“`html
Sperm Under Siege: Can a Common Parasite really Decapitate Human Sperm?
Alarming research suggests a common parasite, Toxoplasma gondii, could be a hidden culprit behind plummeting male fertility rates globally. A groundbreaking April 2025 study revealed that this parasite can directly damage human sperm, even causing them to “lose their heads” upon contact.
Male fertility has been declining for decades. Studies show sperm counts and quality have decreased since the 1940s, with male infertility rates climbing nearly 80% between 1990 and 2019. Now, scientists are investigating whether toxoplasmosis plays a significant role.
The Toxoplasmosis Threat: More Than Just Cat litter
Toxoplasma gondii isn’t just a concern for cat owners. This single-celled parasite lurks in various places,posing a risk to a large portion of the global population.
- Contaminated Food: Uncooked meat, unwashed fruits, and shellfish can harbor infectious parasite eggs.
- Environmental Exposure: Infected cats shed Toxoplasma eggs in their feces, contaminating soil and water.
Between 30% and 50% of the world’s population is estimated to be permanently infected with Toxoplasma. While many experience mild or no symptoms initially, the parasite forms dormant cysts in the brain, heart, and muscle tissue, possibly reactivating later in life.
How Toxoplasma Targets Male Reproductive Organs
toxoplasma can spread to almost every organ in the body. Evidence suggests that it can also target male reproductive organs, including the testes and prostate.
Studies on animals and humans reveal concerning links:
- Testicular Infection: The parasite has been found in the testes of both immunocompromised and healthy individuals.
- Prostate Cysts: Research indicates that Toxoplasma can form cysts in the prostate.
- Semen Contamination: The parasite has been detected in the ejaculate of various animals, including humans, raising concerns about sexual transmission.
Did You Know? Studies show that men infected with Toxoplasma are more likely to have semen anomalies and infertility issues, although not all studies confirm this association.
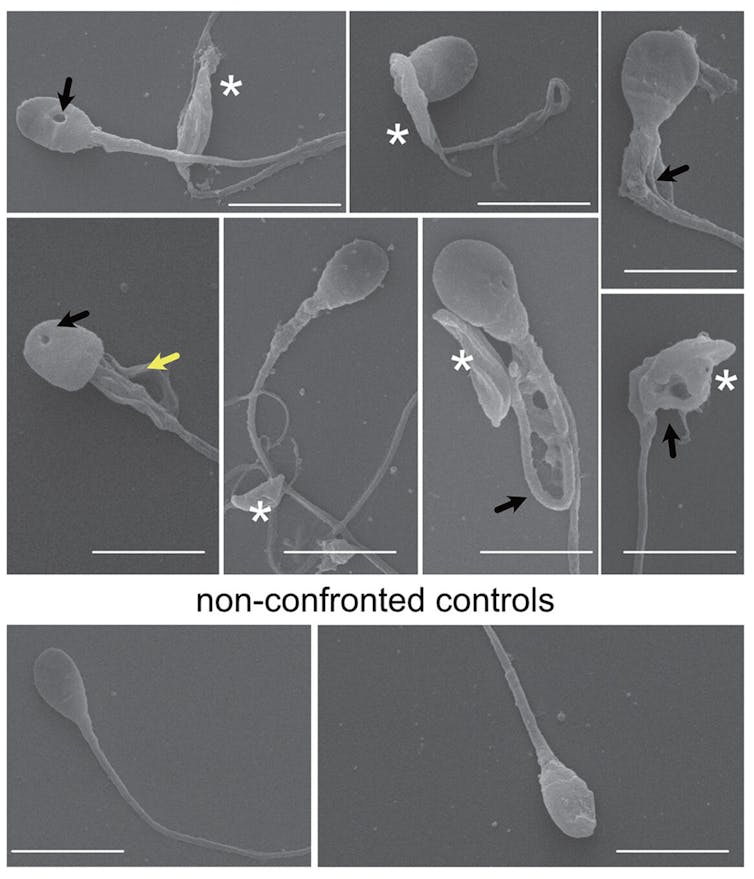
The “Decapitation” Effect: Direct Sperm Damage
The recent 2025 study shed light on the direct impact of Toxoplasma on human sperm.Researchers observed that within minutes of exposure, a significant percentage of sperm cells were “beheaded.” Moreover, surviving sperm were frequently enough twisted, misshapen, or riddled with holes.
Beyond direct contact, the parasite can trigger chronic inflammation in the male reproductive tract, further compromising sperm production and function.
Pro tip: While the link isn’t definitive, reducing Toxoplasma exposure may be a proactive step toward better sperm health.
Table: Comparing Sperm Health Factors
| Factor | Impact on Sperm Health |
|---|---|
| Toxoplasmosis | Potential sperm decapitation, malformation, and reduced count. |
| Obesity & Poor Diet | Linked to decreased sperm quality and hormone imbalances. |
| Environmental Toxins | Associated with sperm damage and reduced fertility. |
| Infectious Diseases (e.g. Gonorrhea, Chlamydia) | Can cause inflammation and blockages in the reproductive tract. |
It’s crucial to note that the connection between toxoplasmosis and male infertility is still under investigation.Some data indicates that rising male infertility rates are not related to toxoplasmosis.
Protecting Yourself: Prevention is Key
Regardless of its exact impact on fertility, preventing toxoplasmosis is vital. Infection during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage or birth defects, and it can be life-threatening for individuals with weakened immune systems. Plus, Toxoplasma is a leading cause of foodborne illness deaths in the U.S.
Here’s how to minimize your risk:
- Practice Safe Food Handling: Cook meat thoroughly, wash fruits and vegetables, and avoid raw shellfish, raw milk, and untreated water.
- Take Care of Your Cat: Promptly clean the litter box and wash your hands thoroughly afterward.
Evergreen Insights on Male Fertility
Maintaining optimal sperm health involves a holistic approach. Besides minimizing exposure to potential threats like Toxoplasma, consider these evergreen strategies:
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, and adequate sleep are crucial.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive alcohol Consumption: These habits can negatively impact sperm quality and count.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt hormone balance and affect fertility.
- Limit Exposure to Environmental Toxins: Reduce contact with pesticides,heavy metals,and other harmful chemicals.
- Consider Fertility Supplements: Consult with a healthcare professional about supplements like zinc, selenium, and CoQ10, which may support sperm health.
frequently Asked Questions About Toxoplasmosis and Male Fertility
