Myanmar earthquake Response: Ongoing Challenges Nine Months After devastating Quakes
Table of Contents
- 1. Myanmar earthquake Response: Ongoing Challenges Nine Months After devastating Quakes
- 2. What is the difference between the Richter scale and the Moment Magnitude Scale,and why is the latter preferred by modern seismologists?
- 3. Unconfirmed Report of magnitude 1.7 Earthquake: Minimal Seismic Activity recorded
- 4. Understanding the Recent Seismic Event
- 5. What Does a Magnitude 1.7 Earthquake Mean?
- 6. Why Might a 1.7 Magnitude Earthquake Go Unnoticed?
- 7. Potential Causes of Minor seismic Activity
- 8. Monitoring Seismic Activity: Resources and Tools
- 9. Earthquake Preparedness: Even for Minor Events
- 10. The Role of Azure AI Services in Seismic Monitoring
Sagaing Region, myanmar – December 1, 2025 – Nine months after twin earthquakes ravaged central Myanmar’s Sagaing Region, the recovery effort continues to face significant hurdles. The initial 7.7 magnitude quake, striking on March 28th, 2025, at 12:50 p.m. local time, was followed just minutes later by a 6.4 magnitude aftershock, plunging communities near Mandalay into crisis. Ongoing aftershocks have consistently hampered rescue and rebuilding operations.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has been closely monitoring the situation and coordinating the international response. Initial reports indicated widespread damage to infrastructure, including homes, hospitals, and critical transportation networks. While a comprehensive damage assessment remains challenging due to ongoing instability and logistical difficulties, the scale of the devastation is substantial.
current Situation & Challenges:
As of today, December 1st, 2025, the State Administration in Myanmar is still grappling with the aftermath. Key challenges include:
* Logistical Nightmares: Delivering aid to remote and affected areas remains a major obstacle. Damaged roads and limited access are slowing the distribution of essential supplies like food, water, shelter, and medical care.
* Healthcare System Strain: The earthquakes severely impacted healthcare facilities, already under pressure.Access to medical services, notably for those with earthquake-related injuries and chronic conditions, is limited.
* Displacement & Shelter: Thousands remain displaced from their homes, facing harsh conditions as the region heads into the cooler, drier season. Providing adequate shelter and sanitation is a critical priority.
* Aftershock Disruptions: Frequent aftershocks continue to trigger landslides and further damage weakened structures, hindering rebuilding efforts and causing ongoing fear among the population.
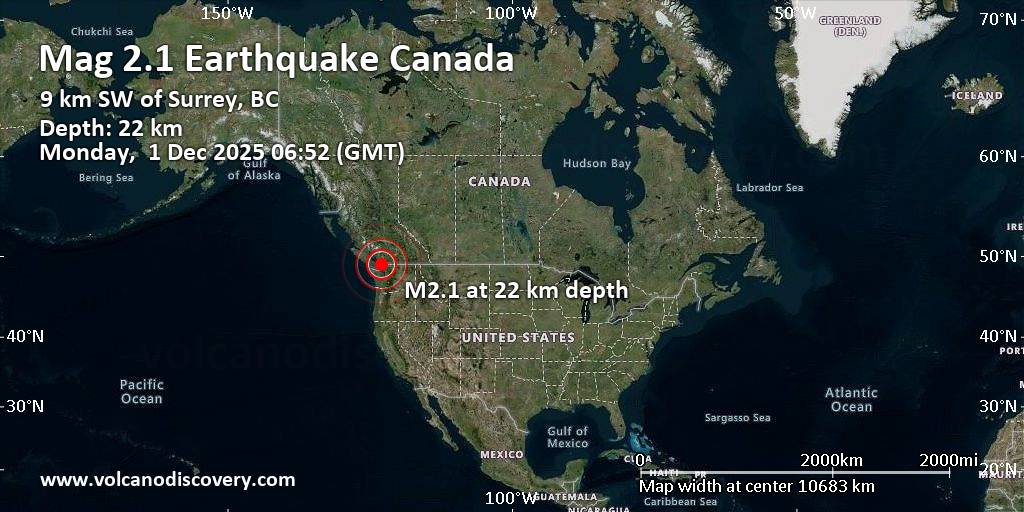
* Recent Seismic Activity: While not directly linked to the March events, a 2.1 magnitude earthquake was recorded today near Mount Vernon, Washington, USA at 19:22 GMT -8, and a 1.8 magnitude quake struck the same region earlier at 17:53 GMT -8. These events, though geographically distant, serve as a stark reminder of the planet’s seismic activity and the importance of preparedness.
International Response & Future Needs:
The WHO and other international organizations are working with the State Administration to provide support. However, the ongoing political instability within Myanmar continues to complicate aid delivery and access to affected populations.
looking ahead, the focus must shift towards long-term recovery and resilience building. This includes:
* infrastructure Reconstruction: Prioritizing the rebuilding of essential infrastructure, with a focus on earthquake-resistant construction techniques.
* Strengthening Healthcare Capacity: Investing in the rehabilitation of damaged healthcare facilities and training of medical personnel.
