“`html
Decoding Risk Transfer: Protecting Businesses in 2024
Navigate the complexities of risk transfer with our extensive guide. Learn strategies to safeguard your business from potential financial liabilities through insurance, contracts, and outsourcing.
Understanding Risk transfer
In today’s volatile business environment, conventional insurance is just the beginning. Risk transfer has evolved into a sophisticated strategy, moving beyond simple policies to encompass various methods that protect organizations from potential financial instability and ensure business continuity.
Risk transfer acknowledges that certain entities are better equipped to manage specific risks, leveraging greater resources, specialized expertise, or the ability to diversify exposures.
What Is Risk Transfer?
Risk transfer is a risk management technique that shifts potential financial liability from one entity to another. This process involves using insurance contracts, legal agreements, and financial instruments to safeguard an organization against specific losses.
Common Risk Transfer Methods
Organizations can deploy several risk transfer methods:
- Insurance Policies: Companies pay premiums to insurance firms for financial protection against losses. If a risk materializes,the insurer compensates the organization for covered losses. Examples include property, general liability, and professional liability insurance.
- Contractual Clauses: these agreements feature legal provisions like indemnification clauses, limitation of liability clauses, and hold harmless agreements.commonly used in contracts, these shift specific responsibilities and risks.
- Outsourcing: By outsourcing operations to external service providers, organizations transfer associated risks. Such as, a business might hire a specialized IT security firm to manage cybersecurity risks.
Business Examples Of Risk Transfer
Risk transfer is applicable across industries, particularly crucial in insurance, cybersecurity, and project management.
Risk Transfer In Insurance
Here are common examples of risk transfer involving insurance:
- General Liability Insurance: This transfers operational risks related to bodily injury or property damage. If someone is injured on company property and takes legal action, the insurance covers any legal settlements.
- Directors and Officers Insurance: D&O insurance protects executives from personal losses due to lawsuits related to their corporate duties.
- Property insurance: Businesses transfer the financial risk of property losses to an insurer. Following events like a fire, the insurance covers related damages.
Risk Transfer In Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity risks pose an ongoing issue for businesses, making risk transfer essential:
- cyber insurance: In case of a cyberattack, cyber insurance reduces related costs. For example, if a business experiences a ransomware attack, the insurance policy covers the ransom or provides resources to restore services.
- Managed Security Services: Businesses transfer specific security risks to managed security services, like outsourcing incident response to a managed security service provider (MSSP). According to a report by cybersecurity Ventures, the global cybersecurity market is predicted to reach $468.17 billion by 2031, indicating a growing reliance on such services.
Risk Transfer In Project Management
Risk transfer in project management involves shifting specific project risks to specialized professionals:
- Subcontracting: These agreements transfer project risks to specialized contractors. As a notable example, in construction, the general contractor transfers risks associated with electrical work to an electrician.
- Quality Control Inspection: Project teams engage third-party inspectors to transfer quality control risks. These inspectors accept liability for quality verification,ensuring compliance.
Benefits Of Risk Transfer Management
Risk transfer strategies offer notable advantages:
- Financial Stability: limits liability associated with specific risks,protecting against large financial losses.
- Operational Resilience: Helps maintain business operations after severe events.
- Resource Optimization: Allows businesses to refocus internal resources on core activities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Provides documentation of compliance with insurance or financial protection requirements.
- Cost savings: Monthly premiums are more predictable than unexpected losses.
- Improved Risk Management: Transfers risks to experienced specialists for better management.
Strategies And Tips For Risk Transfer Success
Fully leverage risk transfers by using these strategies:
- Identify And Quantify Risks: Understand risks before attempting to transfer them.
- Consider The Cost-Benefit Ratio: Weigh premium costs against potential losses and risk probability.
- Verify Contract Precision: Review contracts and policies to ensure they provide the intended protection.
- Choose Partners With Financial Stability: Ensure partners can fulfill obligations.
- Regularly Review Risk Transfers: Update arrangements as business and risk landscapes change.
- Employ A Comprehensive Risk Management Program: Combine transfer strategies with avoidance, mitigation, and retention.
