China’s Food Safety Crisis: Beyond Isolated Incidents, a Looming Tech Transformation?
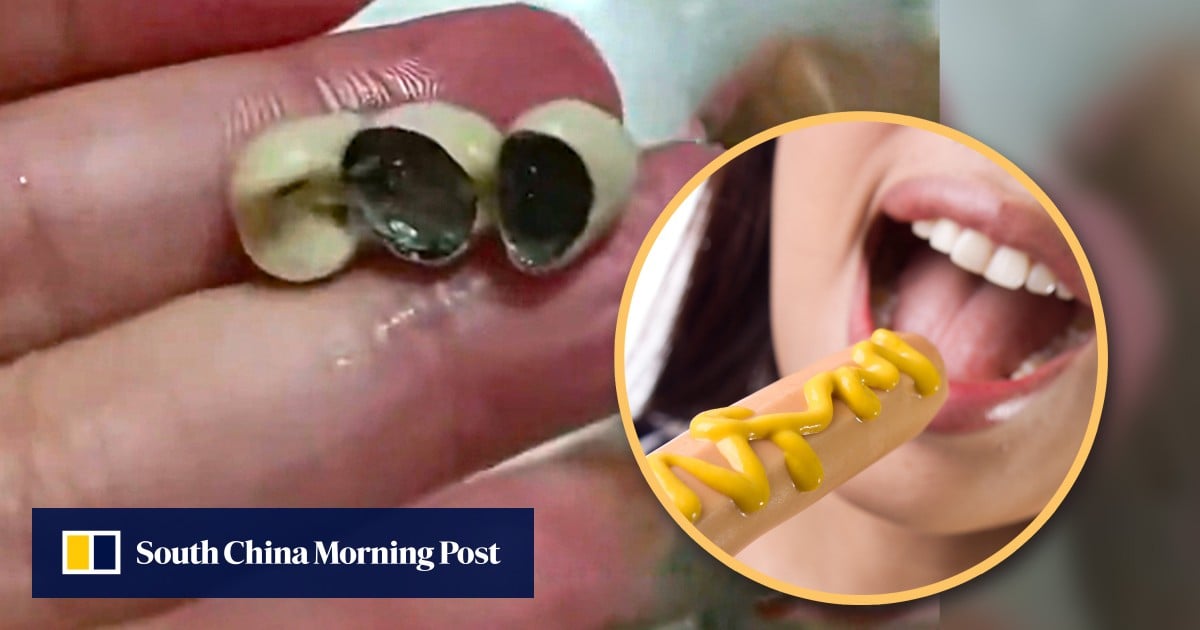
Recent reports of human teeth – both artificial and potentially real – turning up in food across China aren’t just shocking; they signal a systemic vulnerability in the nation’s vast and complex food supply chain. From sausages in Jilin province to dim sum in Guangdong and even a Sam’s Club cake in Shanghai, these discoveries, occurring within a matter of days, aren’t random. They’re a flashing warning light demanding a radical overhaul, and the solution may lie not just in stricter regulations, but in the rapid adoption of advanced traceability technologies.
The Disturbing Pattern: A Breakdown of Recent Cases
The incidents, beginning on October 13th, quickly gained traction on Chinese social media. A mother in Jilin province discovered three artificial teeth in a sausage purchased for her child. Simultaneously, a father in Dongguan found two teeth in his dim sum from Sanjin Soup Dumplings. The following day, a customer at a Shanghai Sam’s Club unearthed an artificial tooth, complete with a metal screw, in a jujube and walnut cake. While investigations are underway, the sheer number of cases within such a short timeframe raises serious questions about quality control and potential lapses in manufacturing processes. The fact that a retailer like Sam’s Club, generally perceived as a purveyor of higher-quality goods, was involved is particularly unsettling.
Beyond Manufacturing: The Role of Supply Chain Complexity
Attributing blame solely to manufacturers is an oversimplification. China’s food supply chain is notoriously fragmented, involving numerous suppliers, processors, distributors, and retailers. This complexity creates ample opportunities for contamination or, in these cases, the accidental (or deliberate) inclusion of foreign objects. Sanjin Soup Dumplings, for example, stated its dumplings are supplied directly from headquarters, yet couldn’t explain the origin of the teeth – highlighting a gap in traceability even within a seemingly controlled system. This lack of end-to-end visibility is a critical weakness.
The Rise of Food Traceability Technologies: A Potential Solution
The current crisis is accelerating the demand for, and investment in, **food traceability** systems. For years, China has been piloting various technologies, but widespread adoption has been slow. Now, the pressure is mounting. These technologies fall into several key categories:
- Blockchain Technology: Offering an immutable record of a product’s journey from farm to table, blockchain can verify authenticity and pinpoint the source of contamination.
- RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) and NFC (Near-Field Communication): These technologies allow for real-time tracking of products throughout the supply chain, providing detailed information on location, temperature, and handling.
- QR Codes & Digital Labels: While currently used for basic information, advancements are enabling dynamic QR codes that reveal a product’s full history upon scanning.
- AI-Powered Visual Inspection: Artificial intelligence is being deployed to automatically detect foreign objects and quality defects during food processing.
These aren’t futuristic concepts; they’re being implemented – albeit unevenly – across the globe. The European Union’s food traceability regulations, for example, are significantly more stringent than those currently in place in China. Learn more about EU food traceability standards.
The Data Challenge: Integrating Siloed Systems
The biggest hurdle isn’t the technology itself, but the integration of these systems. Currently, data is often siloed within individual companies, making it difficult to create a truly comprehensive and transparent supply chain. Government initiatives promoting data sharing and standardization are crucial. Furthermore, consumer acceptance of data collection and privacy concerns must be addressed. The success of these technologies hinges on building trust and ensuring data security.
Looking Ahead: Predictive Analytics and Proactive Food Safety
The future of food safety in China – and globally – extends beyond simply tracking products. The integration of predictive analytics, powered by machine learning, will allow authorities to identify potential risks *before* they materialize. By analyzing data from various sources – including weather patterns, supplier performance, and consumer reports – these systems can predict outbreaks of contamination and proactively intervene. This shift from reactive to proactive food safety management is essential for building consumer confidence and preventing future crises. The recent incidents underscore the need for a more holistic approach to food safety, one that leverages technology, data, and collaboration across the entire supply chain.
What role do you see for consumer-facing apps in verifying food safety and provenance? Share your thoughts in the comments below!