Glp-1 Drugs Vs. Obesity Surgery: A Weight Loss Showdown
Table of Contents
- 1. Glp-1 Drugs Vs. Obesity Surgery: A Weight Loss Showdown
- 2. Study Highlights: Glp-1 Drugs Versus Surgical Outcomes
- 3. The Challenge Of Long-Term Glp-1 Drug Use
- 4. Expert Endorsement For Surgical Consideration
- 5. Comparative Analysis: Glp-1 Drugs Vs. Obesity Surgery
- 6. The Rising Popularity Of Weight Loss Solutions
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions About Glp-1 Drugs and Obesity Surgery
- 8. For a person with a BMI over 30, what are the potential long-term benefits and drawbacks of choosing weight loss medication, rather than obesity surgery, to help them manage their weight?
- 9. Obesity Surgery vs. Medication: Unveiling the Dramatic Weight Loss Effect
- 10. Understanding the Impact of Obesity
- 11. Obesity Surgery: A Powerful Intervention
- 12. The “5x Weight Loss Effect” and Surgery
- 13. Weight Loss Medication: A Complementary Approach
- 14. Choosing the Right Path: Surgery vs.Medication
- 15. Real-World Example: A Case Study
- 16. The Importance of ongoing weight Management
- 17. Practical Tips for Weight Loss Success
Washington,D.C. – in a groundbreaking study presented at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) annual conference, researchers have compared the effectiveness of Glp-1 drugs versus obesity surgery in achieving significant weight loss. The findings challenge the long-term efficacy of Glp-1 drugs, such as semaglutide and tirzepatide, against the more enduring results of surgical interventions.
Study Highlights: Glp-1 Drugs Versus Surgical Outcomes
The study, conducted between 2018 and 2024, analyzed data from 5,855 individuals with a Body Mass Index (Bmi) of 35 or higher.The research scrutinized the outcomes of 1,254 individuals who underwent obesity surgery against 3,854 individuals treated with weekly injections of semaglutide or tirzepatide. The results indicated that while Glp-1 drugs offer an initial weight loss benefit, their long-term impact is less pronounced compared to surgical options.
Dr. Brown from New York University, a lead author of the study, noted that clinical trials have reported a 15-21% weight loss with Glp-1 drugs. Though, he cautioned that patients might need to consider obesity surgery or adjust their expectations to achieve their desired weight loss goals.
While consistent Glp-1 drug administration showed more weight loss in the first year, the total weight loss rate after two years was only 7%, significantly lower than that achieved through surgery.
The Challenge Of Long-Term Glp-1 Drug Use
Obesity, recognized as a chronic condition, frequently enough necessitates lifelong medication to sustain weight loss. However, the high cost of Glp-1 drugs, coupled with potential side effects and a perception of unneeded treatment after initial weight loss, poses significant challenges. Recent data reveals that 53.6% of patients discontinue Glp-1 drug treatment within one year, and this figure escalates to 72.2% after two years.
In contrast,obesity surgery permanently reduces the stomach’s size,thereby limiting food intake and enabling patients to lose between 20-50% of their weight.
Expert Endorsement For Surgical Consideration
Anne Rogers, chairman of Asmbs, suggests considering obesity surgery as an option or combination therapy if Glp-1 drugs do not yield sufficient weight loss or if side effects or costs become prohibitive. Rogers emphasized that the choice of medical treatment should align with individual goals and be determined through expert consultation.
Disclaimer: this article provides general data and does not constitute medical advice. always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Comparative Analysis: Glp-1 Drugs Vs. Obesity Surgery
To better understand the differences between Glp-1 drugs and obesity surgery, here’s a comparative overview:
| Feature | Glp-1 Drugs | Obesity Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Weight Loss | 15-21% | 20-50% |
| Long-Term weight Loss (2 years) | 7% | Significantly Higher |
| Treatment Duration | Lifelong | permanent (one-time procedure) |
| Adherence Rate | Low (high discontinuation rate) | High (permanent results) |
| Cost | High (ongoing medication) | One-time cost |
| Side Effects | Potential side effects | Surgical risks |
The data suggests that while Glp-1 drugs can be effective initially, obesity surgery offers a more enduring and impactful solution for long-term weight management.
The Rising Popularity Of Weight Loss Solutions
The demand for effective weight loss solutions has surged in recent years. According to a report by Mckinsey & Company, the weight-management market is projected to reach $400 billion by 2030. This growth is driven by increasing obesity rates and a greater awareness of the health risks associated with excess weight.
The study highlights the importance of considering all available options, including lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and surgical procedures, to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Did You Know? The CDC reports that obesity affects over 40% of adults in the United States, increasing their risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions About Glp-1 Drugs and Obesity Surgery
- What Are Glp-1 Drugs? Glp-1 drugs, like semaglutide, mimic a natural hormone to regulate blood sugar and are used for weight loss.
- How Effective Are Glp-1 Drugs? Initially, they show promise, but their long-term effectiveness is less than surgical options.
- Why Choose Obesity Surgery? it offers more ample and lasting weight loss compared to medication.
- What Are The drawbacks Of Long-Term Glp-1 Use? High costs and side effects can make consistent use challenging.
- Am I A Candidate For Surgery? Those with a Bmi over 35 or who haven’t seen results with drugs might consider surgery.
- What Risks Does Surgery Involve? Like all surgeries, there are risks, but the benefits often outweigh them.
Have you considered any weight loss treatments? Which method do you think is more sustainable in the long run? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below.
For a person with a BMI over 30, what are the potential long-term benefits and drawbacks of choosing weight loss medication, rather than obesity surgery, to help them manage their weight?
