Mars’s “Inca City” and Beyond: How New Discoveries are Reshaping Our Understanding of the Red Planet
Could Mars harbor secrets to understanding the origins of life, and even pave the way for human colonization? Recent images from NASA’s Perseverance rover suggest the Red Planet is far more geologically complex – and potentially more hospitable – than previously imagined. The discovery of formations resembling ancient ruins, coupled with evidence of a remarkably ancient past, is forcing scientists to rethink everything we thought we knew about Mars, and accelerating the timeline for potential future missions.
The Illusion of Ruins: Unraveling the Martian “Inca City”
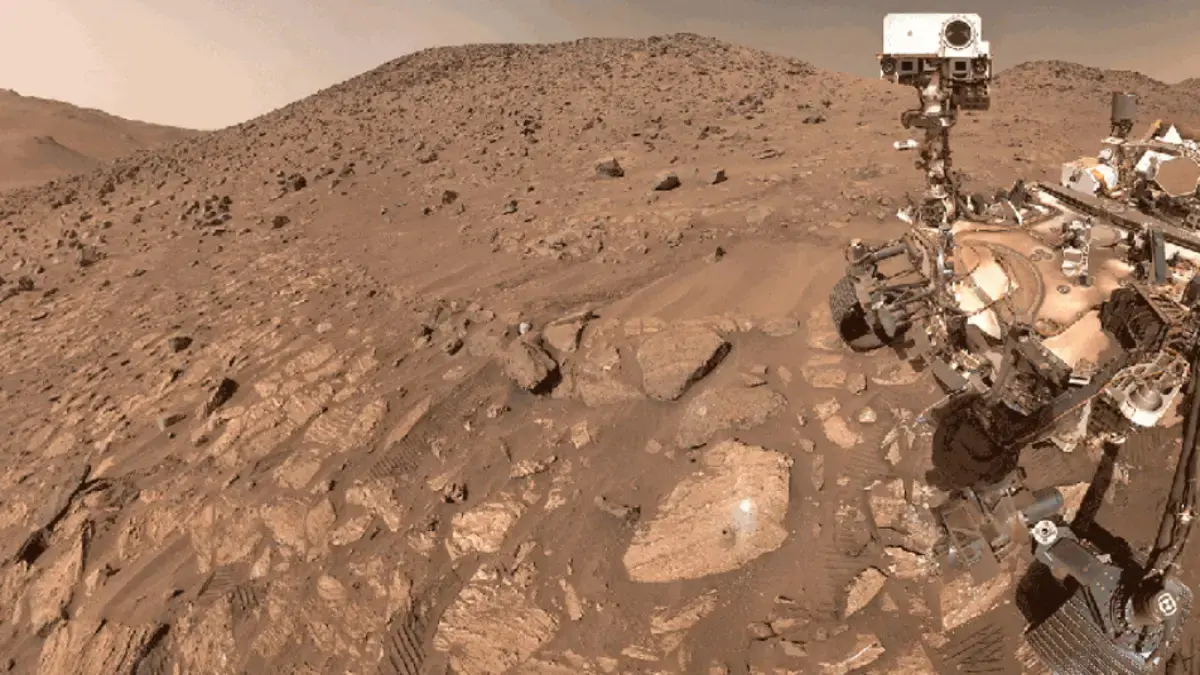
The images causing a stir depict a region in the Angustus Labyrinthus, near the South Martian Pole, dubbed the “Inca city” due to its striking geometric patterns. First detected by the Mariner 9 probe in the 1970s, the new high-resolution images from Perseverance reveal an unprecedented level of detail. However, the European Space Agency (ESA) has clarified that these aren’t the remnants of a lost Martian civilization. Instead, they are the result of ancient asteroid impacts that fractured the planet’s crust.
These fractures allowed magma to rise, forming erosion-resistant dikes. Over billions of years, differential weathering exposed these structures, creating the illusion of ruins. This process highlights the power of geological forces to create patterns that mimic intelligent design, a phenomenon observed on Earth as well.
