Mirai Botnet Exploits DVR Vulnerability: A Deep Dive into CVE-2024-3721
A Menacing New Variant of The Mirai Botnet Is Actively Targeting Tbkvision Digital Video Recorders (dvrs), Exploiting A Command Injection flaw To Enslave Devices Into Its Growing Network.
Tracked As Cve-2024-3721, This Vulnerability Allows Attackers To Remotely Execute Commands On Vulnerable Dvrs, turning Them Into Bots For Distributed denial-Of-Service (Ddos) Attacks And Other Malicious Activities.
The Anatomy of the Attack
The Command Injection Vulnerability, cve-2024-3721, Was Initially Disclosed By Security Researcher “Netsecfish” In April 2024. A Proof-Of-Concept (Poc) Was Published, Detailing How A Specially Crafted Post Request Could Be used To Execute Shell Commands By Manipulating Specific Parameters.
Kaspersky Labs Has Now Detected Active Exploitation Of This Vulnerability In Its Linux honeypots. This New Mirai Variant Is Utilizing Netsecfish’s Poc To Drop An Arm32 malware binary.
Once Installed, This Binary Establishes Communication With A Command And Control (C2) Server, Enlisting The Dvr Into The botnet. From There, The Compromised Device Can Be Used For Various Malicious Purposes, Primarily Ddos Attacks.
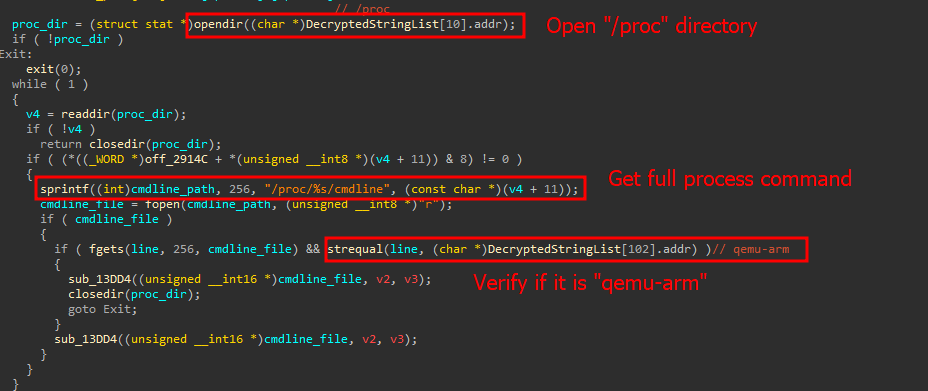
Source: Kaspersky
Impacted Regions and Device Exposure
Netsecfish’s Initial Reports Indicated Roughly 114,000 Internet-Exposed Dvrs were Vulnerable. Kaspersky’s More Recent Scans Show Approximately 50,000 Exposed devices Still At Risk. While The Number Has Decreased, It Still Represents A Considerable Attack Surface.
Kaspersky’s Telemetry Suggests that Most Infections Are Concentrated In China, India, Egypt, Ukraine, Russia, Turkey, And Brazil. However, Due To Restrictions On Kaspersky Products In Certain Regions, This Data Might Not Fully Represent The Botnet’S True Global Targeting Focus.
Did You Know? The Mirai botnet was first discovered in 2016 and has been responsible for some of the largest DDoS attacks ever recorded.
The Patching Problem
The Availability Of Security Patches Remains Unclear. As of Now, Tbkvision Has Not Publicly Announced The Release Of Any Updates To Address cve-2024-3721. Bleepingcomputer Has Reached Out To Tbkvision For Comment And Is Awaiting A Response.
Pro Tip: If you are unable to patch your device, consider isolating it on a separate network segment to limit potential damage.
Complicating Matters,The Affected Dvrs (Dvr-4104 And Dvr-4216) Have Been Extensively Re-Branded Under Various Names,Including Novo,Cenova,Qsee,Pulnix,Xvr 5 In 1,Securus,Night Owl,Dvr Login,Hvr Login,And Mdvr. This Makes Identifying And Patching Vulnerable Devices Significantly More Challenging.
