The tax credit can be revoked if the non-existence of one of the required conditions is discovered or if the documentation contains untruthful or false elements, as per the third and final article of the decree.
Historical and Future Implications
This tax credit initiative is part of a broader effort to support the publishing industry, which has faced numerous challenges in recent years, including declining advertising revenues and increasing production costs. By providing financial relief, the government aims to ensure the sustainability of newspaper publishing and maintain the availability of diverse and reliable news sources.
How to Apply for the Tax Credit
Interested parties can access the list of subjects admitted to the tax credit for the purchase of the card for the year 2024 via the provided link. It is crucial to follow the guidelines and submit the necessary documentation through the Revenue Agency’s telematic services to ensure timely processing of the tax credit.
Romanian Reading Habits: Book Sales up, but Are Romanians Really Reading?
Table of Contents
- 1. Romanian Reading Habits: Book Sales up, but Are Romanians Really Reading?
- 2. A Paradox in the Romanian Book Market
- 3. The Numbers Don’t Lie: Romanians Lag in Book Consumption
- 4. Behind the Sales: More Than Just Books
- 5. Factors Influencing Romanian Reading Habits
- 6. Comparing Book market Turnover and Inflation
- 7. The Importance of Reading: An Evergreen Perspective
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions About reading in Romania
- 9. PAA Question 1:
- 10. Romanian Book Sales vs. Reading Habits: Understanding teh Literary Landscape
- 11. Tracking Book Sales in Romania: Data and Trends
- 12. Key Sales Metrics and Statistical Data
- 13. Impact of External Factors on Sales
- 14. Reading Habits in Romania: Preferences and Behaviors
- 15. Popular Genres and Reader Preferences
- 16. Reading Frequency and Preferences
- 17. The Role of Libraries and Community Programs
- 18. The Impact of Digital Reading and E-books
- 19. Growth in E-book Sales
- 20. The Influence of Online Bookstores and Platforms
- 21. Romanian Book Market: Challenges and Opportunities
- 22. Challenges in the Market
- 23. Opportunities for Growth and Development
Bucharest, June 14, 2025 – While Romanian bookstores report increased turnover, a closer examination reveals a concerning trend: a decline in actual reading habits among Romanians. The apparent growth in the book market is shadowed by deeper issues of book consumption and literacy.
A Paradox in the Romanian Book Market
At first glance, the romanian book market appears to be thriving. Bookstores are bustling, and publishers seem successful. However, this rosy picture obscures a more complex reality. A recent study highlights a concerning decline in reading engagement despite increased sales figures.
Although publishers and bookstores saw a 76% increase in turnover between 2008 and 2023, this growth is negated by a 100% inflation rate during the same period. Moreover,the increased turnover is largely attributed to sales of non-book items.
The Numbers Don’t Lie: Romanians Lag in Book Consumption
romania ranks last in Europe regarding book consumption. Startling statistics reveal that only 27% of Romanians read at least one book in the past year. 42% have not read a single book, and a mere 14.5% report reading a book within the last month.
According to a 2024 European Reading Survey, the average European citizen reads approximately 12 books per year, compared to RomaniaS less than one book per capita.
This disparity raises questions about the factors influencing reading habits and the overall state of literacy in the country.
Behind the Sales: More Than Just Books
The majority of bookstore profits are not from book sales. Instead, revenue comes from selling stationery, gifts, games, and toys.This reliance on non-book merchandise masks the underlying issue of declining book readership.
furthermore, of the approximate 50 lei (€10) price of a book, only 25% goes to the publishing house. This leaves publishers with limited resources to invest in new titles and authors.
Factors Influencing Romanian Reading Habits
several factors contribute to the low rates of book reading in Romania:
- Economic Factors: Lower disposable incomes mean books are often considered a luxury rather than a necessity.
- Access to Books: Limited access to bookstores and libraries,especially in rural areas,hinders book consumption.
- Competition: Digital entertainment, such as social media and streaming services, competes for people’s time and attention.
- Education: Gaps in the education system and a lack of emphasis on reading for pleasure contribute to lower literacy rates.
Comparing Book market Turnover and Inflation
| Year Range | Turnover Increase | Inflation Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 2008-2023 | 76% | 100% |
The Importance of Reading: An Evergreen Perspective
Reading is not merely a pastime; it is indeed a fundamental skill that fosters critical thinking,creativity,and empathy. Societies with high literacy rates tend to be more prosperous, innovative, and engaged.
Investing in reading and literacy programs is crucial for Romania’s long-term advancement. this includes supporting libraries, promoting reading in schools, and making books more accessible and affordable.
Encourage reading in children from a young age by reading aloud to them, visiting libraries, and making books a regular part of family life.
Furthermore, initiatives that promote Romanian literature and culture can help cultivate a sense of national pride and encourage more people to engage with books.
Frequently Asked Questions About reading in Romania
- Why Are Romanian Reading Habits Declining Despite Increased Bookstore Turnover? The increase in bookstore turnover is primarily due to sales of non-book items, and not indicative of increased book consumption.
- What Percentage Of Romanians Have Read A Book In The Last Year? Only 27% of Romanians have read a book in the last year.
