WinRAR Vulnerabilities Continue to Fuel Sophisticated Cyberattacks
Cybersecurity experts are warning of ongoing exploitation campaigns leveraging critical vulnerabilities within WinRAR, the widely used file archiving utility.Recent discoveries reveal sophisticated attack methods, employing tools such as the Mythic Agent exploitation framework and known malware families like SnipBot, RustyClaw, and Melting Claw. Thes attacks, observed by independent researchers ESET and BI.ZONE, highlight the persistent threat posed by unpatched WinRAR installations.
The Paper Werewolf Campaign Leverages WinRAR Exploits
A threat actor known as “Paper Werewolf” has been actively deploying exploits targeting winrar users throughout July and August. BI.ZONE research indicates these attacks typically involve malicious archives sent via email, impersonating employees of legitimate organizations like the All-russian Research Institute. the primary objective is to install malware, granting attackers unauthorized access to compromised systems.
The origins of Paper Werewolf’s access to these vulnerabilities remain under examination. BI.ZONE suggests the group may have acquired the exploit details from dark market forums. The coordinated nature of these attacks, alongside independent discoveries by ESET, raises questions about whether different threat actors are collaborating or independently sourcing the same exploit information.
Complex Execution Chains Uncovered
ESET detailed three distinct execution chains used in these attacks. One chain, observed in targeted attacks, deploys a malicious DLL hidden within an archive. This DLL utilizes a technique known as COM hijacking, enabling its execution through trusted applications like Microsoft Edge. Upon execution, the embedded shellcode retrieves the machine’s domain name and compares it with a predefined value.
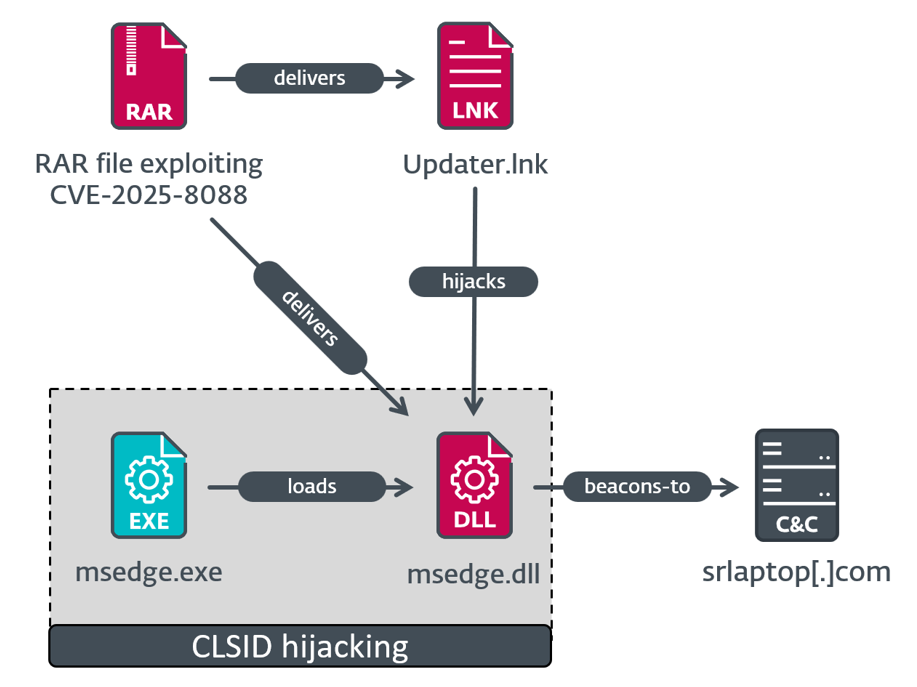
When a match is confirmed, the shellcode proceeds to install a customized version of the Mythic Agent, a powerful framework for command and control operations. This allows attackers to maintain persistent access and exfiltrate data.
A second execution chain involves a malicious Windows executable that delivers a final payload, specifically the SnipBot malware, a known component of the RomCom family. This malware employs evasive tactics,terminating itself when detected in a virtual machine or sandbox surroundings,a common practice among cybersecurity researchers.
The third observed chain leverages two other notorious pieces of RomCom malware: RustyClaw and Melting Claw. The use of these established malware families further underscores the advanced capabilities of the threat actors involved.
WinRAR’s history of Exploitation
This is not the first time WinRAR has been at the center of important security concerns. In 2019,a critical code-execution vulnerability in WinRAR saw widespread exploitation shortly after it was patched. More recently, in 2023, a WinRAR zero-day vulnerability was actively exploited for over four months before its discovery.
The widespread adoption of WinRAR, coupled with its update mechanism, makes it a notably attractive target for malware distributors. Unlike applications with automatic update features, WinRAR requires users to manually download and install patches. This reliance on user action creates a window of prospect for attackers.
ESET has also confirmed that Windows versions of the command-line utilities UnRAR.dll and the portable UnRAR source code are similarly vulnerable. to mitigate these risks, users are strongly advised to update to WinRAR version 7.13 or later, which addresses all known vulnerabilities. Though, given the consistent emergence of new WinRAR zero-days, vigilance remains paramount.
| Threat Actor | Observed Activity | Malware/Tools Used | Exploitation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paper Werewolf | July-August Campaigns | Mythic Agent, SnipBot, RustyClaw, Melting Claw | COM Hijacking, Malicious DLLs, Executables |
Did You Know? WinRAR databases are often targeted because they can be used to package and distribute various types of malware, making it easier for attackers to reach a wider audience.
With new vulnerabilities constantly being discovered, how often do you typically check for software updates on your system?
What are your primary methods for ensuring the security of your digital assets against emerging threats?
Staying Secure: Essential Practices for software Users
The recurring exploitation of WinRAR vulnerabilities serves as a stark reminder of the importance of proactive cybersecurity hygiene. Even widely trusted software can become a vector for attack if not properly maintained.
Pro Tip: Regularly update all your software, including operating systems, browsers, and utility applications like file archivers. Enable automatic updates where possible, and manually check for updates frequently.
Beyond software updates,employing robust antivirus and anti-malware solutions is crucial. These tools can detect and neutralize threats before they can execute malicious code. Be cautious of unsolicited email attachments and links, even if they appear to come from a known source, as phishing remains a primary method for delivering malware.
Understanding the lifecycle of software vulnerabilities is also key. While vendors work to patch discovered flaws, there can be a period between discovery and patching where users are exposed. During these times, extra vigilance or avoiding the use of the vulnerable software, if possible, can provide an additional layer of protection.
Frequently Asked Questions About WinRAR Security
What are the main risks associated with WinRAR vulnerabilities?
The main risks involve unauthorized access to your systems, data theft, and the installation of various types of malware, including ransomware and spyware.
Which WinRAR versions are considered vulnerable?
Versions prior to WinRAR 7.13 are known to be vulnerable to recently discovered exploits. It is crucial to update to the latest version available.
How do attackers exploit WinRAR vulnerabilities?
Attackers typically use specially crafted archive files that, when opened, trigger malicious code execution through methods like COM hijacking or by delivering embedded malware payloads.
What is the Mythic Agent used for in these attacks?
mythic Agent is an open-source exploitation framework used by attackers to establish command and control over compromised systems, facilitating further malicious activities.
Why is manual updating a security concern for WinRAR?
WinRAR lacks automatic update features, meaning users must actively download and install patches. This manual process can lead to users running outdated, vulnerable versions if they neglect updates, leaving them susceptible to attacks.
