Table of Contents
- 1. Federal Reserve Navigates Economic Uncertainty Amidst Yield Curve shifts
- 2. Economic Contraction Looms As Fed Mulls Rate Adjustments
- 3. Investment Strategies In A Shifting Market
- 4. Yield Curve Inversion: A Sign Of The Times?
- 5. Federal Reserve’s Response: Historical Context
- 6. Navigating The Waters: Key Considerations For Investors
- 7. Understanding The Federal Reserve’s Role: Evergreen Insights
- 8. Frequently asked Questions About The Federal Reserve
- 9. What were the key characteristics of the February 2020 yield curve, and how did the COVID-19 pandemic impact its shape and movements?
- 10. February 2020 Yield Curve: Key updates and Market Insights
- 11. Understanding the Yield Curve
- 12. Yield Curve Shapes and Their Meanings
- 13. Key Events and Trends in February 2020
- 14. The Impact of COVID-19
- 15. Bond Yield Movements
- 16. Implications for Investors
- 17. Investment Strategies
- 18. The Recession Indicator
Washington D.C. – Recent economic data suggests a pivotal moment for the Federal Reserve as it grapples wiht possibly shifting monetary policy. The Central Bank’s hawkish stance, previously firm, is now facing pressure to adapt to emerging economic realities. The key question is: Will the Federal Reserve successfully navigate these turbulent waters?
Economic Contraction Looms As Fed Mulls Rate Adjustments
The Federal Reserve is widely expected to announce adjustments to its benchmark interest rate. This comes amid concerns that the current tightening cycle may lead to an economic contraction. Some analysts predict the Fed will chase the natural rate down to zero.
Instead of the anticipated rise in interest rates,some experts now foresee a sharp decline. The yield, already below February levels, underscores this changing landscape. Should short-term rates fall below 1% without a corresponding increase in the 10-year yield to 2% or 3%, an economic downturn becomes increasingly probable.
Investment Strategies In A Shifting Market
Despite the overall uncertainty, opportunities may still exist. long bond positions could yield gains. The housing market appears resilient and relatively defensive, suggesting stability even amid potential volatility. However,the stock market’s trajectory remains uncertain. A bear market is possible, though not guaranteed.
Regardless of broad market trends, a trader’s market is anticipated. Beaten-down stocks could present attractive long-term investment opportunities for savvy investors.
Yield Curve Inversion: A Sign Of The Times?
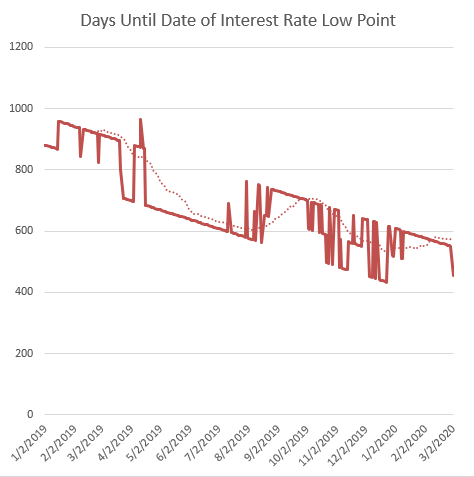
The yield curve has been inverted at the short end since early 2019. Initially, September 2021 was projected as the point for rate normalization. Though, recent flattening of the curve suggests a potential shift. December 2021 or even March 2022 are now being considered as possible timelines for the rate low point.
The Coronavirus pandemic has further intricate the situation, driving yields down, particularly at the short end. Markets anticipate a federal reserve response. Despite recent negative indicators, the yield curve has slightly tilted upward, moving the expected rate low point to June 2021.
This suggests a confirmation of a standard yield curve-related contraction. The market expects the Federal Reserve to act with agility to mitigate the contraction’s depth and duration. The effectiveness of this response remains to be seen.
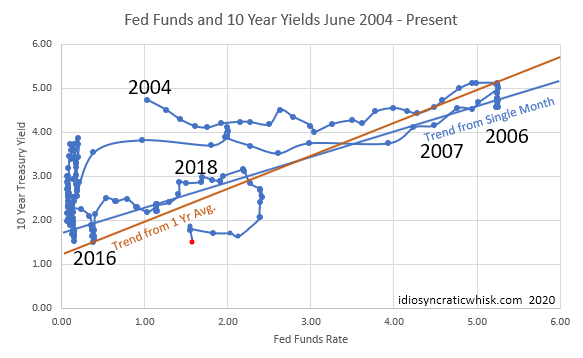
Federal Reserve’s Response: Historical Context
The Federal Reserve’s reaction to economic downturns has evolved significantly over the decades. In the past, the Fed often employed aggressive rate cuts to stimulate the economy. More recently, quantitative easing (QE) has also become a key tool. QE involves the Fed purchasing government bonds or other assets to inject liquidity into the market and lower long-term interest rates.
Did You Know? The Federal Reserve was established in 1913 to provide a more stable and flexible financial system.
The effectiveness of these measures is a subject of ongoing debate. Some argue that they can create asset bubbles and lead to inflation. Others maintain that they are essential for preventing deep recessions and supporting economic recovery.
Pro Tip: Stay informed about the Federal reserve’s policy announcements and monitor economic indicators closely to make informed investment decisions.
In the current environment, investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance and investment objectives. Diversification is crucial to mitigate potential losses. Consider a mix of asset classes, including stocks, bonds, and real estate.
Monitoring the yield curve is also essential. A flattening or inverted yield curve can signal an impending recession. Be prepared to adjust your portfolio accordingly.
