“`html
Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Rare Autoimmune Disorder Linked To Infections
Breaking Health News: Researchers are investigating a potential link between common infections and the onset of Guillain-barré Syndrome (GBS), a rare but serious autoimmune condition. this condition impacts the lives of thousands globally each year.
What Is Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a rare autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nervous system. This can lead to numerous health complications if left untreated.
This attack can result in muscle weakness, numbness, tingling, and even paralysis. In severe cases, GBS can be life-threatening, especially if the breathing muscles or autonomic functions are affected.
While GBS can affect individuals of any age, it is more prevalent among adults and the elderly. The exact cause of GBS remains unknown; however, most cases occur following a bacterial or viral infection.
How Infections Relate To GBS
GBS itself is not contagious, meaning it cannot spread from person to person like the flu or COVID-19.However,certain infections associated with GBS are transmissible,increasing the likelihood of developing the syndrome.
Here are key associations:
- Viral and Bacterial Infections: Most GBS cases are preceded by a bacterial or viral infection that triggers an abnormal immune response.
- Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Infections: Upper respiratory tract infections (colds, sinus infections, pneumonia) and gastrointestinal infections, particularly those caused by Campylobacter bacteria, are significant triggers.
- immunizations: In extremely rare instances, GBS has developed following flu, COVID-19, or other vaccinations, although the risk is substantially lower than from the infections themselves.
Common Infections Linked to GBS
Several infections have been linked to GBS:
- Campylobacter jejuni: A leading cause of food poisoning, found in undercooked poultry and contaminated water.
- Influenza (Flu): Some GBS cases are associated with flu viruses.
- cytomegalovirus (CMV): A widespread viral infection, especially in those with weakened immune systems.
- Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV): Causes mononucleosis (mono) and is associated with some GBS cases.
- Zika Virus: This mosquito-borne virus has been linked to increased GBS incidence in affected regions.
Prevention Strategies
As GBS is frequently enough triggered by preceding infections, reducing your risk of infection is crucial:
- Wash hands frequently to prevent bacterial and viral infections.
- Cook food, especially poultry, thoroughly to avoid Campylobacter infections.
- Get vaccinated against influenza,COVID-19,and other preventable diseases.
- Drink safe, clean water to avoid contaminated sources.
- Practice mosquito protection in areas where Zika virus is common.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper hygiene to boost the immune system.
What are the common early signs of Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)?
Guillain-Barré syndrome: Symptoms, Treatment & Spread – Your Complete Guide
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a rare neurological disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the nerves. This can lead to muscle weakness and, in severe cases, paralysis. Understanding the symptoms, treatment, spread, and overall experiance of GBS is crucial for early detection and effective management. this thorough guide provides detailed information about this challenging condition, helping you navigate the complexities of Guillain-Barré Syndrome and its impact.
What is Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)? Definition and Overview
Guillain-Barré Syndrome, often referred to as GBS, is a serious autoimmune disorder. It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nerves – the nerves that carry signals between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. this autoimmune response damages the myelin sheath (a fatty coating that protects nerve fibers) or the nerve axons themselves, disrupting the ability of the nerves to transmit signals effectively. The primary goal of early diagnosis is to minimize long-term nerve damage and maximize GBS recovery time.
Causes of Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Risk Factors and Triggers
While the exact cause of Guillain-Barré Syndrome remains unknown, it’s frequently triggered by an infection, usually a respiratory or gastrointestinal infection.Several factors are associated with an increased risk of developing GBS. Understanding the potential triggers is important. Here is a list of common triggers and associated risks including, those associated with potential vaccines:
- Infectious Diseases: Bacterial or viral infections like Campylobacter jejuni, cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), influenza, and Zika virus infection.
- Surgery: Patients can develop GBS following a notable surgical procedure.
- Vaccinations: In rare cases,vaccinations,such as those for influenza,may be associated with an increased risk,although studies continue to evaluate the risk.
- Other Illnesses: HIV/AIDS and lymphoma are associated with increased risk.
Research is continually evolving to clarify the specific mechanisms and risk factors associated with GBS.
guillain-Barré Syndrome Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs
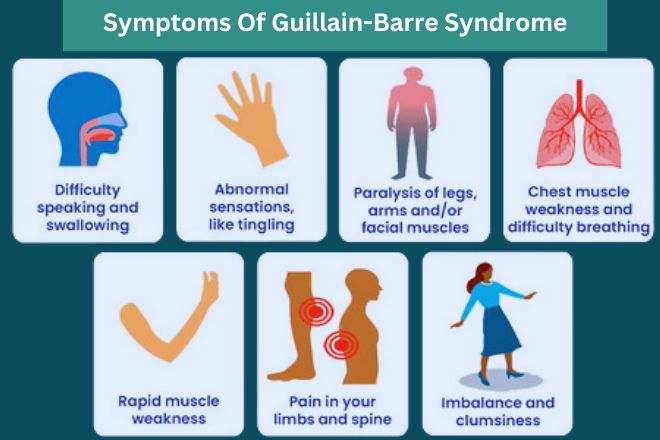
Recognizing the symptoms of guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. The symptoms of GBS vary widely from person to person. They usually start with tingling, weakness, or pain, frequently enough in the legs and feet. It’s categorized as sensory and or motor symptoms. the hallmark of GBS includes both sensory and motor disturbances causing weakness.
