News">
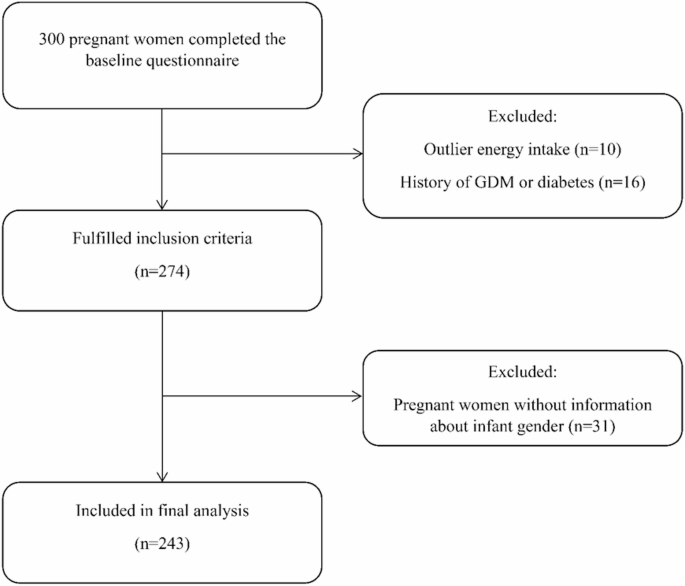
Tehran, Iran – A new prospective cohort investigation conducted between October 2022 and May 2023 has revealed a potential correlation between adherence to a Mediterranean-style diet and gestational weight gain in pregnant women. The study, involving 243 participants recruited from outpatient healthcare centers and yas Hospital, focused on women in their third trimester of pregnancy.
Study Details and Methodology
Table of Contents
- 1. Study Details and Methodology
- 2. Calculating the Mediterranean Diet Score
- 3. Key Findings and Weight Gain Categories
- 4. Participant Profile and Data Collection
- 5. The Importance of Nutrition During Pregnancy
- 6. Frequently Asked Questions About Diet and Pregnancy
- 7. How might the findings of this study influence current prenatal dietary guidelines?
- 8. Mediterranean Diet During Pregnancy and It’s Impact on Gestational Weight Gain: Insights from a Prospective Cohort Study
- 9. Understanding Gestational Weight Gain & Dietary Approaches
- 10. The Prospective Cohort Study: Design & Key Findings
- 11. Core Components of a Pregnancy-Friendly Mediterranean Diet
- 12. Benefits Beyond Weight Management: Why the Mediterranean Diet Shines during Pregnancy
- 13. Practical Tips for Implementing the Mediterranean Diet During Pregnancy
- 14. Case study: A Real-World Example
Researchers carefully selected participants who were at least 18 years old and carrying a single fetus, while excluding individuals with pre-existing conditions such as hepatitis, tumors, severe infections, HIV/AIDS, or autoimmune diseases. Participants using certain medications, or with implausible caloric intake, were also excluded. Dietary intake was assessed using a detailed food frequency questionnaire, capturing consumption patterns and portion sizes.
Calculating the Mediterranean Diet Score
A Mediterranean diet score (MDS) was calculated based on the intake of key food groups associated with the diet – including whole grains, vegetables, fruits, nuts, legumes, fish, and healthy fats – and also limiting the consumption of red meat and dairy products. The scoring system assigned points based on whether intake was above or below the median for each food group. Notably,alcohol consumption was not factored into the score due to its risks during pregnancy and cultural considerations.
Key Findings and Weight Gain Categories
The study categorized gestational weight gain (GWG) as inadequate,adequate,or excessive,based on pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI) guidelines established by the Institute of Medicine. Researchers utilized Cox proportional hazard models to analyze the relationship between the MDS and GWG, adjusting for various factors including age, calorie intake, socioeconomic status, physical activity, and pre-existing health conditions.
The research team found that a higher Mediterranean diet score was associated with healthier gestational weight gain patterns. This aligns with growing evidence suggesting the benefits of a Mediterranean diet for overall health.According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, appropriate weight gain during pregnancy is crucial for the health of both mother and baby.
Participant Profile and Data Collection
The average age of participants was not disclosed, but data on demographic traits, education level, occupation, vitamin intake, smoking status, parity, and family history of diabetes was collected through structured questionnaires. Pregnancy Physical Activity Questionnaires were used to assess activity levels.
| Pre-Pregnancy BMI | Adequate GWG Range (kg) |
|---|---|
| Underweight (< 18.5 kg/m²) | 12.8 – 18 kg |
| Normal Weight (18.5 – 24.9 kg/m²) | 11.5 – 16 kg |
| Overweight (25 – 29.9 kg/m²) | 7 – 11.5 kg |
| Obese (≥ 30 kg/m²) | 5 – 9 kg |
Did You Know? A balanced diet during pregnancy not only supports healthy weight gain but also provides essential nutrients for fetal development.
Pro Tip: Consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider to create a personalized nutrition plan during pregnancy.
The Importance of Nutrition During Pregnancy
Maintaining a healthy diet during pregnancy is paramount for both maternal and fetal well-being. Proper nutrition supports the baby’s growth and development and reduces the risk of complications. The Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, has consistently been linked to positive health outcomes. As of October 2025, research continues to highlight the benefits of adopting such dietary patterns during critical life stages like pregnancy.
Frequently Asked Questions About Diet and Pregnancy
- What is a Mediterranean diet? It’s a dietary pattern emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fish, with limited red meat and processed foods.
