Europe is facing a growing threat from mosquito-borne diseases, with a significant increase in reported cases of illnesses like West Nile virus and Chikungunya fever. Health authorities are issuing warnings as changing climate conditions and the expanding range of the Asian tiger mosquito contribute to the spread of these previously rare conditions. The European Center for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) has recently highlighted the escalating risk, urging vigilance among residents and travelers.
Rising Cases and Geographical Spread
Table of Contents
- 1. Rising Cases and Geographical Spread
- 2. The Asian Tiger Mosquito: A Key Factor
- 3. Climate Change and Disease Transmission
- 4. Protecting Yourself from Mosquito Bites
- 5. understanding Mosquito-Borne Diseases
- 6. Frequently Asked Questions about Mosquito-Borne Diseases
- 7. What public awareness campaigns are most effective in reducing mosquito breeding sites in urban environments?
- 8. Mosquito-borne Viruses Set New Transmission Record: insights and implications
- 9. Global Surge in Mosquito-borne Diseases – What’s Driving the increase?
- 10. Key Viruses Driving the Increase
- 11. Factors Fueling the Transmission Spike
- 12. Symptoms and Diagnosis: Recognizing the Warning Signs
- 13. Prevention Strategies: protecting yourself and Your Community
By mid-August, 335 cases of locally transmitted West Nile virus had been reported across eight European countries, tragically resulting in 19 deaths. Italy is currently the most affected nation, accounting for 247 of these cases, and Greece follows with 35 reported infections. Officials anticipate a peak in transmissions during August and September.This year alone, 27 outbreaks of Chikungunya virus have been identified throughout the continent. In a concerning first, a locally acquired case of Chikungunya was confirmed in Alsace, France in early July, indicating a northward expansion of the transmission risk.
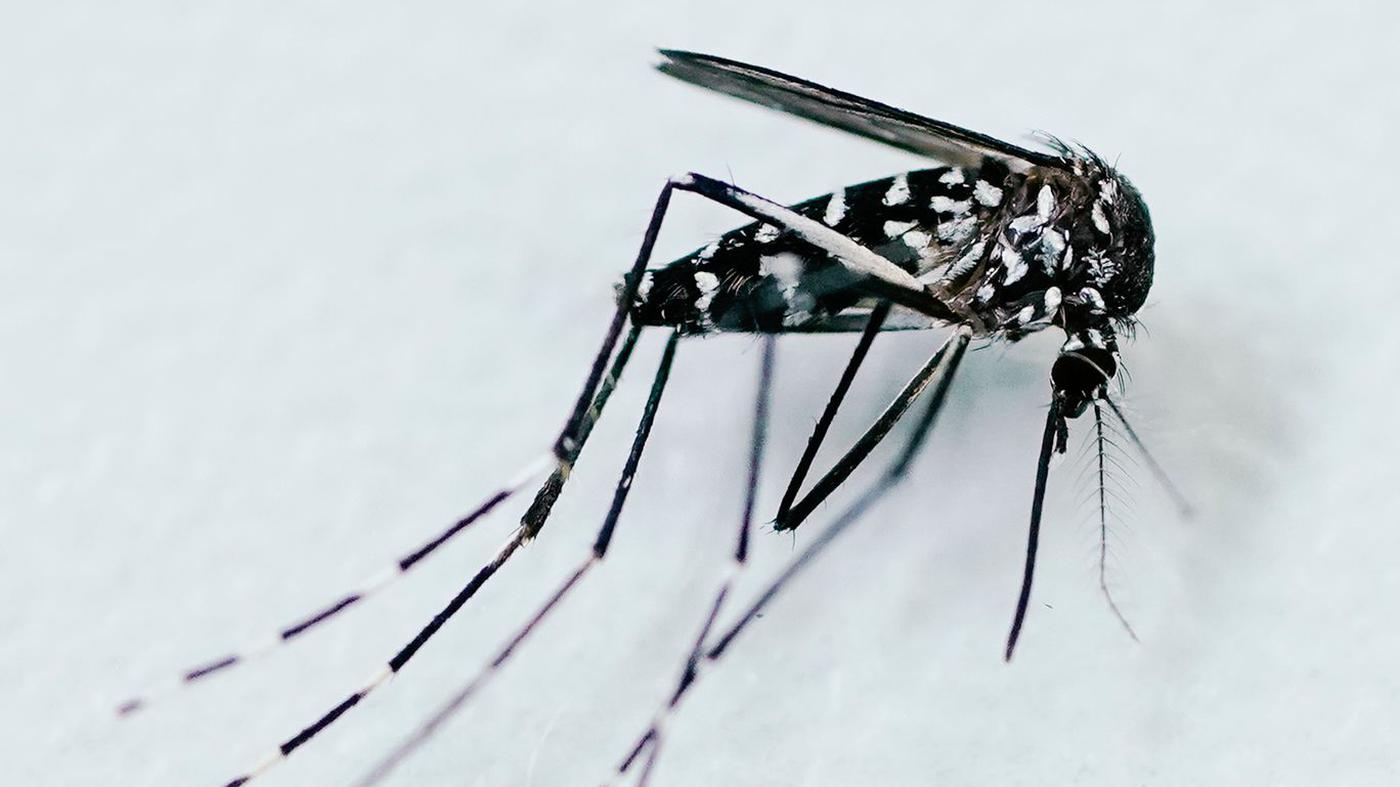
The Asian Tiger Mosquito: A Key Factor
the Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) is a primary driver of this increase. This invasive species, now present in 16 European countries including Germany, is highly efficient at transmitting viruses like Chikungunya. According to recent data from the World Health Organization (WHO), the global prevalence of Chikungunya is on the rise, prompting recommendations for vaccination before travel to affected regions. WHO on Chikungunya
Did You Know? The Asian tiger mosquito can breed in very small amounts of water, such as discarded tires or flower pot saucers, making it especially challenging to control.
Climate Change and Disease Transmission
Experts attribute the surge in mosquito-borne diseases to a combination of factors, with climate change playing a central role. Rising temperatures, prolonged summers, milder winters, and altered precipitation patterns create increasingly favorable conditions for mosquito survival and reproduction. These conditions allow for a longer transmission season and facilitate the spread of mosquitoes to new areas. According to a 2024 report by the European Environment Agency, the frequency of heat waves in Europe has increased considerably in the last two decades, directly impacting vector-borne disease transmission.