What strategies are you employing to navigate the current economic climate? What are your thoughts on the Federal Reserve’s next move?
Understanding The Federal Reserve’s Role: Evergreen Insights
The Federal Reserve (also known as the Fed) plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability of the U.S. financial system. It has several key functions:
- Conducting monetary policy to manage inflation and unemployment.
- Supervising and regulating banks to ensure their safety and soundness.
- Maintaining the stability of the financial system.
- Providing financial services to the U.S. government, financial institutions, and foreign official institutions.
| Function | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Monetary Policy | Adjusting interest rates and the money supply | Influences inflation, employment, and economic growth |
| Bank Supervision | Monitoring and regulating banks | Ensures financial stability and protects consumers |
| Financial Stability | Identifying and addressing risks to the financial system | Prevents financial crises and supports economic activity |
Frequently asked Questions About The Federal Reserve
- How Does The Federal Reserve impact Interest Rates?
- The Federal Reserve influences interest rates by adjusting the federal funds rate, which affects the borrowing costs for banks and, subsequently, consumer and business loans.
- What Is A yield Curve, And Why Is It Important For Understanding The Federal Reserve’s Actions?
- A yield curve represents the difference between interest rates of varying lengths of government debt. It provides insights into market expectations for future interest rate changes and economic growth, influencing Federal Reserve policy.
- What Are The Potential Consequences Of The Federal Reserve Lowering Interest Rates To Near Zero?
- Lowering interest rates to near zero can stimulate borrowing and investment but may also lead to concerns about inflation and the effectiveness of monetary policy.
- How Might A Long Bond position Be Affected By Federal reserve Actions?
- A long bond position could benefit from declining interest rates if the federal Reserve lowers rates, as bond prices typically rise when rates fall.
- What factors Influence The Federal Reserve’s Decisions Regarding Interest Rate Adjustments?
- The Federal Reserve considers various economic indicators, including inflation, employment figures, and overall economic growth, when making decisions about interest rate adjustments.
- How Does The Federal Reserve’s Response To Economic Downturns Impact The stock Market?
- The Federal Reserve’s actions during economic downturns can influence investor sentiment and stock market performance, often leading to increased volatility and trading opportunities.
Share your thoughts and comments below.stay tuned for further updates on this developing story.
What were the key characteristics of the February 2020 yield curve, and how did the COVID-19 pandemic impact its shape and movements?
February 2020 Yield Curve: Key updates and Market Insights
The February 2020 yield curve presented a complex landscape for investors and economists alike. This period was marked by significant shifts in bond yields, impacting market sentiment and providing crucial signals regarding the economic outlook. A deep dive into this period reveals vital details on market trends, economic impacts, and strategic investment considerations.
Understanding the Yield Curve
The yield curve is a graphical representation of the interest rates on bonds with different maturity dates. It helps to visualize the relationship between bond yields and their time to maturity. Key characteristics of the yield curve include its shape (normal, inverted, or flat) and the implications of each shape for future economic activity. It’s an essential tool for bond yield analysis and understanding market expectations.
Yield Curve Shapes and Their Meanings
Different yield curve shapes provide insights into market expectations:
- Normal Curve: Occurs when longer-term bonds have higher yields than shorter-term bonds, reflecting expectations of economic growth and inflation.
- Inverted Curve: When short-term bonds have higher yields than long-term bonds. Historically, this has been a reliable indicator of an impending recession.
- Flat Curve: yields are similar across all maturities, suggesting uncertainty in the market.
Key Events and Trends in February 2020
February 2020 was a pivotal month, overshadowed by the burgeoning COVID-19 pandemic. As the Coronavirus began to spread worldwide, its impact on the financial markets, including the yield curve, was palpable. Investors, anticipating economic slowdown, were adjusting their portfolios and seeking safe-haven assets.
The Impact of COVID-19
The initial reaction to COVID-19 included:
- Flight to Safety: Investors moved into safer assets, like US Treasury bonds, driving down Treasury yields.
- Economic Uncertainty: Concerns about lockdowns, supply chain disruptions, and diminished consumer consumption heightened market volatility.
- Flattening of the Curve: The yield curve started to flatten as yields across maturities converged.
Bond Yield Movements
Throughout February 2020, bond yields saw significant shifts. This period illustrated the impact of economic uncertainty on yields and created a prime opportunity for yield curve analysis across different maturity dates.
| Bond Maturity | Yield Change (Approximate) | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2-Year Treasury | Decreased Substantially | Reflecting expectations of near-term rate cuts by the Federal Reserve. |
| 10-Year Treasury | Decreased Substantially | Indicating concerns about long-term economic growth. |
| 30-Year Treasury | Decreased | Signaling continued market appetite for long-term stability. |
Implications for Investors
The shape and movements of the yield curve in February 2020 provided valuable insights for investment strategy. Understanding these signals was critical for navigating the market turbulence.
Investment Strategies
Based on the yield curve’s signals, investors could consider:
- Portfolio Diversification: Diversifying into different asset classes like gold or other safe-haven assets.
- duration Management Adjusting the bond portfolio duration to match the anticipated interest rate environment.
- Risk Management: Employing hedging strategies to mitigate potential losses.
The Recession Indicator
The shape of the yield curve can frequently be a precursor to economic downturns. Several factors contributed to the market’s outlook during February 2020.
The Federal Reserve monitors the yield curve closely to inform monetary policy decisions.
Keep in mind, the yield curve is a dynamic indicator, and its signals should be interpreted in conjunction with other economic indicators.
