“`html
Breakthrough cancer Treatment Uses LED Light and Tin to Kill Cells
Table of Contents
- 1. Breakthrough cancer Treatment Uses LED Light and Tin to Kill Cells
- 2. A New Era in Cancer Therapy
- 3. How It Works: Harnessing Light and Tin
- 4. Key Findings from the Recent Study
- 5. Future Directions and Accessibility
- 6. Understanding Cancer Treatment Options
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions About this New Cancer Treatment
- 8. What specific wavelengths of LED light have shown the most promise in selectively targeting and destroying cancer cells, according to the UT Austin research?
- 9. groundbreaking Study: UT Austin Research Demonstrates LED Light’s Precision in Targeting Cancer Cells While Preserving Healthy Tissue
- 10. the Science Behind Light-Activated Cancer Therapy
- 11. Understanding Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) and its Evolution
- 12. How UT Austin’s Research Improves PDT
- 13. Cancer Types Showing Promise with LED-Based PDT
- 14. The Role of LED Technology: Beyond Illumination
Austin, Texas – A groundbreaking new approach to cancer treatment, developed through a collaborative effort between the University of Texas at Austin and the University of Porto in Portugal, is showing remarkable promise. This innovative therapy combines the precision of LED light with the unique properties of tin nanoflakes to selectively neutralize cancer cells while safeguarding healthy tissue.
A New Era in Cancer Therapy
The research, born from the UT Austin Portugal Program, addresses critical limitations of current cancer treatments. Traditional methods like chemotherapy frequently enough come with debilitating side effects and can impact healthy cells alongside cancerous ones. This new technique aims to overcome these challenges by offering a more targeted and less invasive solution.
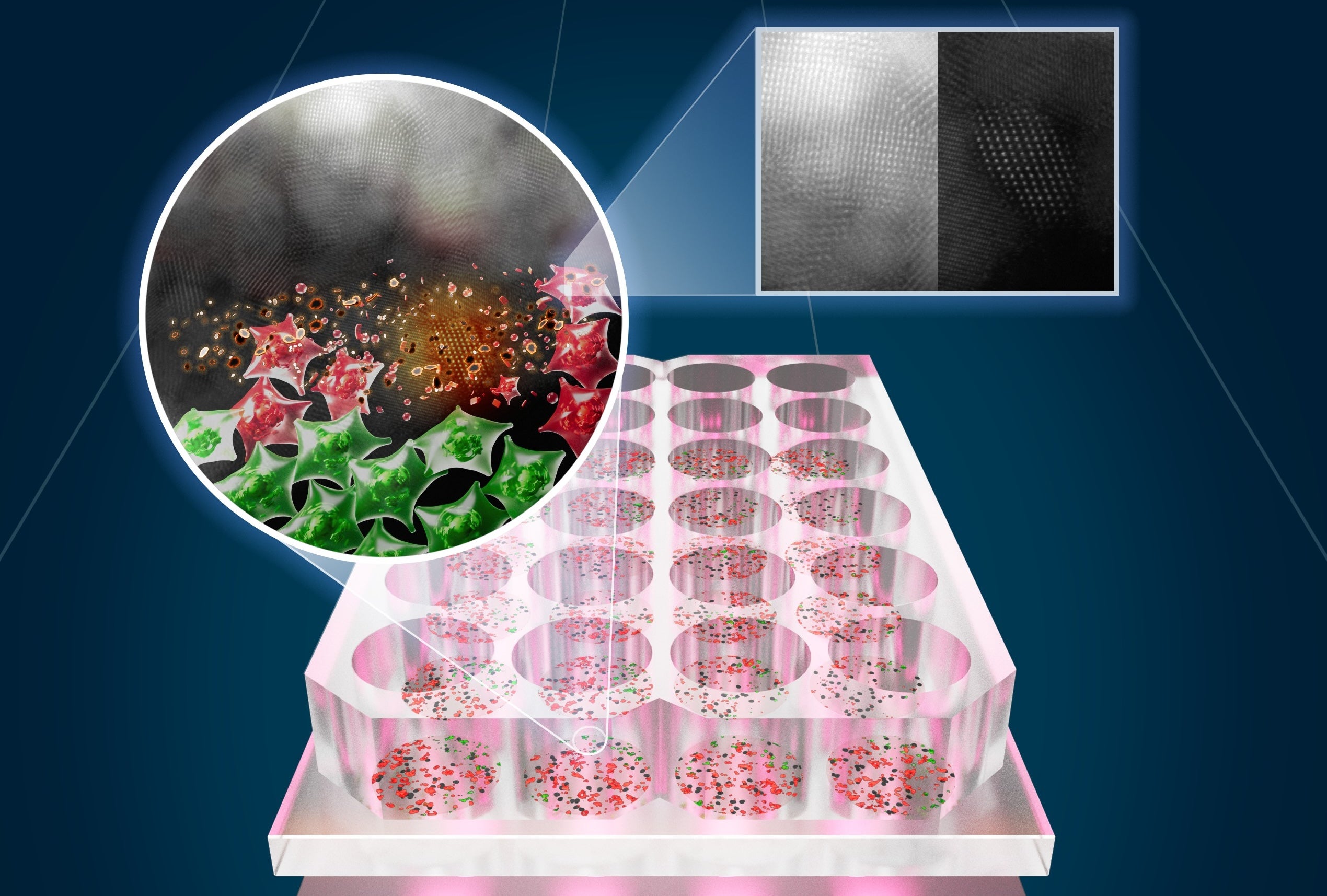
 SnOx nanoflakes with LED light” width=”1024″ height=”683″>
SnOx nanoflakes with LED light” width=”1024″ height=”683″>How It Works: Harnessing Light and Tin
At the heart of this advancement lies the use of “SnOx nanoflakes” – microscopic particles containing tin. When activated by LED light, these nanoflakes generate heat, precisely targeting and destroying cancer cells. Unlike conventional laser-based photothermal therapy, this method utilizes readily available and cost-effective LED technology, reducing both financial burdens and the need for specialized equipment. According to the National Cancer Institute, in 2023, there were approximately 1.9 million new cancer cases diagnosed in the united States alone, highlighting the urgent need for innovative treatment options.
Key Findings from the Recent Study
A recent study published in ACS Nano demonstrated the effectiveness of this treatment against both colorectal and skin cancer cells. Researchers observed up to 92% of skin cancer cells and 50% of colorectal cancer cells being eliminated within just 30 minutes of exposure, with no discernible harm to healthy skin cells. This selectivity is a crucial aspect of the therapy’s potential.
| Cancer Type | Cancer Cell Kill Rate (30 minutes) | Impact on Healthy Cells |
|---|---|---|
| skin Cancer | Up to 92% | None observed |