The Researcher Who Discovered The Tbkvision Flaw Has A History Of uncovering Security Issues In End-Of-Life Devices. In 2024, Netsecfish Also Disclosed A Backdoor Account Issue And A Command Injection Vulnerability Affecting Tens Of Thousands Of End-Of-Life D-Link Devices; Active Exploitation Was Detected Shortly After the Poc Releases.
Attack Vectors and Mitigation
- Identify Vulnerable Devices: Determine if your dvrs are Tbkvision Dvr-4104 or Dvr-4216 models, or re-branded versions.
- Check Firmware Updates: Check the manufacturer’s website for available firmware updates.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate Dvrs on a separate network segment to prevent lateral movement.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Look for suspicious outbound traffic from Dvrs.
- Consider Replacement: If no patches are available, consider replacing the device with a more secure alternative.
Mitigation Strategies: A Extensive Approach
Addressing The Threat Posed By The Mirai Botnet Requires A Multi-Faceted Approach. Organizations And Individuals Must Take Proactive Steps To Secure Their Devices And Networks.
Here’s a breakdown of essential mitigation strategies:
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Implement Intrusion Detection Systems (Ids): Deploy IDSs to monitor network traffic for malicious activity.
- Educate Users: Train users to recognize and avoid phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics.
- Keep Software Up-To-Date: Regularly update all software and firmware to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Use Strong Passwords: Enforce the use of strong,unique passwords for all devices and accounts.
Reader Engagement: What security measures have you implemented to protect your IoT devices? Are there any specific challenges you’ve faced in securing your network?
Understanding the Threat Landscape
The Mirai Botnet’s Recent activity highlights The Ever-Present Threat Posed By Iot (Internet Of Things) Devices. These Devices, Often Lacking Robust Security Measures, Are Prime Targets for Attackers Looking To Build Botnets For Malicious Purposes.
In october 2023, A Report By Forescout Revealed That Iot Device Vulnerabilities Increased By 57% Year-Over-Year, Underscoring The Growing Need For Enhanced Security Measures.
The Ease With Which Attackers Can Exploit These vulnerabilities, As Demonstrated By The Mirai Botnet’s Exploitation of Cve-2024-3721, Makes It Crucial For Organizations And Individuals To Take Proactive Steps To Secure Their devices.
Here’s a comparison of common botnet types:
| Botnet Type | Primary Use | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Mirai | DDoS Attacks | Targets IoT devices, uses default credentials for infection. |
| Zeus | Financial Theft | Steals banking credentials and financial information. |
| Emotet | Malware Distribution | Spreads other malware, often through spam emails. |
The Evergreen nature of Security
Cybersecurity is not a one-time fix but an ongoing process. As new vulnerabilities are discovered and exploited, continuous monitoring, patching, and education are vital.
Reader Engagement: What steps do you take to stay informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities in the cybersecurity landscape?
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the Mirai botnet?
- The Mirai botnet is a type of malware that infects devices like DVRs and uses them to perform malicious activities such as DDoS attacks. It is one of the first IoT botnets and it is still one of the most perilous.
- What is CVE-2024-3721?
- Cve-2024-3721 is a command injection vulnerability found in TBK DVR devices that allows attackers to execute arbitrary commands. It is indeed a critical vulnerability that can lead to complete compromise of the affected device.
- How does the Mirai botnet exploit this vulnerability?
- The Mirai botnet uses a crafted POST request to exploit the CVE-2024-3721 vulnerability, injecting malicious commands into vulnerable DVR devices. The attacker can then install their malware and control the device remotely.
- Which devices are affected by this Mirai botnet variant?
- Tbk Dvr-4104 and Dvr-4216 digital video recording devices, along with their re-branded versions, are vulnerable to this Mirai botnet attack. It is indeed critically important to check the model number and firmware version of your device to determine if it is affected.
- What can I do to protect my DVR from the Mirai botnet?
- Ensure your DVR firmware is up to date, and if no updates are available, consider replacing the device with a more secure alternative. Also, isolate the device on a separate network segment if possible. You should also change the default password of your DVR to a strong, unique password.
Share this article and let us know your thoughts in the comments below. Staying informed is the first step in staying secure!
