understanding Survival Rates and Trends in Cardiac Arrest
Table of Contents
- 1. understanding Survival Rates and Trends in Cardiac Arrest
- 2. A Complete Look at Cardiac Arrest Data: The Swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry
- 3. improving Outcomes: Key Takeaways and future Directions
- 4. What can people do to help improve cardiac arrest survival rates in their communities?
- 5. Understanding Survival Rates and Trends in Cardiac Arrest: An Interview with Expert Dr. Elin Lindgren
- 6. Key Factors Influencing Survival Rates
- 7. The Swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry: A Treasure Trove of Data
- 8. Enhancing Survival Rates: Key Takeaways and Future Directions
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a serious public health concern, claiming a significant number of lives annually. In Sweden,approximately 10,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occur each year,with bystander-initiated cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) initiated in roughly 6,000 cases. While survival rates vary depending on location, understanding the factors influencing outcomes is crucial for improving patient care.
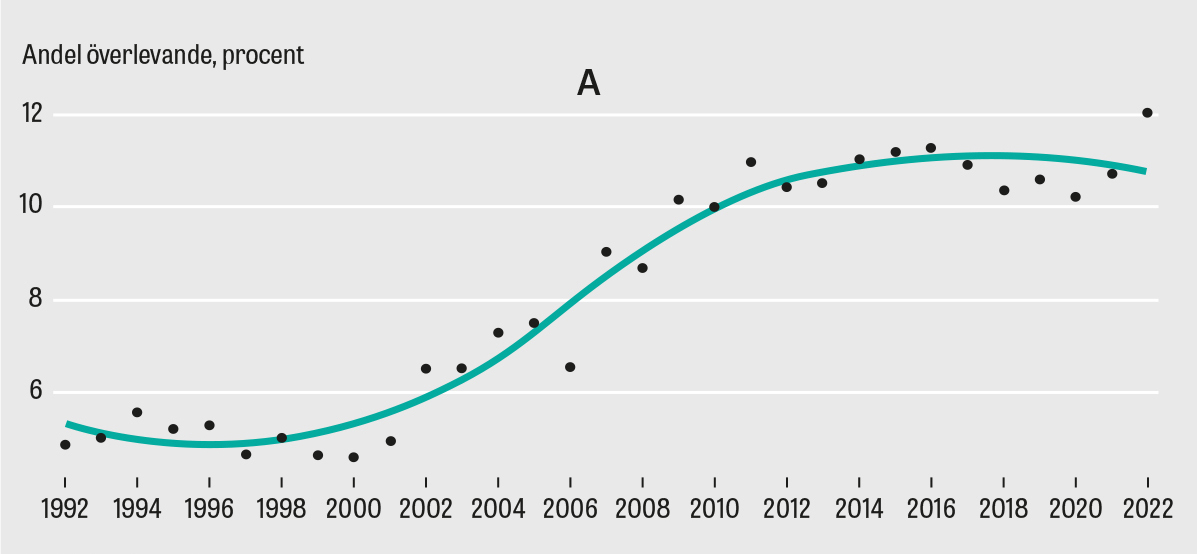
Survival rates for SCA outside of hospital settings in Sweden currently stand at 12%, compared to 36% within hospitals. These figures highlight the critical role of timely intervention and access to advanced medical care. Notably, SCA often presents as the initial manifestation of heart disease, underscoring the importance of early detection and preventative measures.
A Complete Look at Cardiac Arrest Data: The Swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry
Since 1990, the Swedish Cardiac arrest Registry has meticulously tracked cardiac arrest cases, providing invaluable insights into trends, survival rates, and interventions. this comprehensive database, adhering to international standards, captures detailed information about each incident, including:
- Location of the cardiac arrest
- Initial heart rhythm
- Presence of bystanders and their actions
- Initiation of CPR and defibrillation
- Medications administered (e.g.,adrenaline,amiodarone)
- Airway management
- Critical time intervals,such as time from cardiac arrest to alarm,CPR initiation,and defibrillation
- ambulance response time
Moreover,the registry tracks patient outcomes,including survival rates at 30 days,hospital discharge status,and quality-of-life assessments conducted months after the event. This comprehensive approach allows researchers and healthcare professionals to identify areas for betterment and implement evidence-based interventions.
