“`html
Novel Brain Stimulation Technique Shows Promise in Alleviating Autism Traits
Tokyo, Japan – Groundbreaking research from the University Of Tokyo indicates that a novel, noninvasive brain stimulation therapy could alleviate certain autistic traits. The innovative approach targets challenges related to social interaction, mental flexibility, and visual perception.By stimulating nerve cells when the brain gets “stuck” in particular states,researchers observed improved flexibility and a reduction in some behaviors associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Brain State-driven Neural Stimulation (BDNS): A New Frontier in Autism Treatment
The pioneering technique, known as Brain State-Driven Neural Stimulation (BDNS), leverages transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), already utilized in treating mood disorders. Over 40 adults diagnosed with a mild form of autism participated in the study. Encouragingly, the therapeutic benefits of BDNS persisted for approximately two months following the final treatment session. This research paves the way for new treatment strategies and offers hope for individuals with ASD.
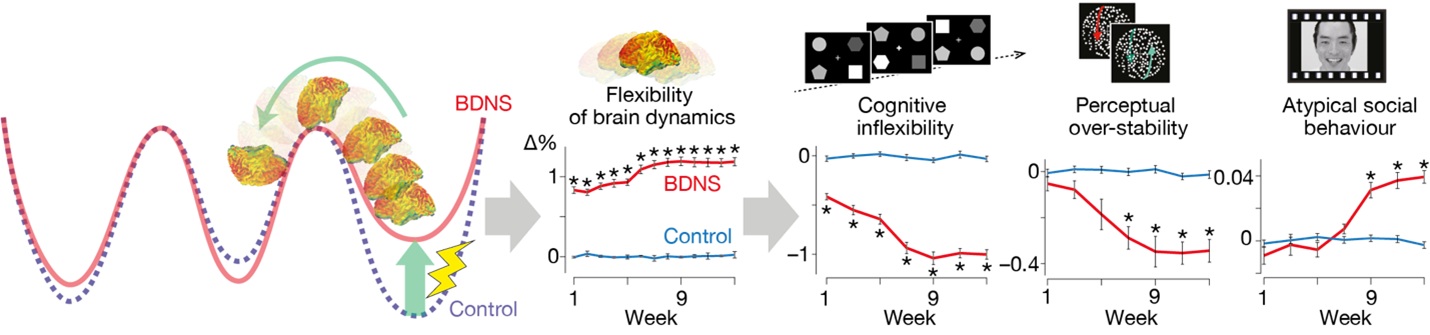
Understanding Neural Rigidity in Autism
Professor Takamitsu Watanabe, a psychiatrist and cognitive neuroscientist at the University Of Tokyo’s international Research Center For Neurointelligence, initiated this research driven by his patients’ experiences. Watanabe’s team discovered that individuals with autism often exhibit “neural rigidity,” characterized by infrequent transitions between brain states, even during rest. This rigidity is now understood to considerably impact both social and nonsocial behaviors observed in ASD.
“Our findings suggest that neural rigidity could be a major cause of this prevalent neurodevelopmental condition at the biological level,” Watanabe stated. The research highlights how diverse behavioral traits in ASD might stem from a single underlying cause.
Study Details and methodology
The study involved 40 adult volunteers with level 1 ASD, the mildest form of the condition. Over a 24-week period, researchers gathered extensive brain data to understand baseline brain dynamics, assess neural rigidity linked to autistic traits, and conduct numerical simulations alongside physical trials aimed at enhancing neural flexibility.
The BDNS method employs transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), which uses magnets placed on the head to stimulate brain cells painlessly and noninvasively.By integrating brain-monitoring systems like functional MRI and electroencephalography, researchers precisely timed short TMS pulses to intervene when participants’ brains were “stuck” in specific states.This tailored approach influenced participants’ brain-state dynamics effectively.
Key findings and Future Directions
Researchers observed notable time lags in BDNS’s effects on different behaviors. Cognitive inflexibility showed rapid improvement within the first week, while perceptual and social traits required six to seven weeks to exhibit notable changes.The team emphasizes the need for larger, more diverse studies encompassing various age groups and ASD levels to validate BDNS’s potential fully.
Further studies are needed to optimize the BDNS protocol for longer-lasting effects, as the benefits in this study diminished approximately two months following the final session. The research team is optimistic about BDNS’s broader applicability, considering its potential use in treating other neuropsychiatric conditions such as ADHD and OCD.
| Condition | Potential benefit of BDNS |
|---|---|
| Autism Spectrum disorder (ASD) | Improved social interaction, mental flexibility, and visual perception |
| Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) | Potential control of overly flexible brain dynamics, relieving hyperactivity |
| Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) | Exploration of BDNS to modulate rigid thought patterns and behaviors |
Did You Know? TMS is already an established treatment for major depression, highlighting its safety profile and potential applicability to other neurological conditions.
Would you consider exploring non-invasive therapies like BDNS for managing autism traits? How might thes advancements change the landscape of mental health treatments in the future?
The Growing Understanding of Autism Spectrum Disorder
The increasing number of ASD diagnoses reflects both improved diagnostic tools and a deeper understanding of this complex developmental condition. ASD affects how individuals interact with their environment and others, leading to challenges in interaction, social interaction, and the presence of restrictive and repetitive behaviors. As of early 2024, the CDC estimates that 1 in 36 children in the U.S. have been identified as having autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Early diagnosis and intervention remain critical for improving outcomes.
Ongoing research continues to unravel the neurobiological underpinnings of ASD, paving the way for targeted therapies that address specific challenges faced by individuals with autism.
Frequently Asked Questions About Autism and BDNS
-
What is Brain State-Driven Neural Stimulation (BDNS)?
BDNS is a noninvasive method using Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) to stimulate brain cells when the brain is “stuck” in a specific state. It aims to improve neural flexibility and alleviate certain autistic behaviors.
-
How does TMS help with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) influences brain-state dynamics, helping to enhance transitions between different brain states. This stimulation can lead to improvements in cognitive flexibility, social traits, and perceptual abilities in individuals with ASD.
-
Who developed the BDNS method for autism treatment?
Professor Takamitsu Watanabe from the university of Tokyo’s International Research Center for Neurointelligence (WPI-IRCN) and co-researcher Hidenori Yamasue from the Hamamatsu University School of Medicine in Japan developed the BDNS method.
-
What kind of autistic traits can BDNS alleviate?
Brain State-Driven Neural Stimulation (BDNS) can alleviate autistic traits related to challenges with social interaction, mental flexibility, and visual perception.
-
How long did the therapeutic effects of BDNS last in the study?
in the study involving adults with mild autism, the therapeutic effects of brain State-driven Neural Stimulation (BDNS) lasted for up to two months after the final session.
-
Can Brain State-Driven Neural Stimulation (BDNS) be used for other conditions besides autism?
Researchers are considering whether Brain State-Driven Neural Stimulation (BDNS) could be applied to other neuropsychiatric conditions, such as ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) and OCD (Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder).
Disclaimer: This article provides information about a new research study and is not intended to provide medical advice. Consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