Silver Mountain and the Dawn of Martian Time
Beyond the intriguing formations, Perseverance has unearthed evidence of Mars’s incredibly ancient past. The rock dubbed “Silver Mountain” is estimated to be around 4 billion years old. This discovery is crucial because it provides a window into the planet’s early climatic and geological conditions. Analyzing its composition could reveal whether Mars once possessed the necessary ingredients for microbial life to emerge.
Did you know? 4 billion years ago, Earth was still undergoing its own intense period of bombardment and geological upheaval. Studying Silver Mountain offers a unique opportunity to compare the early evolution of two potentially habitable planets.
The Mystery of St. Pauls Bay: A Clue to Martian Processes
Another puzzling formation, St. Pauls Bay, consists of hundreds of small, dark gray spheres. Scientists are still investigating its origin, but suspect multiple geological processes were at play. The composition and arrangement of these spheres could provide insights into the types of volcanic activity or sedimentary processes that occurred on ancient Mars.
Implications for Future Missions: Beyond Exploration, Towards Habitation
These discoveries aren’t just academic exercises. NASA and ESA emphasize that understanding Mars’s complex geology is essential for planning future manned missions. The data gathered by Perseverance will inform decisions about landing site selection, resource utilization, and potential hazards.
Resource Mapping and In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU)
One of the most exciting prospects is the potential for In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU) – using Martian resources to create fuel, water, and building materials. Understanding the distribution of water ice, minerals, and other valuable resources is paramount. The geological formations identified by Perseverance could indicate areas rich in these resources, reducing the cost and complexity of long-duration missions.
Expert Insight: “The data from Perseverance is fundamentally changing our understanding of Mars’s geological history,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a planetary geologist at the California Institute of Technology. “It’s not just about finding evidence of past life; it’s about understanding the planet’s potential to support future human settlements.”
Assessing Land Stability and Hazard Mitigation
The fractured crust and complex geological features also present challenges. Future missions will need to carefully assess land stability and mitigate potential hazards like landslides or dust storms. Perseverance’s data will help engineers design robust habitats and infrastructure that can withstand the harsh Martian environment.
The Expanding Search for Life: A New Era of Martian Exploration
The discoveries made by Perseverance are fueling a renewed sense of optimism in the search for life beyond Earth. While the “Inca city” may not be a lost civilization, the evidence of a potentially habitable past – and the ongoing geological activity – suggests that Mars may still hold secrets waiting to be uncovered.
The Role of Sample Return Missions
The next crucial step is the Mars Sample Return campaign, a joint effort between NASA and ESA to bring samples collected by Perseverance back to Earth for detailed analysis. These samples will undergo rigorous testing in state-of-the-art laboratories, potentially revealing definitive evidence of past or present life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ISRU and why is it important for Mars missions?
ISRU, or In-Situ Resource Utilization, refers to the practice of using resources found on Mars – like water ice and minerals – to create essential supplies like fuel, water, and building materials. This reduces the need to transport these resources from Earth, significantly lowering the cost and complexity of long-duration missions.
How did the “Inca city” formations actually form?
The formations are the result of ancient asteroid impacts that fractured the Martian crust. Magma then rose through these fractures, forming erosion-resistant dikes. Over billions of years, differential weathering exposed these structures, creating the illusion of ruins.
What is the significance of the 4-billion-year-old rock, Silver Mountain?
Silver Mountain provides a window into Mars’s early geological and climatic conditions. Analyzing its composition could reveal whether the planet once had the necessary ingredients to support microbial life.
What are the biggest challenges facing future manned missions to Mars?
Challenges include radiation exposure, the psychological effects of long-duration space travel, ensuring a reliable life support system, and mitigating potential hazards related to the Martian environment, such as dust storms and land instability.
The exploration of Mars is entering a new golden age. With each new discovery, we move closer to answering fundamental questions about our place in the universe and the possibility of life beyond Earth. The future of Martian exploration is bright, and the secrets of the Red Planet are slowly but surely being revealed.
What are your predictions for the future of Mars exploration? Share your thoughts in the comments below!