Israeli Demolition of Family home in West Bank Fuels Collective Punishment Accusations
Table of Contents
- 1. Israeli Demolition of Family home in West Bank Fuels Collective Punishment Accusations
- 2. What legal arguments support the claim that Israeli home demolitions constitute collective punishment under international law?
- 3. Family Home Demolished Amid West Bank Tensions: Allegations of Collective Punishment in Israel-Palestine Conflict
- 4. Recent Demolition and Rising Concerns
- 5. Understanding the Practice of Home Demolitions
- 6. allegations of Collective Punishment & International Law
- 7. The Impact on palestinian Communities
- 8. Case Study: The Al-Rajabi Family (2023)
- 9. Obstacles to Obtaining Building Permits
- 10. The Role of International Actors
- 11. Related Search Terms & Keywords
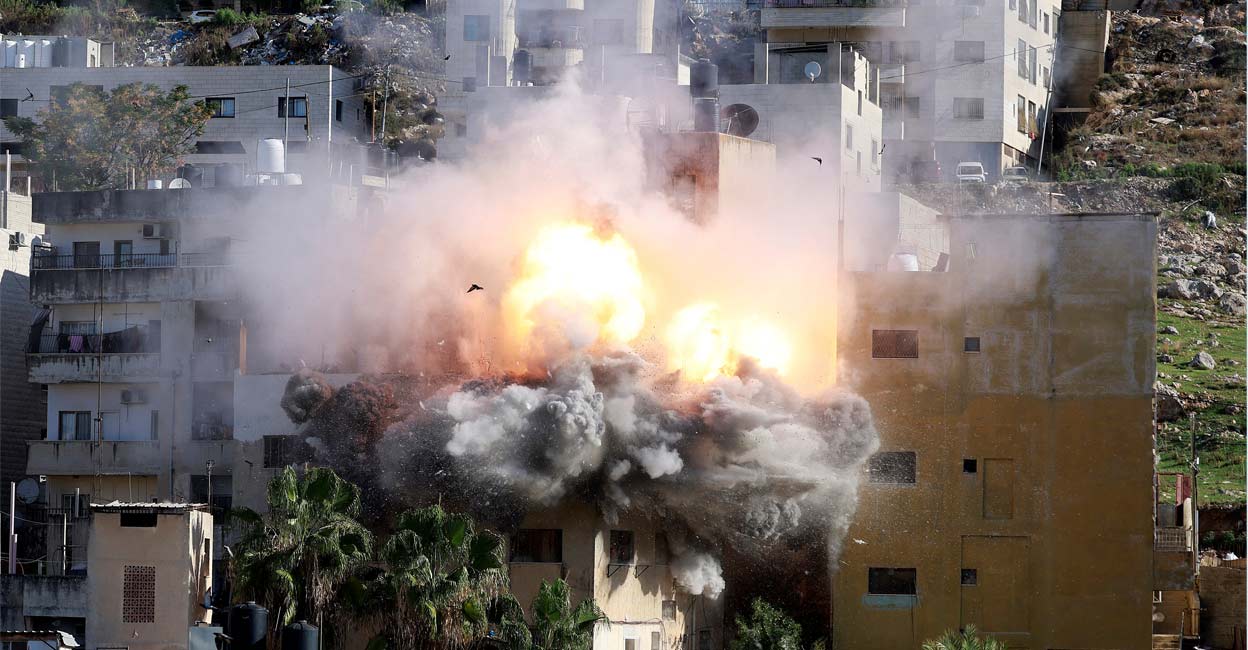
Nablus, occupied West bank – The Sanoubar family in Nablus are reeling after Israeli forces demolished their apartment building on Tuesday, leaving over 30 family members homeless. The demolition occurred with just two minutes’ warning, according to the family, and is linked to the alleged actions of Abdul Karim Sanoubar, a 30-year-old bombing suspect currently detained in Israel.
The building belonged to the extended family of Sanoubar, who is accused of conspiring to perpetrate bus bombings in Bat Yam near Tel Aviv in February – an incident which fortunately resulted in no injuries or deaths as the explosives detonated while the buses were parked. Sanoubar evaded capture for five months before being apprehended in a two-day manhunt in Nablus, during which Israeli forces raided hospitals and residential areas.
The demolition has sparked outrage and accusations of collective punishment, a practice widely condemned as a violation of international law by human rights groups.
“We’re not the terrorists; they are,” declared Moayed Sanoubar, Abdul Karim’s uncle, following the destruction. “This is completely unjust.” his father, Amer, 61, described the act as the latest in a series of punitive measures imposed on the family. “They did this to frighten us,” he stated, gesturing towards the ruins overlooking west Nablus. “They wont to make sure no young Palestinian ever thinks of carrying a single bullet. It is meant as a deterrent action against the entire Palestinian people.”
The Israeli army confirmed the demolition was part of “Operation Five Stones,” a “counterterrorism” operation launched in late November. the family has been informed that the land has also been confiscated, preventing any possibility of rebuilding.
