Korea Housing Finance Corporation Explores ETF Route to Boost Mortgage-Backed Securities Trading
Table of Contents
- 1. Korea Housing Finance Corporation Explores ETF Route to Boost Mortgage-Backed Securities Trading
- 2. Previous Plans Shelved
- 3. Index development: A Major Obstacle
- 4. Understanding Mortgage-Backed Securities
- 5. ETF Launch Faces Uncertainty
- 6. The Growing Importance of ETFs in Global Finance
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions About MBS and etfs
- 8. How do prepayment risks within MBS potentially affect the overall yield and duration of an MBS-focused ETF?
- 9. Evaluating the Impact and Challenges of Mortgage-Backed Securities on Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) Success
- 10. The Role of MBS in ETF Portfolios
- 11. Understanding Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS)
- 12. How MBS Impact ETF Performance
- 13. Challenges and Risks Associated with MBS in ETFs
- 14. Navigating the Landscape: ETF Selection and Due Diligence
- 15. Real-World Example: The 2008 Financial Crisis & MBS ETFs
- 16. Benefits of Investing in
Seoul, South Korea – October 23, 2025 – The Korea Housing Finance Corporation is examining the potential of utilizing Exchange Traded Funds, or ETFs, as a strategy to invigorate trading in mortgage-backed securities (MBS). However, industry experts caution that the development of a suitable index remains a significant challenge.
Financial sector sources revealed on Wednesday that the investment bank is actively considering methods to incorporate MBS into domestic ETF offerings. The overarching goal is to enhance market liquidity by providing additional trading avenues and attracting investment from international sources.
Previous Plans Shelved
Earlier discussions centered on reducing the minimum investment threshold for MBS to encourage individual investor participation. Though, sources indicate that this proposal, originating from the Housing Finance Institute, was ultimately not pursued by the Korea Housing Finance Corporation, largely due to concerns about its investment appeal relative to goverment bonds.
Index development: A Major Obstacle
While revitalization plans are still under review, significant hurdles remain. Creating an ETF that accurately tracks specific securities, like bonds, necessitates the development of a reliable index. This requires consistent and readily available real-time transaction data from bond rating agencies and other market participants – a challenge in the currently subdued Korean distribution market.
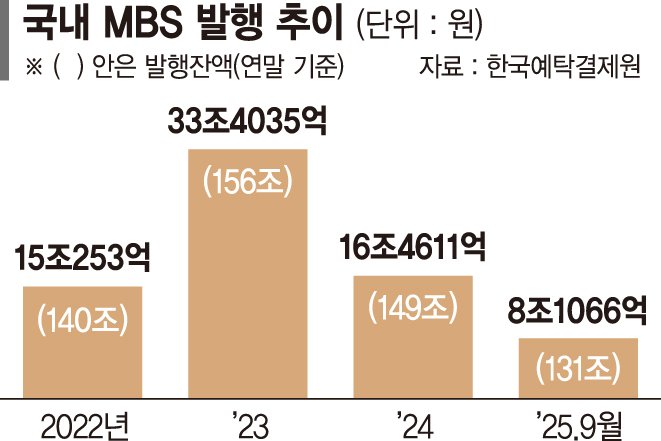
The existing ‘K-MBSI’ index, launched in November 2022, is calculated on a daily basis, rendering it unsuitable for use as a tracking index for an ETF. The daily calculation provides insufficient granularity for accurate ETF replication.
Understanding Mortgage-Backed Securities
MBS are a type of asset-backed security, where banks bundle mortgages-loans secured by real estate-and sell them as investments. These securities typically carry a AAA credit rating due to the guarantee provided by the underlying mortgages. While favored by institutional investors like insurance companies and banks for their stability, they are less frequently traded, often being held to maturity for duration management.
According to a financial investment industry official, the presence of call options and the risk of early repayment within MBS contribute to lower trading volumes. Without robust trading activity, accurately determining a market price becomes difficult, hindering the construction of a dependable index.
ETF Launch Faces Uncertainty
Even with a viable index in place, there is no guarantee that asset management companies will rush to launch ETFs tracking it.The current domestic ETF landscape is heavily focused on thematic investments, like semiconductors, and broad market indices such as the S&P 500 and NASDAQ.There is limited demand for bond-focused ETFs that don’t fit these popular categories.
The limited potential for success also poses a challenge in attracting liquidity providers, such as securities firms, to actively quote prices and participate in the market. Furthermore, any ETF with assets under management falling below 5 billion won risks being designated as a small fund and potentially delisted from the exchange.
Reporter Kim Tae-il
※ Copyright © 2025 Archyde,All rights reserved.