| Colorectal cancer | Up to 50% | None Observed |
Future Directions and Accessibility
The research team, led by Jean Anne Incorvia and Artur Pinto, is now focused on refining the technology and expanding its applications. They aim to further investigate the interaction between light and heat at the cellular level, and explore alternative materials to enhance the treatment’s effectiveness. A key goal is to develop portable devices that would allow for convenient, at-home treatment, notably for skin cancers, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits.
“Our ultimate goal is to make this technology available to patients everywhere, especially places where access to specialized equipment is limited, with fewer side effects and lower cost,” stated Pinto. “for skin cancers in particular, we envision that one day, treatment could move from the hospital to the patient’s home.”
Did you know? Photothermal therapy, the underlying principle of this new treatment, has been explored for decades, but challenges with cost, precision, and safety have hindered its widespread adoption until now.
Pro Tip: Early detection is crucial in successful cancer treatment. Regular check-ups and screenings can substantially improve outcomes.
Understanding Cancer Treatment Options
Cancer treatment is a rapidly evolving field. While surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy remain standard approaches, emerging therapies like photothermal therapy are offering new hope to patients. These innovative treatments often focus on minimizing side effects and improving the quality of life for those battling cancer. the National Cancer Institute provides extensive resources on various cancer types and treatment options: https://www.cancer.gov/
Frequently Asked Questions About this New Cancer Treatment
- What is photothermal therapy? It’s a cancer treatment that uses light to generate heat, selectively destroying cancer cells.
- How does this treatment differ from chemotherapy? This therapy targets cancer cells directly with light and tin nanoflakes, minimizing harm to healthy cells, unlike chemotherapy’s systemic effects.
- Is this treatment currently available to patients? While promising, this treatment is still in the research phase and not yet widely available.
- What are SnOx nanoflakes? These are microscopic particles containing tin that become activated by LED light, generating heat to kill cancer cells.
- What are the potential benefits of using LED light instead of lasers? LEDs are more affordable, accessible, and potentially safer than lasers for this type of therapy.
- What types of cancer has this treatment been tested on? Initial studies have shown effectiveness against colorectal and skin cancer cells.
- What is the UT Austin Portugal Program? A collaborative partnership fostering scientific and technological advancements between the University of Texas at Austin and Portugal.
What are your thoughts on this exciting new development in cancer treatment? Share your comments below!
What logistical challenges did the UT Austin team face regarding hydrogen refueling during the 365-mile road trip,and what does this indicate about the current state of hydrogen infrastructure in Texas?