Beyond the demolition, the Sanoubar family faces widespread imprisonment. Abdul Karim’s brothers,Ahmad and Omar,are currently held under Israel’s controversial system of administrative detention – allowing indefinite imprisonment without trial. Amer Sanoubar reports he has been detained three times since his son’s arrest, and his wife and daughter have also been imprisoned. Repeated raids on the family’s apartments have resulted in the destruction of furniture and possessions, adding to the family’s hardship.
The ongoing actions, according to Amer sanoubar, are a deliberate attempt to coerce his son into surrendering. The demolition of their home serves as a stark illustration of the escalating tensions and punitive measures impacting Palestinian families in the occupied west Bank.
What legal arguments support the claim that Israeli home demolitions constitute collective punishment under international law?
Family Home Demolished Amid West Bank Tensions: Allegations of Collective Punishment in Israel-Palestine Conflict
Recent Demolition and Rising Concerns
On December 2nd, 2025, a Palestinian family home in the West Bank village of Silwad was demolished by Israeli forces. This incident has sparked widespread condemnation from international human rights organizations and renewed accusations of collective punishment within the ongoing israel-Palestine conflict. The demolition,carried out under the pretext of security concerns,has left a family of six homeless and fueled further unrest in the region. This event underscores the complex and deeply sensitive issues surrounding home demolitions in the occupied territories.
Understanding the Practice of Home Demolitions
Israeli authorities employ home demolitions in the West Bank for several stated reasons, including:
* Punitive Demolitions: Targeting the homes of individuals accused of attacks against Israelis. This practice is highly controversial and considered illegal under international law by many.
* Lack of Building Permits: Palestinians face significant obstacles in obtaining building permits from Israeli authorities, leading to widespread construction without permits.These structures are then vulnerable to demolition.
* Military Necessity: Demolitions justified as necessary for military operations or security infrastructure.
The legality of these demolitions is a central point of contention. Critics argue that even demolitions based on lacking permits are effectively punitive, given the systemic denial of permits to Palestinians. The term “administrative demolitions” is frequently enough used to describe demolitions carried out without a court order.
allegations of Collective Punishment & International Law
The demolition in Silwad has reignited the debate over collective punishment. international humanitarian law, specifically the Fourth Geneva Convention, prohibits collective punishment – imposing sanctions on individuals for the actions of others.
* The Fourth Geneva Convention: Article 33 explicitly forbids measures of intimidation or terror, including collective punishment, against civilian populations.
* Human Rights Watch & Amnesty International: Both organizations have consistently documented and condemned Israel’s practice of home demolitions as a form of collective punishment and a violation of international law.
* UN Reports: Numerous UN reports have highlighted the detrimental impact of home demolitions on Palestinian communities and called for an end to the practice.
The Israeli government defends its policy by stating that it targets individuals responsible for violence and that demolitions are a deterrent against future attacks.However, critics argue that this approach disproportionately harms innocent family members and exacerbates the cycle of violence.
The Impact on palestinian Communities
Home demolitions have a devastating impact on Palestinian communities, extending far beyond the immediate loss of shelter.
* Displacement & Humanitarian Crisis: Demolitions contribute to displacement and exacerbate the existing humanitarian crisis in the West Bank.
* Psychological Trauma: The loss of a home and the disruption of family life cause significant psychological trauma, especially for children.
* Economic Hardship: Demolitions destroy livelihoods and contribute to economic instability.
* Increased Tensions: These actions fuel resentment and contribute to escalating tensions between Israelis and palestinians.
Case Study: The Al-Rajabi Family (2023)
In February 2023, the home of the Al-Rajabi family in Wadi Hummus, East Jerusalem, was demolished after a family member was accused of carrying out a shooting attack.This case drew international attention and sparked protests. The demolition left 13 family members,including children,homeless. The Al-Rajabi case exemplifies the devastating consequences of punitive demolitions and the challenges faced by Palestinian families in East Jerusalem.
Obstacles to Obtaining Building Permits
The process of obtaining building permits in area C of the West Bank (under full Israeli control) is notoriously tough for Palestinians.
* Restrictive Zoning Regulations: Israeli authorities impose strict zoning regulations that limit palestinian construction.
* High Costs & Bureaucracy: The submission process is complex, time-consuming, and expensive.
* Political Motivations: Critics allege that the denial of permits is often politically motivated,aimed at restricting Palestinian progress and consolidating Israeli control over the land.
* Settlement Expansion: While Palestinians struggle to obtain permits, Israeli settlements in the West Bank continue to expand, often with ease of construction.
The Role of International Actors
International actors, including the United Nations, the European union, and individual governments, play a crucial role in addressing the issue of home demolitions.
* Diplomatic Pressure: Applying diplomatic pressure on israel to halt demolitions and comply with international law.
* Humanitarian Aid: Providing humanitarian assistance to families affected by demolitions.
* Monitoring & Reporting: Monitoring and documenting demolitions and reporting on violations of international law.
* Supporting Legal Challenges: Supporting legal challenges to demolition orders.
* West bank demolitions
* Israel-Palestine conflict
* Collective punishment
* Fourth Geneva Convention
* Palest