Breaking: New Images of Mars Reveal Geological Activity And Atmospheric Haze
Table of Contents
- 1. Breaking: New Images of Mars Reveal Geological Activity And Atmospheric Haze
- 2. Arcadia Planitia: A Region Of Interest
- 3. Impact Crater Analysis
- 4. Martian Weather: The Haze Effect
- 5. Yardangs: Sculpted By Wind
- 6. Mars: Key Facts
- 7. Evergreen Insights
- 8. Reader Engagement Questions
- 9. Frequently Asked Questions
- 10. Here’s a PAA-related question based on the provided text:
- 11. ESA Mars Image: Unveiling the Colors of the Red Planet
- 12. Decoding the Martian Palette: Understanding the Colors
- 13. purple on Mars: A Sign of Iron and Alteration
- 14. Yellow and Orange: Tracking the presence of Iron Oxides
- 15. The Techniques behind the Colors: Image Processing and Filters
- 16. Real-World Examples from ESA Missions
- 17. Benefits: Decoding the Martian Landscape
Mars, often called the Red Planet, has revealed a stunning array of yellows, oranges, and browns in brand-new satellite imagery released. These images, delivered by advanced space technology, capture not only the planet’s diverse surface tones but also highlight active geological processes and unique atmospheric conditions.
The high-resolution imagery provides critical insights into the Martian landscape, including a prominent impact crater and the subtle trails of dust devils traversing the surface. This data is invaluable for scientists studying Mars’ past, present, and potential for future habitation.
Arcadia Planitia: A Region Of Interest
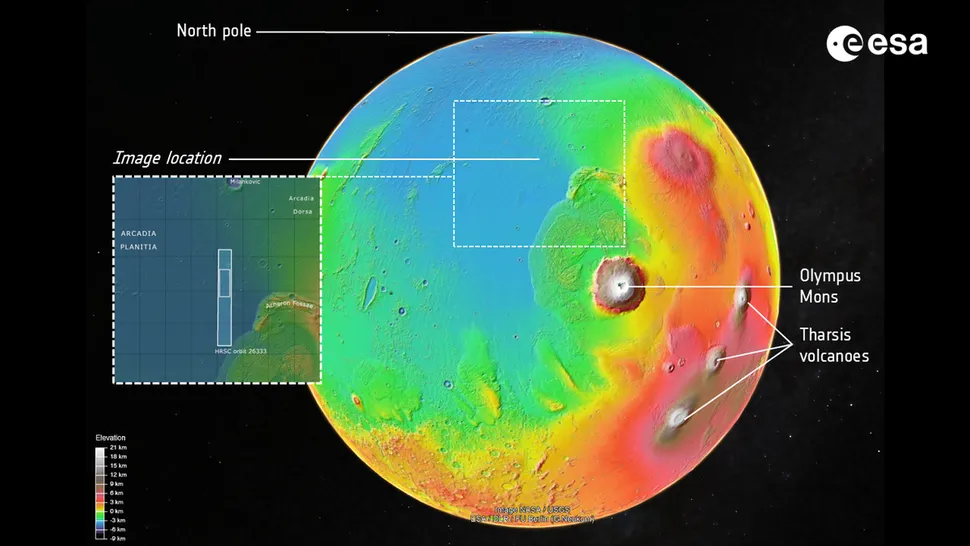
Arcadia Planitia,a key area featured in the new imagery,is of particular interest to researchers. It’s a vast, relatively smooth plain in the northern hemisphere of Mars, believed to harbor significant subsurface water ice. This makes it a prime location for potential future human missions, offering resources for sustaining life and producing rocket fuel. The presence of water ice also provides clues about Mars’ climate history.
Impact Crater Analysis
Located in the lower right quadrant of the recent images, a large impact crater spans approximately 9 miles (15 kilometers). The distinct layered materials surrounding this crater suggest notable quantities of water ice were present during its formation. The relatively pristine condition of the crater indicates it formed recently on the geological timescale.
Martian Weather: The Haze Effect
Have you noticed a slight blur in the images? this is due to the Martian atmosphere. Winds lift tiny particles of dust and debris, creating a subtle, yet pervasive, haze. This phenomenon not only affects image clarity but also plays a crucial role in the planet’s climate dynamics.