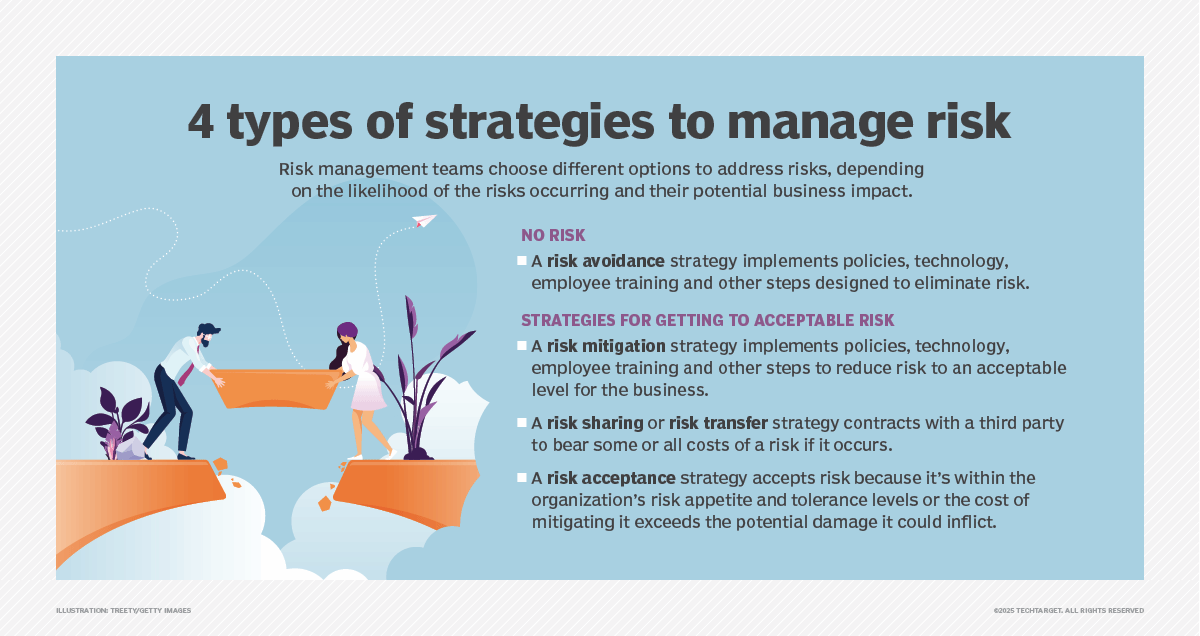
Risk Transfer Vs. Risk Sharing Vs. Risk Retention
Risk transfer is often compared with risk sharing and risk retention.
| Risk Transfer | Risk Sharing | Risk Retention | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shifts responsibility via formal arrangement. | Distributes risk among stakeholders. | Organization accepts and manages risks. |
| Cost Structure | Fixed premiums or fees. | variable expenses based on outcomes. | Direct absorption of losses. |
| Control | External party gains control. | Collaborative decision-making. | Complete organizational control. |
| Relationship Type | Client-provider relationship. | Collaborative partnership. | Internal management. |
| Best For | Well-defined, insurable risks. | Complex risks needing diverse expertise. | High-frequency, low-severity risks. |
| Examples | Insurance policies; outsourcing. | Joint ventures; insurance pools. | Self-insurance; captive insurance. |
| Financial Impact | Predictable costs; reduced volatility. | Distributed costs and potential gains/losses. | Requires cash reserves. |
| Strategic Fit | Peripheral risks. | Risks benefiting from collaboration. | Risks connected to core functions. |
The Future of Risk Transfer
As businesses face increasingly complex and interconnected risks, the future of risk transfer will likely involve more dynamic and integrated solutions.
Emerging trends include the use of artificial intelligence (AI) for risk assessment and predictive modeling, which can help organizations better understand and quantify their risks before transferring them. Additionally, blockchain technology may enhance openness and security in risk transfer contracts, making the process more efficient and trustworthy. According to a 2023 report by McKinsey, companies that actively use data analytics and AI in risk management see a 20% reduction in risk-related losses.
The integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into risk management is also gaining traction. Businesses are increasingly looking for risk transfer solutions that align with their sustainability goals and ethical standards. This might include insuring green projects or partnering with service providers committed to social responsibility.
Pro Tip
Regularly assess your risk landscape and adapt your risk transfer strategies to stay ahead of emerging threats and regulatory changes. staying proactive ensures that your risk management remains effective and aligned with your business objectives.
How do you see new technologies shaping risk transfer in your industry?
Frequently Asked Questions About Risk Transfer
-
What exactly is risk transfer and how does it benefit my business?
Risk transfer is a risk management strategy where you shift potential financial losses from your business to another party, like an insurance company or a specialized vendor. This protects your business’s financial stability and ensures operational resilience.
-
What are the most common risk transfer methods available?
Common methods include insurance policies, contractual clauses (like indemnification agreements), and outsourcing specific functions to external service providers. Each method offers unique protection tailored to different risks.
-
How does cyber