The Growing Importance of ETFs in Global Finance
Exchange Traded Funds have become increasingly popular investment vehicles over the past two decades, experiencing exponential growth in assets under management. According to Statista,global ETF assets reached approximately $6.14 trillion in 2023, and are projected to continue growing substantially. This trend is driven by their low costs, clarity, and ease of trading.
ETFs offer diversification across various asset classes, including stocks, bonds, and commodities. They are also used for tactical asset allocation and hedging strategies by institutional investors.
| Asset Class | global ETF AUM (2023 – est.) |
|---|---|
| Equities | $4.5 Trillion |
| Fixed Income | $1.2 Trillion |
| Commodities | $250 Billion |
Did You know? The first U.S. ETF,the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY),was launched in 1993 and remains the largest ETF by assets under management.
Pro Tip: Before investing in any ETF, carefully review its prospectus to understand its investment objective, strategy, and associated risks.
Frequently Asked Questions About MBS and etfs
What are your thoughts on the potential for MBS ETFs to gain traction in the Korean market? Do you believe the challenges in index development can be overcome?
How do prepayment risks within MBS potentially affect the overall yield and duration of an MBS-focused ETF?
Evaluating the Impact and Challenges of Mortgage-Backed Securities on Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) Success
The Role of MBS in ETF Portfolios
Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) have become a meaningful component of manny fixed-income Exchange-Traded Funds (etfs).These securities, representing claims on the cash flows from pools of mortgages, offer diversification and potential yield advantages. However, their inclusion isn’t without complexities. Understanding the interplay between MBS, fixed income etfs, and broader market conditions is crucial for investors. The core appeal lies in the potential for stable income, but risks like prepayment risk and interest rate risk must be carefully considered.
Understanding Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS)
MBS are created when mortgages are pooled together and sold as bonds to investors. These bonds pay out a portion of the monthly mortgage payments made by homeowners. There are different types of MBS:
* Agency MBS: Issued by government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs) like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. These carry an implicit government guarantee, making them generally safer.
* Non-Agency MBS: Issued by private entities. These typically have higher yields but also carry greater credit risk.
* CMO (Collateralized Mortgage Obligations): More complex MBS that redistribute cash flows to create securities with different maturities and risk profiles. Understanding CMO structures is vital for advanced investors.
The performance of MBS is heavily influenced by factors like mortgage rates, housing market conditions, and economic growth.
How MBS Impact ETF Performance
Fixed income ETF returns are directly affected by the underlying assets, including MBS. Here’s a breakdown:
* Yield: MBS can contribute to higher yields within an ETF, especially in a low-interest-rate surroundings.
* Duration: MBS typically have longer durations than other fixed-income securities, making them more sensitive to interest rate changes. ETF duration is a key metric to watch.
* Prepayment Risk: When interest rates fall, homeowners are more likely to refinance their mortgages. This leads to faster principal repayment on MBS, reducing the ETF’s yield and potentially impacting its total return.This is a significant factor in MBS analysis.
* Extension Risk: Conversely, when interest rates rise, prepayment slows down, extending the life of the MBS and potentially decreasing its value.
Challenges and Risks Associated with MBS in ETFs
Investing in MBS ETFs isn’t without its challenges. Several risks need to be addressed:
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: Rising interest rates can negatively impact MBS prices, leading to losses for ETF investors.
- Prepayment Risk (Detailed): As mentioned, unpredictable prepayment speeds can disrupt cash flow projections and affect ETF returns. Modeling prepayment speeds is a complex task.
- credit Risk (Non-Agency MBS): Non-agency MBS are exposed to the risk of borrowers defaulting on their mortgages.
- Liquidity Risk: During periods of market stress, the liquidity of MBS can decrease, making it challenging for etfs to sell their holdings at desired prices.
- Complexity: Understanding the intricacies of MBS structures, particularly CMOs, requires specialized knowledge.
Choosing the right MBS ETF requires careful consideration. Here are some key factors:
* ETF Composition: Understand the types of MBS held by the ETF (agency, non-agency, CMOs).
* Duration: Assess the ETF’s duration and how it aligns with your interest rate outlook.
* Expense Ratio: Consider the ETF’s expense ratio, which can impact your overall returns.
* Liquidity: Check the ETF’s trading volume and bid-ask spread to ensure sufficient liquidity.
* Fund Manager Expertise: Research the fund manager’s experience and track record in managing MBS portfolios.
Real-World Example: The 2008 Financial Crisis & MBS ETFs
The 2008 financial crisis vividly demonstrated the risks associated with MBS. The collapse of the housing market led to widespread mortgage defaults, causing significant losses for investors in MBS and MBS-backed ETFs.Many ETFs experienced substantial declines in value, highlighting the importance of understanding the underlying risks. This event underscored the need for robust risk management and due diligence when investing in these products. The crisis also led to increased regulation of the MBS market.