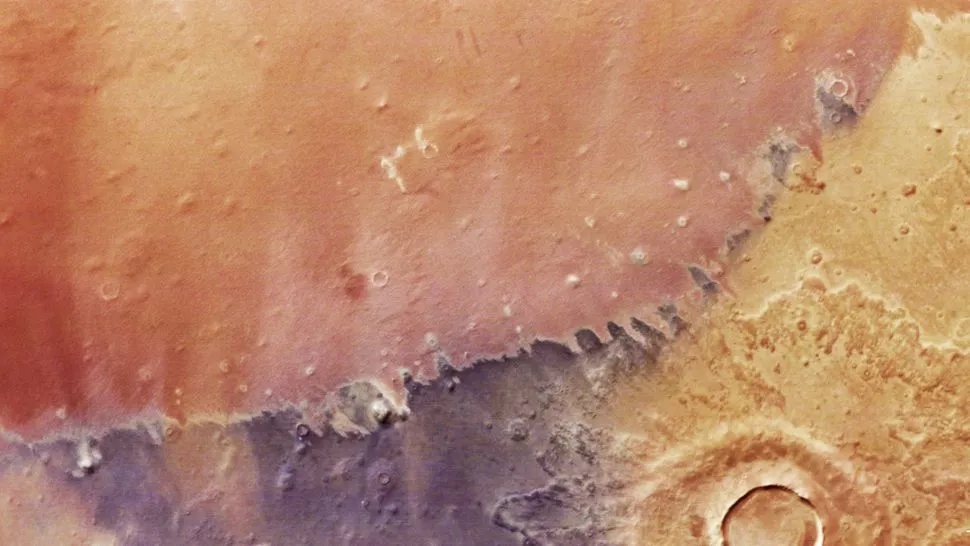
Yardangs: Sculpted By Wind
The reddish region visible in the upper part of the images is characterized by features known as “yardangs.” These ridges are formed by wind erosion, where weaker rock is gradually worn away, leaving behind more resistant formations. Yardangs are a testament to the powerful influence of wind on the Martian landscape, and they are similar to formations found in arid regions on Earth.
Below the yardangs lies a purplish-brown terrain, distinguished by its high silicate and low iron content. These colour variations are attributed to differences in sand properties such as density and size, impacting how these grains accumulate and move across the Martian surface.
Mars: Key Facts
| Feature | Description | significance |
|---|---|---|
| Arcadia Planitia | Vast plain with suspected subsurface water ice. | Potential resource for future human missions. |
| impact Crater | 9-mile wide crater with layered material. | Indicates past presence of water ice; relatively recent formation. |
| Atmospheric Haze | Caused by wind-blown dust particles. | Affects image clarity and influences climate. |
| Yardangs | Wind-eroded ridges in reddish regions. | Demonstrates the erosive power of wind on Mars. |
Evergreen Insights
The ongoing exploration of Mars continues to yield invaluable data, reshaping our understanding of planetary science.Recent findings,including analysis of Martian meteorites,suggest that Mars may have had a more Earth-like atmosphere billions of years ago. Nasa’s Mars Exploration Programme is planning future missions to further investigate the planet’s geology, atmosphere, and potential for past or present life.
Did You Know? Mars has the largest volcano and the deepest, longest canyon in the solar system.
Reader Engagement Questions
- What other geological features on Mars do you find most intriguing,and why?
- How might the discovery of water ice on Mars impact future space exploration efforts?
Frequently Asked Questions
- What causes the reddish color of Mars?
- The reddish hue of Mars is due to iron oxide,or rust,on its surface. This iron oxide is the result of chemical reactions between iron and oxygen.
- How cold does it get on Mars?
- Temperatures on Mars can range from a high of about 70 degrees Fahrenheit (21 degrees celsius) at the equator during the day to a low of about -220 degrees Fahrenheit (-140 degrees Celsius) at the poles.
- Is there any evidence of past or present life on Mars?
- While no definitive evidence of life has been found,scientists continue to explore Mars for signs of past or present microbial life. The discovery of organic molecules and evidence of past water activity are promising leads.
- What are the major challenges of sending humans to Mars?
- Some of the major challenges include the long travel time, exposure to radiation, the need for life support systems, and the psychological effects of isolation.
- How long does it take to travel to Mars?