| Disease | Primary Vector | Key Symptoms | Geographic Impact (2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| West Nile Virus | Culex Mosquitoes | Fever, headache, fatigue, rash | Italy, Greece, Spain, Hungary |
| Chikungunya Fever | Asian Tiger Mosquito | High fever, joint pain, muscle aches | France, Italy, Spain |
Protecting Yourself from Mosquito Bites
The ECDC strongly advises individuals, particularly the elderly, children, and those with weakened immune systems, to take preventative measures against mosquito bites. These include the use of insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus; wearing long sleeves and pants; and installing mosquito netting on windows and beds. Local authorities are also implementing mosquito control programs, including larval surveillance and targeted insecticide spraying.
Pro Tip: Eliminate standing water around your home to prevent mosquitoes from breeding. Regularly empty flower pots, bird baths, and gutters.
understanding Mosquito-Borne Diseases
Mosquitoes are known to transmit a wide array of diseases, impacting millions of people worldwide. Beyond West Nile virus and Chikungunya, other significant threats include malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus. These diseases can cause severe illness and, in certain specific cases, even death. Awareness of the risks and proactive prevention measures are crucial for protecting public health.
The World Mosquito Program is pioneering innovative approaches to mosquito control, including the release of Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes, which reduce the ability of mosquitoes to transmit viruses. World Mosquito Program. This biological control method offers a enduring and environmentally pleasant alternative to conventional insecticide-based strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions about Mosquito-Borne Diseases
- What is the most effective mosquito repellent? Insect repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus are considered the most effective.
- Are mosquito-borne diseases treatable? Treatment options vary depending on the specific disease.Some infections can be managed with supportive care, while others require antiviral medication.
- Can I get a mosquito-borne disease in Europe? Yes, the risk of contracting mosquito-borne diseases in Europe is increasing, particularly in Southern and Eastern European countries.
- How can I protect my children from mosquito bites? Dress children in protective clothing, use insect repellent approved for children, and ensure they sleep under mosquito netting.
- What should I do if I suspect I have a mosquito-borne illness? Seek medical attention promptly and inform your doctor about your recent travel history.
As the threat of mosquito-borne diseases continues to grow in Europe, public health officials emphasize the importance of vigilance and preventative measures. Are you taking adequate steps to protect yourself and your family? What additional measures do you think should be implemented to control the spread of these diseases?