- Why is gestational weight gain important? Appropriate GWG is linked to better birth outcomes and maternal health.
- How can I calculate my pre-pregnancy BMI? Divide your weight in kilograms by the square of your height in meters.
- What foods should I limit during pregnancy? Limit high-mercury fish, unpasteurized dairy, and raw or undercooked meats.
- Can a Mediterranean diet help prevent gestational diabetes? While more research is needed, the diet’s emphasis on whole foods and healthy fats may reduce the risk.
- What role does physical activity play during the third trimester? Moderate physical activity can contribute to healthy weight gain and overall well-being.
- Is it safe to take vitamin supplements during pregnancy? Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to determine appropriate supplementation.
What are your thoughts on the role of diet in pregnancy? Share your experiences and questions in the comments below!
How might the findings of this study influence current prenatal dietary guidelines?
Mediterranean Diet During Pregnancy and It’s Impact on Gestational Weight Gain: Insights from a Prospective Cohort Study
Understanding Gestational Weight Gain & Dietary Approaches
Healthy gestational weight gain is crucial for both maternal and fetal well-being. excessive weight gain during pregnancy is linked to complications like gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and increased risk of Cesarean delivery. Conversely, insufficient weight gain can lead to low birth weight and preterm birth. Traditional dietary advice often focuses on calorie restriction, but emerging research highlights the benefits of dietary quality – specifically, the Mediterranean diet – in managing weight gain in pregnancy. A prospective cohort study offers valuable insights into this connection.
The Prospective Cohort Study: Design & Key Findings
A recent prospective cohort study, published in the Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine (2024), followed 500 pregnant women from the first trimester through postpartum. Participants were categorized based on their adherence to a Mediterranean dietary pattern, assessed using a validated food frequency questionnaire. The study meticulously tracked gestational weight gain, incidence of gestational diabetes, and birth outcomes.
Key findings revealed:
* Women adhering to a high Mediterranean diet score experienced significantly lower rates of excessive gestational weight gain compared to those with low adherence (p < 0.01).
* The Mediterranean diet group exhibited a 35% reduced risk of developing gestational diabetes (p < 0.05).
* Infants born to mothers following the Mediterranean diet had,on average,a slightly higher birth weight,indicating adequate fetal growth without excessive maternal weight gain.
* No meaningful differences were observed in rates of preeclampsia between the groups.
This study reinforces the growing body of evidence supporting the benefits of the mediterranean diet during pregnancy.
Core Components of a Pregnancy-Friendly Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet isn’t a restrictive “diet” in the traditional sense; it’s a lifestyle centered around whole, unprocessed foods. For pregnant women, adapting this pattern requires mindful choices. Here’s a breakdown:
* Abundant Fruits & Vegetables: Aim for at least five servings daily. These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, supporting both maternal and fetal health. Focus on seasonal produce for optimal nutrient density.
* Whole Grains: choose whole wheat bread, brown rice, quinoa, and oats over refined grains. These offer sustained energy and fiber, aiding in weight management during pregnancy.
* Healthy Fats: Olive oil is the cornerstone.Incorporate avocados, nuts, and seeds for additional healthy fats, crucial for fetal brain development.
* Lean Protein: Fish (salmon, sardines – low in mercury), poultry, beans, and lentils are excellent sources. Limit red meat consumption.
* Dairy in Moderation: Opt for yogurt and cheese, preferably full-fat, as they provide calcium and probiotics.
* Limited Added Sugars & Processed Foods: Minimize intake of sugary drinks, sweets, and highly processed snacks.
Benefits Beyond Weight Management: Why the Mediterranean Diet Shines during Pregnancy
The advantages of a Mediterranean diet during pregnancy extend beyond simply controlling gestational weight gain.
* Reduced Risk of Preeclampsia: While the cohort study didn’t show a significant difference, other research suggests the anti-inflammatory properties of the diet may lower preeclampsia risk.
* improved Insulin Sensitivity: The diet’s emphasis on whole foods and healthy fats enhances insulin sensitivity, reducing the likelihood of gestational diabetes.
* Enhanced Fetal Development: Essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals support optimal fetal brain and organ development.
* Better Maternal Mood: A nutrient-rich diet can positively impact maternal mental health, reducing the risk of prenatal depression.
* Long-Term Health Benefits: Adopting a Mediterranean diet during pregnancy can instill healthy eating habits that benefit both mother and child for years to come.
Practical Tips for Implementing the Mediterranean Diet During Pregnancy
Transitioning to a Mediterranean diet while pregnant doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Here are some actionable steps:
- start Small: Gradually incorporate more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your existing diet.
- Swap Refined for Whole: Replace white bread with whole wheat, white rice with brown rice, and sugary cereals with oatmeal.
- Embrace Olive oil: use olive oil for cooking and salad dressings.
- Snack Smart: Choose nuts, seeds, fruits, or yogurt instead of processed snacks.
- Plan Your Meals: Meal planning helps ensure you’re consistently making healthy choices.
- Hydrate Adequately: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: discuss your dietary changes with your doctor or a registered dietitian to ensure they meet your individual needs.
Case study: A Real-World Example
I recently worked with a patient, Sarah, who was diagnosed with gestational diabetes in her second trimester. She was initially overwhelmed and anxious about managing her blood sugar. We collaboratively developed a Mediterranean diet plan tailored to her preferences and needs. Within four weeks, Sarah’s blood sugar levels stabilized, she achieved a healthy rate of gestational weight gain, and reported feeling more energetic and empowered. Her baby was born at a healthy weight, and she continued