- A one-way trip to Mars typically takes about six to nine months, depending on the alignment of Earth and Mars and the speed of the spacecraft.
Share your thoughts and join the discussion! What do you find most fascinating about the new images of Mars? Leave a comment below.
ESA Mars Image: Unveiling the Colors of the Red Planet
The European Space agency (ESA) and its partners, like the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter and the Mars Express mission, have gifted us with stunning images of Mars. But what do the vibrant colors – purple, yellow, orange – actually mean? Understanding these colors is key to interpreting the Martian landscape and unlocking its secrets. This article dives into the science behind the hues and explores the geological story they tell. We’ll examine the ESA Mars image data to reveal what each color represents, providing a detailed look at Mars color analysis and Martian geology and its colors.
Decoding the Martian Palette: Understanding the Colors
The colors in ESA Mars images aren’t just for show. They’re a direct result of the composition of the Martian surface materials and how they interact with sunlight. Different minerals and elements reflect light in unique ways, creating the diverse palette we observe. Martian surface composition is key to understanding these colors. The use of different filters and image processing techniques also produces the final colors seen.
purple on Mars: A Sign of Iron and Alteration
Purple hues, although less common, hint at the presence of particular iron-bearing minerals and the effects of alteration processes. In many cases, purple shades, especially in ESA’s Mars images, are related to the scattering of light in fine-grained materials and can be further investigated using spectroscopy.
Generally, regions with this coloration may also highlight areas where the mineral composition has been changed through interactions with water. Understanding Martian mineralogy helps to decode these color variations.
Yellow and Orange: Tracking the presence of Iron Oxides
Yellow and orange are some of the most common colors observed in ESA Mars images. these colors predominantly indicate the presence of iron oxides, also known as rust.Mars gets its distinctive reddish appearance from these minerals, especially hematite and goethite. These compounds are formed through the oxidation of iron-rich rocks, the process of iron reacting with oxygen and water. The variations in color, from light yellow to deep orange, frequently enough reflect differences in the amount and type of iron oxide present.Researching iron oxides on Mars provides further clues.
- Hematite: Often responsible for the darker, sometimes reddish-brown hues.
- Goethite: Can exhibit a yellow to orange color.
The overall presence of iron oxides provides strong evidence of a past or present wet environment,which is a critical factor in the search for any signs of life on Mars. Analyzing Martian surface characteristics reveals the processes that have shaped the planet.
The Techniques behind the Colors: Image Processing and Filters
It’s essential to remember that ESA Mars images often undergo image processing. Scientists employ various techniques to enhance features and reveal information about the Martian surface. These methods can alter the color appearance of the scene, but they are critical to scientific interpretation. The use of false-color images accentuates specific mineralogical features beyond what the human eye might detect.
- Filtering: Using different filters (e.g., red, green, blue) to capture specific wavelengths of light.
- Color Enhancement: Adjusting color balance to highlight subtle differences in mineral composition.
These technical actions greatly enhance the understanding of Mars image interpretation. Understanding the ESA Mars mission techniques makes for a better explanation.
Real-World Examples from ESA Missions
Through the ESA’s Mars Express mission, several discoveries have been made using the high Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC).This instrument captures images in distinct color channels, allowing scientists to identify various minerals.
Let’s look at some examples:
| Location | Color Observed | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Valles Marineris | Yellow/Orange | Iron oxides (rust), evidence of past water activity. |
| Polar Regions | Varied, including patches of Orange/Yellow | Presence of frost, dust, and ice mixes. |
Numerous other images and data collected by the ESA helps in the deep understanding of Martian research. For instance studying the ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter which has an array of scientific instruments, help to further the studies. The ESA Mars program continues to give vital details of the planet.
Benefits: Decoding the Martian Landscape
Understanding the coloration of Mars gives various benefits. They include:
- Unveiling Geological History: Color helps to map rocks and sediments, providing insight into the planet’s formation and environmental changes.
- Identifying Mineral Composition: Allows the tracking of the presense of certain minerals, which may further the insights for resources on Mars.
- Understanding Past Water Activity: Iron oxides are a key indicator of ancient water, a crucial component in the search for any life on Mars**.
the insights gained from color observations enhance our understanding of the solar system, paving the way for future exploration and discoveries about the possibility of any Martian life.