- How Does Inflation Affect The Book Market In Romania? Inflation offsets the apparent growth, making books less affordable.
- What Portion Of The Price Of A Book Goes To The Publishing House In Romania? Approximately 25% goes to the publishing house, limiting resources for new publications.
- What Contributes To The Low Book Consumption Among Romanian Citizens? Economic factors, limited access, competition from digital entertainment, and educational gaps.
- Are There Initiatives To Promote Reading For Children And Adults in Romania? Yes, reading clubs, book fairs, and educational programs exist to promote literacy.
What are your thoughts on the state of reading in Romania? What measures can be taken to encourage more people to pick up a book? Share your comments below.
PAA Question 1:
Romanian Book Sales vs. Reading Habits: Understanding teh Literary Landscape
Tracking Book Sales in Romania: Data and Trends
Understanding the landscape of Romanian book sales requires looking at statistical data and market trends. Analyzing bestsellers in Romania and overall sales figures provides valuable insight into reader preferences and the health of the Romanian book market. Key performance indicators (KPIs) include the number of books sold, revenue generated, and the impact of literary festivals and public campaigns.
Key Sales Metrics and Statistical Data
Official statistics from the Romanian Ministry of Culture and similar organizations offer yearly reports on book sale statistics in Romania.These reports typically cover:
- Volumes sold: Total number of books sold across all genres.
- Revenue generated: Total financial value of book sales.
- Genre breakdown: Sales figures categorized by genre (e.g.,fiction,non-fiction,children’s books).
- Market share: The percentage of sales controlled by different publishers and distribution channels.
Real-time data from major book retailers, both physical and online, also offers a glimpse into current book sales trends.
Impact of External Factors on Sales
Several factors influence Romanian book sales figures.
- Economic conditions: Economic stability and disposable income impact purchasing power.
- Cultural events: Literary festivals and book fairs like the Gaudeamus Book Fair substantially boost sales, generating awareness and promoting authors.
- Government Support: Initiatives supporting Romanian literature.
- Digital transformation: The popularity of e-books in Romania and online book purchases.
Reading Habits in Romania: Preferences and Behaviors
Romanian reading habits offer a glimpse into the cultural landscape. Surveys and market research, focusing on Romanian reading trends, highlight popular genres, reading frequencies, and preferences in format. Analyzing reading habits by generation, understanding trends in frequency, and the use of libraries help to paint a clear picture.
Popular Genres and Reader Preferences
What are Romanians reading? Understanding the moast popular genres is crucial. Data suggests that:
- Fiction: Remains a perennial favorite, from classical literature to contemporary novels.
- historical Fiction: Books that explore Romanian history and culture are vrey popular.
- Children’s Books: Strong demand, reflecting an emphasis on literacy growth.
- Non-fiction: Books on self-improvement, biographies and history receive meaningful attention.
Reading Frequency and Preferences
How frequently enough do Romanians read? This varies, but certain patterns exist.
- Frequency of reading: Regular reading is more common among younger generations, and those with higher education levels.
- Preferred formats: E-books vs.physical books in Romania, and also the role of audiobooks impact choice.
Real-world example Reading clubs promote a vibrant reading culture across Romania. These groups allow people to discuss Romanian literature, international works, and offer community.
The Role of Libraries and Community Programs
Romanian public libraries and reading initiatives in Romania are critical to promoting literacy and providing access to books,especially in areas where book purchase is limited. These include:
- Library usage patterns: A consistent influx of members proves the need of public libraries.
- Community outreach programs: Libraries often host activities to encourage children and adults alike.
The Impact of Digital Reading and E-books
The digital age has significantly affected reading habits in Romania.Comparing e-books versus physical books in romania provides insight into the changing trends
Growth in E-book Sales
The popularity of e-books is on the rise. This shift is driven by:
- Accessibility: E-books are easily accessible.
- Cost: E-books are more affordable than physical books.
The Influence of Online Bookstores and Platforms
Online bookstores cater to readers who favour online purchases. This includes the largest online platform in Romania – elefant.ro. They offer:
- Variety: A selection which exceeds standard bookstores.
- Convenience: Readers’ ability to browse and purchase at their convenience.
Romanian Book Market: Challenges and Opportunities
The romanian book market faces unique challenges and promising opportunities. success hinges on adapting to current trends.
Case study: A mid-sized Romanian publisher, initially struggling with customary sales, increased profits over 25% after investing in the E-book format.
Challenges in the Market
- Price of books: The price of books compared with average income levels in Romania can be a barrier.
- Distribution challenges: Distribution channels impact smaller publishers.
- Competition: The market’s competitive nature.
Opportunities for Growth and Development
- Digital marketing: Online promotion and social media for book promotion..
- Community engagement: Encouraging reading clubs.
- Government support and subsidies: Funding programs that support authors and publishers.
Practical Tip: run a contest promoting a particular author. Offering a physical book as the first prizes will boost activity.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Bestseller Examples | Fiction (Contemporary, Romanian), Historical Fiction, Children’s Books |
| Digital Influence | Growing popularity of e-books, online bookstores, and platforms |
| key Challenges | Book prices and distribution channels |
| Market Opportunities | Digital promotion, community engagement, government support |