Obesity Surgery vs. Medication: Unveiling the Dramatic Weight Loss Effect
Battling obesity can be a challenging journey, with a myriad of options available.Understanding the differences and potential outcomes of obesity surgery versus weight loss medication is crucial. This article dives deep into the comparative effectiveness of these treatments, focusing on the potential for a meaningful weight loss effect.We’ll explore the benefits, drawbacks, and who might be the best candidate for each approach, helping you make informed decisions on your path to better health.
Understanding the Impact of Obesity
Obesity, defined by a high Body Mass Index (BMI), is a significant global health concern.The World Health Association (WHO) highlights the numerous health consequences associated with being overweight or obese.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Obesity can lead to heart disease,including cardiopathies and strokes.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A strong correlation exists between obesity and the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: Conditions like osteoarthritis are more prevalent in individuals with obesity.
- Certain Cancers: Increased risk of developing various cancers, including endometrial, breast, and colon cancer.
Addressing obesity is therefore crucial. The following sections further outline your treatment options and their associated effects.
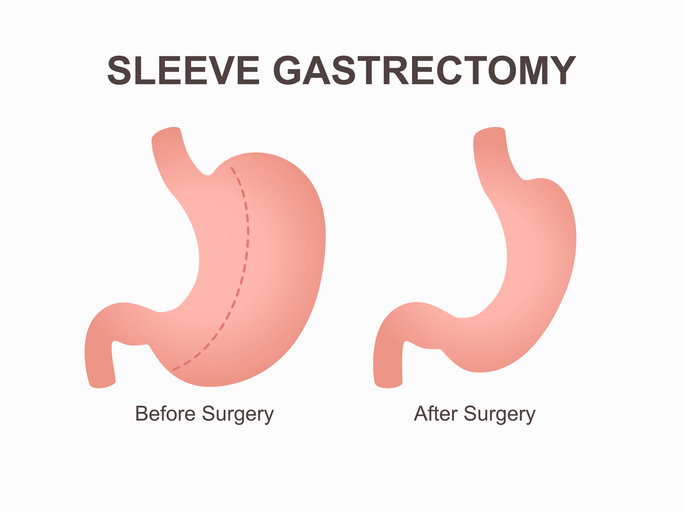
Obesity Surgery: A Powerful Intervention
Bariatric surgery, commonly known as obesity surgery, involves various procedures designed to reduce food intake or absorption. These surgeries can lead to significant and sustained weight loss. Key bariatric surgery procedures include:
- Gastric Bypass: Alters the digestive system by creating a smaller stomach pouch.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: removes a portion of the stomach, creating a smaller, sleeve-shaped stomach.
- Adjustable Gastric Banding: A band is placed around the upper stomach to restrict food intake.
weight loss surgery can result in considerable weight loss, often representing a considerable percentage of excess weight. The extent of weight loss varies based on the procedure, individual lifestyle changes, and adherence to postoperative guidelines.
The “5x Weight Loss Effect” and Surgery
While the exact “5x weight loss effect” isn’t a standardized metric, it signifies a strong comparison point showing the potential for greater weight reduction with bariatric surgery. Patients who undergo surgical interventions frequently enough experience considerably more weight loss compared to those relying solely on medication and lifestyle changes. This is partly due to the dramatic impact on caloric intake and nutrient absorption that bariatric procedures have.
| Feature | Obesity Surgery | Weight Loss Medication |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Alters digestion and/or absorption | Suppresses appetite or affects nutrient absorption |
| Typical Weight Loss | Significant (frequently enough 50-80% of excess weight) | Moderate (potentially 5-15% of total body weight) |
| Long-Term Effectiveness | Generally high, with lifestyle changes | Variable, often reliant on continuous use |
| Invasiveness/Risks | Higher (surgical procedure, potential complications) | Lower (potential side effects) |
Weight Loss Medication: A Complementary Approach
weight loss medication can be a useful tool when combined with a comprehensive approach to weight management. These medications function in various ways,including:
- Appetite suppression: Making you feel less hungry.
- Reduced fat absorption: Blocking the absorption of dietary fat.
- Increasing metabolism: Speeds up your body’s ability to lose weight.
Medications for obesity are typically prescribed and require monitoring by a healthcare professional. Unlike surgical interventions, the weight loss from medication may be more moderate, but for suitable candidates can prove beneficial.
Choosing the Right Path: Surgery vs.Medication
Determining the best treatment option requires a thorough assessment by a healthcare provider.Several factors are considered, including the individual’s:
- BMI
- co-existing Health Conditions: e.g., diabetes and cardiovascular issues.
- Lifestyle and Eating Habits
- Commitment to Change
Obesity surgery might be suggested for peopel who have a very high BMI or other serious health issues. Weight loss medication can be an option for those with slightly lower BMIs or as adjunctive therapy combined with diet and exercise. These treatments are not alternatives, but complimentary. it’s essential to discuss all pros, cons, and potential adverse effects with your doctor. Always prioritize your personal health history.
Real-World Example: A Case Study
- Patient Age and History: A 45-year-old woman with a BMI of 42 and recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes.
- Treatment: Decided on a Gastric Sleeve after proper consideration.
- Weight Loss Result: Within 18 months,she lost 70% of her excess weight and her diabetes whent into remission.
The Importance of ongoing weight Management
Whether you choose surgery or medication, long-term success hinges on enduring lifestyle adjustments. This includes consistent exercise, a balanced diet, and regular follow-up with medical professionals. The key is recognizing that both treatments are avenues for improvement and not necessarily a swift fix to the problem of obesity.
Practical Tips for Weight Loss Success
- Follow a balanced diet. Choose whole, unprocessed foods and limit sugary drinks.
- Stay active Make physical activity a regular part of your routine.
- Stay Hydrated. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Seek support. Engage with a support group or counselor.
