Underwater Volcano Eruption: Axial Seamount’s Impending Activity
An underwater volcano, known as Axial Seamount, located approximately 300 miles off the coast of Oregon, appears to be on the verge of an eruption. Scientists are closely monitoring the seismic activity and structural changes to forecast the impending event, aiming to refine eruption prediction models. This remote location presents a unique opportunity to study volcanic processes without posing a direct threat to human populations.
Axial Seamount: A Volcano Under Scrutiny
For decades, scientists have kept a watchful eye on Axial Seamount. A recent surge in activity, characterized by increased earthquake frequency and the volcano’s swelling structure, suggests that an eruption could occur anytime between now and the end of the year, according to experts at Oregon State University. This monitoring is crucial for understanding the behavior of underwater volcanoes.
Decoding the Signals: Earthquake Swarms and Swelling Seafloor
Researchers from Oregon State University, the University of washington, and the University of North Carolina Wilmington are employing a network of seafloor sensors to listen to Axial Seamount. Instruments recorded over 1,000 earthquakes daily during late March and early April.The seafloor’s steady rise indicates magma accumulation, a key precursor to volcanic eruptions.
Did You Know? Axial Seamount’s last eruption in 2015 produced a lava flow approximately 450 feet thick—about two-thirds the height of Seattle’s Space Needle!
Low Risk,High Scientific Value
Unlike some Hawaiian volcanoes,an eruption of Axial Seamount poses no direct threat to humans because the peak is submerged about a mile deep underwater and located hundreds of miles offshore. Even a important eruption would likely be undetectable on land.
“There’s no explosion or anything, so it would really have no impact on people,” one expert stated. “Even if you were out on a boat right over the seamount when it’s erupting, you probably would never know it.”
A Spectacle Undersea: Past Eruptions of Axial Seamount
axial Seamount’s eruptions have been remarkable events. During the 2015 eruption, an enormous volume of magma was released, creating considerable lava flows. This underscores the scale of activity occurring beneath the ocean’s surface.
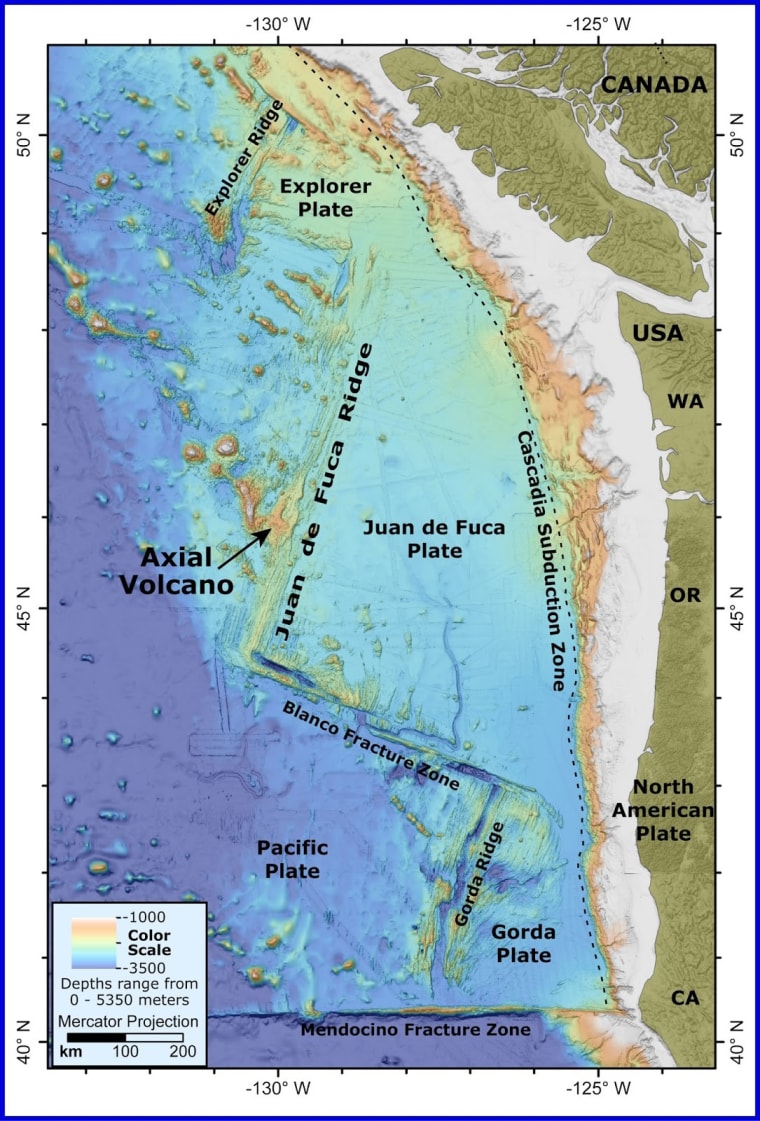
Geological Hotspot: The Unique Setting of Axial Seamount
Axial Seamount sits on a hotspot where molten rock rises from Earth’s mantle. Its location on the boundary between the Pacific and Juan de Fuca plates, which are moving apart, further fuels volcanic activity and generates new ocean crust.