What public awareness campaigns are most effective in reducing mosquito breeding sites in urban environments?
Mosquito-borne Viruses Set New Transmission Record: insights and implications
Global Surge in Mosquito-borne Diseases – What’s Driving the increase?
2025 is witnessing an unprecedented surge in mosquito-borne viral diseases globally.Data from the World health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicate a record number of cases for diseases like Dengue fever, Zika virus, West Nile virus, and Chikungunya. This isn’t simply a seasonal fluctuation; several converging factors are contributing to this alarming trend. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective prevention and control.
Key Viruses Driving the Increase
Dengue Fever: Remains the most meaningful threat, with cases escalating in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and increasingly, parts of Europe. The emergence of Dengue virus serotype 3 in previously unaffected regions is a major concern.
Zika Virus: While the initial global health emergency declaration has passed, Zika continues to circulate, posing a risk to pregnant women due to its association with microcephaly. Sporadic outbreaks are reported in Africa,asia,and the Americas.
West Nile Virus: Predominantly affecting North america, Europe, and Australia, West nile virus cases are rising, with a higher proportion of neuroinvasive disease (affecting the brain and spinal cord).
Chikungunya: Characterized by debilitating joint pain, Chikungunya is spreading in Africa, Asia, and the Caribbean. Re-emergence in areas with previously established outbreaks is common.
japanese Encephalitis: Primarily a concern in Asia,Japanese encephalitis continues to cause significant morbidity and mortality,particularly in rural agricultural areas.
yellow Fever: Though vaccine-preventable, outbreaks still occur in Africa and South America, often linked to low vaccination coverage.
Factors Fueling the Transmission Spike
Several interconnected factors are driving this record-breaking transmission rate.
- Climate Change: Rising global temperatures and altered rainfall patterns are expanding the geographic range of mosquito vectors. Warmer temperatures accelerate the mosquito life cycle and increase biting rates. Increased rainfall creates more breeding sites.
- Urbanization & Population Density: Rapid urbanization, particularly in developing countries, leads to increased human-mosquito contact. Poor sanitation and inadequate waste management create ideal breeding grounds in urban environments.
- Globalization & Travel: Increased international travel and trade facilitate the rapid spread of viruses to new regions. Infected travelers can introduce viruses to areas with susceptible populations and competent mosquito vectors.
- Vector Resistance: Mosquitoes are developing resistance to commonly used insecticides, making control efforts less effective. This necessitates the growth of new control strategies.
- Reduced Public Health Infrastructure: In many affected regions, public health infrastructure is strained, limiting surveillance, prevention, and control efforts. funding cuts and resource limitations hinder effective response.
- Lack of Awareness: limited public awareness about mosquito-borne diseases and preventive measures contributes to increased risk.
Symptoms and Diagnosis: Recognizing the Warning Signs
Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for managing mosquito-borne viral infections. Symptoms vary depending on the virus, but common signs include:
Fever: Often high and sudden onset.
Headache: Severe and persistent.
Joint Pain: Characteristic of Dengue and Chikungunya.
Muscle Pain: Common in Dengue and Zika.
Rash: Can vary in appearance and distribution.
Fatigue: Prolonged and debilitating.
Neurological Symptoms: (West Nile, Japanese Encephalitis) – including stiff neck, confusion, seizures, and paralysis.
diagnosis: Typically involves blood tests to detect viral RNA or antibodies. Rapid diagnostic tests are becoming increasingly available, but their accuracy can vary. Differential diagnosis is important,as symptoms can overlap with other febrile illnesses.
Prevention Strategies: protecting yourself and Your Community
Effective prevention requires a multi-pronged approach.
Personal Protective Measures:
Insect Repellent: Use EPA-registered insect repellents containing DEET, picaridin, IR3535, or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
Protective Clothing: Wear long sleeves, long pants, and socks when outdoors, especially during peak mosquito activity hours (dawn and dusk).
Mosquito Nets: Use mosquito nets, particularly while sleeping.
Window and Door Screens: Ensure windows and doors have intact screens to prevent mosquito entry.
Environmental Control:
Eliminate Breeding Sites: Remove standing water from containers such as tires,flower pots,and buckets.
regular Cleaning: Clean gutters and drains to prevent water accumulation.
Larviciding: Use larvicides to kill mosquito larvae in breeding sites.
Source Reduction: Modify the environment to eliminate or reduce mosquito breeding habitats.
Community-Based Programs:
*Public Awareness Campaigns