Common Early Signs and Symptoms:
Initially, individuals with GBS often experience these symptoms:
- Weakness: Weakness that begins in the legs and spreads upwards.
- Tingling: Pins and needles sensation in the legs, feet, arms, and hands.
- Pain: Pain that can vary from muscle aches to severe cramps.
- Loss of Reflexes: diminished or absent reflexes.
- Other Sensory Changes: Numbness.
Severe GBS Symptoms & Progression of the Disease
As GBS progresses, symptoms can worsen; this is why early recognition is essential.In more advanced stages, symptoms may include:
- Difficulty with Speaking, Swallowing, and Chewing: Muscles used for these functions can be affected.
- Difficulty Breathing: Respiratory muscle weakness can become life-threatening.
- Rapid Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Fluctuations: Autonomic nervous system involvement can cause these changes.
The progression of GBS is generally rapid.Symptoms typically peak within several weeks, after which the symptoms stabilize and enter into the recovery phase. Watch for these specific changes and contact a health professional immediately if you suspect Gullain-Barré Syndrome. Early intervention is very critically important and improves the potential for a better GBS recovery.
Diagnosing Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Tests & Procedures
Diagnosing Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specific tests. The goal is to differentiate GBS from other neurological conditions with similar symptoms so you can start treatment as soon possible.Diagnosing GBS usually requires a careful and targeted approach.
Diagnostic Methods for GBS
The following tests may be used in the diagnosis of GBS:
- Neurological Examination: Evaluating reflexes, muscle strength, sensory function, and coordination.
- lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): Examining the cerebrospinal fluid for elevated protein levels, which is characteristic of GBS.
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) and Electromyography (EMG): measuring the electrical activity of nerves and muscles to identify nerve damage.
- Other Blood Tests: Perform blood tests to rule out other possible causes of symptoms.
These diagnostic steps are essential for confirming a GBS diagnosis and guiding treatment strategies.
Guillain-Barré Syndrome Treatment: Management and Therapies
The primary goals of treatment for Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) are to reduce the severity of the illness, to alleviate symptoms, and to accelerate recovery. Early intervention is very important to prevent complications. Although there is no cure for GBS, several treatments are effective in managing the condition and supporting recovery.
Effective Treatment Options for GBS
The two main treatments:
- Plasma Exchange (Plasmapheresis): This procedure removes antibodies from the blood that are attacking the nerves.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg): High doses of antibodies are given to interfere with the harmful antibodies that attack the nerves.
Additional treatments may include:
- Pain Management: Medications to alleviate pain.
- Physical Therapy: To help regain strength and improve function.
- Respiratory Support: Mechanical ventilation might potentially be necessary to assist with breathing.
These strategies have proven effective in improving outcomes and significantly reducing GBS recovery time.
Guillain-Barré Syndrome Recovery: What to Expect
The recovery from Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) varies significantly from person to person. The patient’s overall health and the severity of the nerve damage impact the progress. Understanding factors related to recovery can help patient’s manage expectations and participate actively in their treatment.
| Recovery Stage | Description | Typical Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Enhancement Phase | Symptoms stabilize and start to improve after treatment. | Within weeks after peak severity. |
| Recovery Phase | Motor and sensory functions gradually return.Physical therapy and rehabilitation are central in this stage. | Can last for several months to years. |
| Long-Term Outcomes | The majority of people with GBS recover fully or with some residual weakness. Some may experience persistent fatigue, weakness, or sensory changes. | Long-term monitoring is helpful. |
The recovery process frequently enough takes several months to a few years. Most people with GBS will eventually achieve full recovery, though some may experience lingering effects. Continued physical therapy and rehabilitation will help to optimize the recovery and help ensure a better long term outcome and improved GBS recovery time. It may also be important to seek out emotional support.
FAQ: Answers to Your Questions About Guillain-Barré Syndrome
This section addresses some of the most frequently asked questions (FAQs) to help you gain a better understanding of GBS.
Common Questions and Answers
Q: Is Guillain-Barré Syndrome contagious?
A: No, GBS is not contagious. It’s an autoimmune disorder, meaning it’s a result of your immune system attacking your own body’s nerves.
Q: How long does it take to recover from guillain-Barré Syndrome?
A: The recovery period can vary widely, from a few weeks to several years. Most people experience significant improvements within six to twelve months. Early treatment influences how long the GBS recovery time lasts on average.
Q: What are the long-term effects of GBS?
A: While many people recover fully, some may experience lasting effects, such as weakness, fatigue, or sensory issues. Some individuals may experience chronic pain.
Q: Is there a cure for GBS?
A: There is no cure. However,treatments such as plasma exchange and IVIg,can reduce the severity of GBS and improve your recovery outlook.
Q: Can GBS reoccur?
A: Recurrence is rare, but possible. If symptoms return after a period of recovery, consult your medical doctor.
Where to Learn More and Get Support for Guillain-Barré Syndrome
If you or someone you know is affected by Guillain-Barré Syndrome,accessing reliable information and connecting with support resources is critical.