* Community-Based Disaster Preparedness: Empowering local communities with the knowledge and resources to prepare for and respond to future disasters.
* Continued International Support: Sustained financial and technical assistance from the international community will be crucial for long-term recovery.
The situation in Sagaing Region remains critical. The world must not forget the people of Myanmar as they navigate the long road to recovery from this devastating natural disaster.
What is the difference between the Richter scale and the Moment Magnitude Scale,and why is the latter preferred by modern seismologists?
Unconfirmed Report of magnitude 1.7 Earthquake: Minimal Seismic Activity recorded
Understanding the Recent Seismic Event
On December 1st, 2025, at approximately 09:33:56, reports surfaced regarding a minor seismic event registering a magnitude of 1.7. While initially reported as an earthquake, confirmation remains pending from major geological survey organizations. this article details the available information, potential causes, and what a magnitude 1.7 earthquake typically entails.We’ll cover earthquake magnitude scales, the likelihood of feeling such an event, and resources for staying informed about seismic activity.
What Does a Magnitude 1.7 Earthquake Mean?
Earthquake magnitude is measured using the Richter scale (though modern seismologists often use the Moment Magnitude Scale for greater accuracy, especially with larger quakes). The scale is logarithmic, meaning each whole number increase represents a tenfold increase in amplitude.
Here’s a breakdown of what different magnitudes generally signify:
* Less than 4.0: Generally not felt, or felt only by a very few people under especially favorable conditions. Often recorded by seismographs but causes no damage.
* 4.0 – 4.9: Felt by many people; moderate shaking. May cause minor damage.
* 5.0 – 5.9: Can cause damage of varying severity to poorly constructed buildings.
* 6.0 – 6.9: Can be destructive in areas up to about 160 kilometers across in populated areas.
* 7.0 or greater: Major earthquake.Can cause serious damage over larger areas.
A magnitude 1.7 earthquake falls firmly into the “not felt” category for the vast majority of people. It’s considered a microearthquake.
Why Might a 1.7 Magnitude Earthquake Go Unnoticed?
Several factors contribute to why a 1.7 magnitude earthquake is unlikely to be widely felt:
* Low Energy Release: The energy released by a 1.7 magnitude quake is minimal.
* Depth of the Epicenter: If the earthquake originates deep underground, the seismic waves weaken significantly before reaching the surface.
* Distance from Population Centers: An earthquake occurring in a remote area will naturally be less likely to be felt.
* Geological Conditions: Certain types of rock absorb seismic waves more effectively than others.
* Background Noise: Everyday vibrations – from traffic, construction, or even wind – can mask the subtle tremors of a small earthquake.
Potential Causes of Minor seismic Activity
While pinpointing the exact cause without confirmed data is arduous, minor earthquakes like this can stem from several sources:
* Tectonic Plate Movement: Even small adjustments along fault lines can generate seismic waves.
* Volcanic Activity: Magma movement beneath the surface can trigger earthquakes.
* Human Activity: Activities like fracking (hydraulic fracturing), reservoir construction, and deep wastewater disposal have been linked to induced seismicity – earthquakes caused by human actions.
* Natural Geological Adjustments: The Earth’s crust is constantly shifting and settling, leading to minor tremors.
Monitoring Seismic Activity: Resources and Tools
Staying informed about earthquake activity is crucial, especially if you live in a seismically active region. Here are some valuable resources:
* United States geological Survey (USGS): https://www.usgs.gov/ – Provides real-time earthquake information, maps, and educational resources.
* European-Mediterranean Seismological Center (EMSC): https://www.emsc-csem.org/ – Offers complete earthquake data for Europe and the Mediterranean region.
* Local Geological Surveys: many countries and regions have their own geological surveys that provide localized earthquake information.
* Earthquake Alert Apps: Several mobile apps provide real-time earthquake alerts based on your location. (e.g., MyShake)
Earthquake Preparedness: Even for Minor Events
While a 1.7 magnitude earthquake poses little to no threat, it’s a good reminder to review basic earthquake preparedness measures:
- Secure Heavy Objects: Anchor bookshelves, televisions, and other heavy items to walls to prevent them from falling during stronger shaking.
- Know Your Safe Spots: Identify safe places in your home, such as under sturdy furniture or against interior walls.
- Develop a Family Emergency Plan: Discuss what to do in the event of an earthquake with your family.
- Assemble an Emergency Kit: Include essential supplies like water, food, a first-aid kit, a flashlight, and a radio.
- Consider Earthquake Insurance: Depending on your location, earthquake insurance might potentially be a worthwhile investment.
The Role of Azure AI Services in Seismic Monitoring
Microsoft’s Azure AI Services, including Translator and Speech services, aren’t directly involved in detecting earthquakes. However, they play a crucial role in disseminating information quickly and accurately during and after seismic events.
* Translator API: can instantly translate earthquake alerts and safety information into multiple languages, ensuring wider reach and understanding. (See:[https://wwwmicrosoftcom/nb-no/translator[https://wwwmicrosoftcom/nb-no/translator