Embarking on a 365-Mile Texas Adventure: The Journey of a Hydrogen-Powered Road Trip by UT Austin
The UT Austin Hydrogen Road Trip: A Pioneering Initiative
the university of Texas at Austin recently completed a groundbreaking 365-mile road trip across Texas,powered entirely by hydrogen fuel cell technology. This isn’t just a presentation of alternative fuel; it’s a meaningful step towards evaluating the feasibility of long-distance hydrogen vehicle travel and building out the necessary hydrogen infrastructure in the state. The journey,undertaken in a modified Toyota Mirai,aimed to assess real-world performance,identify logistical challenges,and gather data crucial for future sustainable transportation solutions. This UT Austin hydrogen project represents a commitment to reducing carbon emissions and fostering innovation in the energy sector.
The 365-mile route was strategically chosen to test the hydrogen vehicle’s range and the availability of hydrogen refueling stations in Texas. The trip began and ended in Austin, with stops planned around existing, albeit limited, hydrogen fueling infrastructure.
* Key Route Highlights: The route included stretches of highway and city driving,simulating typical road trip conditions. Specific cities visited included Waco, Dallas, and Fort Worth.
* Refueling Challenges: A primary challenge was the sparse network of hydrogen stations.The team meticulously planned refueling stops,frequently enough requiring precise timing and coordination. This highlighted the urgent need for expanded hydrogen fuel cell vehicle (FCEV) infrastructure.
* Vehicle Modifications: The Toyota Mirai underwent modifications to enhance data collection capabilities. Sensors monitored fuel consumption,performance metrics,and environmental conditions throughout the journey.
* Real-Time Monitoring: A dedicated team tracked the vehicle’s progress and performance in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments and data analysis.
The technology Behind the Trip: Hydrogen Fuel Cells Explained
The core of this adventure lies in hydrogen fuel cell technology. Unlike gasoline-powered vehicles, FCEVs don’t burn fuel. Instead, they combine hydrogen with oxygen to produce electricity, with water as the only emission.
* How Hydrogen Fuel Cells Work: Hydrogen gas is stored in high-pressure tanks within the vehicle. It then flows into the fuel cell stack, where it reacts with oxygen from the air. This reaction generates electricity, powering the electric motor.
* Benefits of Hydrogen Fuel Cells:
* Zero Tailpipe Emissions: Only water vapor is emitted, contributing to cleaner air.
* High Efficiency: Fuel cells are more efficient than internal combustion engines.
* Fast Refueling: Refueling with hydrogen is comparable in time to filling a gasoline tank.
* Hydrogen Production Methods: The environmental impact of hydrogen fuel depends on how it’s produced.Methods include:
* Steam Methane Reforming (SMR): The most common method, but it releases carbon dioxide.
* Electrolysis: Using electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. When powered by renewable energy, this is a truly green hydrogen solution.
* Biomass Gasification: Converting organic matter into hydrogen.
Data Collection and Analysis: Insights from the Road
The UT Austin team collected a wealth of data during the 365-mile trip, providing valuable insights into the performance of hydrogen vehicles and the challenges of long-distance travel.
* Fuel Efficiency: Data revealed the vehicle’s fuel efficiency under various driving conditions. This facts is crucial for optimizing vehicle design and improving range.
* Infrastructure Assessment: The trip highlighted the critical need for more hydrogen refueling stations, especially along major transportation corridors.
* Performance in Texas Climate: Texas’s hot climate presented unique challenges, impacting fuel cell performance and cooling requirements.
* Cost Analysis: The team analyzed the cost of hydrogen fuel compared to gasoline, considering factors like production, transportation, and dispensing. This is vital for assessing the economic viability of hydrogen vehicles.
The Future of Hydrogen in Texas: Expanding the Infrastructure
The UT Austin road trip serves as a catalyst for expanding hydrogen infrastructure in Texas and accelerating the adoption of hydrogen-powered transportation.
* State and Federal Funding: Increased investment in hydrogen infrastructure is essential. Both state and federal funding programs are available to support the development of hydrogen refueling stations and production facilities.
* Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between government, industry, and research institutions is crucial for driving innovation and scaling up hydrogen technology.
* hydrogen Hubs: The development of regional hydrogen hubs – centralized locations for hydrogen production, storage, and distribution – will be key to building a robust hydrogen economy. Texas is actively pursuing funding to become a major hydrogen hub.
* Renewable Hydrogen Production: Focusing on renewable hydrogen production through electrolysis powered by solar and wind energy will maximize the environmental benefits of hydrogen fuel.
Benefits of Hydrogen fuel Cell Technology
Beyond the environmental advantages, hydrogen fuel cell technology offers several compelling benefits:
* Energy Security: Reduces reliance on foreign oil.
* Economic Growth: Creates new jobs in the hydrogen industry.