One significant finding highlighted by the registry is the impact of timely intervention. Notably, the registry’s online platform, “HLR live,” provides real-time data visualization, enabling healthcare providers and policymakers to monitor trends, compare performance across regions, and identify areas requiring attention.
improving Outcomes: Key Takeaways and future Directions
The Swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry serves as a valuable resource for understanding SCA trends, improving patient outcomes, and ultimately saving lives. Key takeaways include:
- Early intervention, particularly CPR and defibrillation, significantly improves survival rates.
- Public awareness campaigns promoting CPR training are crucial for increasing bystander intervention.
- Continuous monitoring and analysis of registry data are essential for identifying areas for improvement in cardiac arrest response systems.
- Investing in research and implementing evidence-based interventions can further enhance survival rates and improve patient outcomes.
By leveraging the insights provided by comprehensive registries like the Swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry, healthcare systems can strive towards reducing the burden of SCA and improving the lives of individuals affected by this critical condition.
What can people do to help improve cardiac arrest survival rates in their communities?
Understanding Survival Rates and Trends in Cardiac Arrest: An Interview with Expert Dr. Elin Lindgren
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a importent global health concern, with millions of lives lost annually.To shed light on this pressing issue, Archyde News had the opportunity to speak with dr. Elin Lindgren, a renowned cardiac arrest researcher and the Director of the Swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry.
Key Factors Influencing Survival Rates
Archyde (A): Dr. Lindgren, could you explain the current survival rates for out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in Sweden and the factors influencing these figures?
Dr. Elin Lindgren (EL): Certainly.In Sweden, we currently have an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest survival rate of about 12%, which, while low, is a considerable betterment from where we were a decade ago.Key factors influencing these rates include timely intervention,specifically bystander-initiated CPR and the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs). Additionally, access to advanced medical care within hospitals yields a higher survival rate of around 36%.
The Swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry: A Treasure Trove of Data
A: Tell us about the Swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry and its impact on improving our understanding of cardiac arrests.
EL: The Swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry has been collecting data since 1990, offering invaluable insights into trends, interventions, and patient outcomes. We track various aspects, including location, initial heart rhythm, bystander intervention, CPR and defibrillation timing, medications administered, and ambulance response times. Our extensive approach enables us to identify areas for improvement and drive evidence-based interventions.
A: The registry’s real-time data visualization platform, “HLR live,” is notable. How has it contributed to improving cardiac arrest response systems?
EL: HLR live has been a game-changer, enabling healthcare providers and policymakers to monitor trends, compare regional performances, and pinpoint areas requiring attention.It has facilitated targeted interventions and continuous quality improvement in our cardiac arrest response systems.
Enhancing Survival Rates: Key Takeaways and Future Directions
A: What are the main takeaways from the swedish Cardiac Arrest Registry, and where do you see the future heading in terms of improving survival rates?
EL: Our key takeaways include the critical role of early intervention, particularly CPR and defibrillation, and the importance of public awareness campaigns promoting CPR training. Continuous monitoring and analysis of registry data are also essential for driving improvements in our cardiac arrest response systems. Looking ahead, investing in research and implementing evidence-based interventions will be crucial for enhancing survival rates and improving patient outcomes.
A: Lastly, what can people do to help improve cardiac arrest survival rates in their communities?
EL: Everyone can play a role. Learning CPR and encouraging others to do the same can significantly improve survival rates. Additionally, advocating for increased access to AEDs in public places and supporting local initiatives aimed at improving cardiac arrest response systems can make a verdadero difference.