Predicting the Unpredictable: Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions
Scientists are analyzing patterns from past eruptions in 1998, 2011, and 2015 to improve eruption forecasting.However, predicting volcanic activity remains complex, with volcanoes exhibiting unpredictable behavior and diverse warning signs.
“It’s much harder than forecasting the weather, even though the weather is a very tough thing to forecast already,” explained a professor of geophysics at the University of North Carolina Wilmington. “There’s still so much that we don’t understand about what triggers eruptions and how magma moves around underneath the Earth’s surface.”
Axial Seamount: A Natural Laboratory for Volcanology
Axial Seamount provides an ideal setting for refining eruption forecasting techniques. The absence of direct human impact allows scientists to test models and predictions without the high stakes associated with populated areas.
Pro Tip: Keep an eye on scientific publications and university research pages for the latest updates on Axial Seamount’s activity. These sources often provide detailed data and analysis.
Future Trends in Volcanic Monitoring and Prediction
Here are some potential future trends based on current research and technology:
- Improved Sensor Technology: Development of more sensitive and durable underwater sensors to detect subtle changes in volcanic activity.
- AI and Machine Learning: Implementation of artificial intelligence algorithms to analyze vast datasets and identify patterns indicative of impending eruptions.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: Enhanced real-time data processing and visualization tools to provide timely information to researchers and perhaps, in the future, to the public.
- Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs): Increased use of AUVs for close-range monitoring and sample collection near active volcanic sites.
Case study: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii
The 2018 eruption of Kilauea serves as a stark reminder of the unpredictable nature of volcanic activity. Despite extensive monitoring, the scale and impact of the eruption exceeded initial expectations, highlighting the need for continuous improvement in forecasting methods.
Comparative Analysis: Axial Seamount vs. Other Volcanic Regions
| Feature | Axial Seamount | Kilauea (Hawaii) | Mount St. Helens (Washington) |
|---|---|---|---|
| location | Offshore, deep underwater | On land, island | On land, continental |
| Eruption Style | Effusive, fluid lavas | Effusive to explosive | Explosive |
| Human Impact | Minimal | Significant | Potentially high |
| Monitoring Difficulty | High (underwater) | Moderate | Relatively low |
Reader Questions to Spark Engagement
Here are some questions to encourage further discussion:
- How can advancements in underwater sensor technology improve our understanding of submarine volcanoes like Axial Seamount?
- What role can international collaboration play in monitoring and studying volcanic activity across the globe?
- What are the ethical considerations involved in long-term volcanic forecasting, especially when dealing with potentially disruptive events?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Axial Seamount?
Axial Seamount is an active underwater volcano located about 300 miles off the coast of Oregon.
When could Axial seamount erupt?
Current forecasts suggest it could erupt anytime between now and the end of the year.
Is there any danger to humans from an Axial Seamount eruption?
No, due to its remote location and depth, an eruption poses no direct threat to humans.
Why is Axial Seamount crucial for scientific study?
It provides a safe habitat to test and refine volcanic eruption forecasting models.
