Early Osteoarthritis Detection: New Biomarkers Offer Hope For Millions
Table of Contents
- 1. Early Osteoarthritis Detection: New Biomarkers Offer Hope For Millions
- 2. The Challenge of Late Diagnosis
- 3. Unveiling the Bone’s Secret Signals
- 4. Fluid-Based Biomarkers: A less Invasive Approach
- 5. Understanding Osteoarthritis As A Whole-Joint Disease
- 6. Key Findings at a Glance
- 7. implications for Treatment and Prevention
- 8. what are the most promising bone‑derived biomarkers that can detect osteoarthritis before cartilage loss occurs?
- 9. early Bone‑Derived Biomarkers Uncover Osteoarthritis Before Cartilage Loss
- 10. The Subchondral Bone’s Role in Osteoarthritis
- 11. Identifying Early Biomarkers: What Are We Looking For?
- 12. The Promise of Synovial Fluid Analysis
- 13. Clinical Applications & Future Directions
- 14. Practical Tips for Joint Health
- 15. The Role of Advanced Imaging
A groundbreaking study, released January 26, 2026, is challenging conventional understanding of Osteoarthritis, or OA, a debilitating condition affecting over 500 million people globally. Researchers have discovered that molecular changes within the subchondral bone—the area beneath the cartilage—can signal the onset of the disease far earlier than previously thought, possibly revolutionizing diagnosis and treatment strategies.
The Challenge of Late Diagnosis
Osteoarthritis is notoriously difficult to detect in its early stages. frequently,diagnosis occurs only after meaningful cartilage damage is evident through X-rays or Mri scans,at which point intervention options are limited. Cartilage, once damaged, possesses a limited capacity for self-repair, making early detection crucial for preserving joint function and quality of life. This has prompted a search for reliable biomarkers that can identify the disease before irreversible damage occurs.
Unveiling the Bone’s Secret Signals
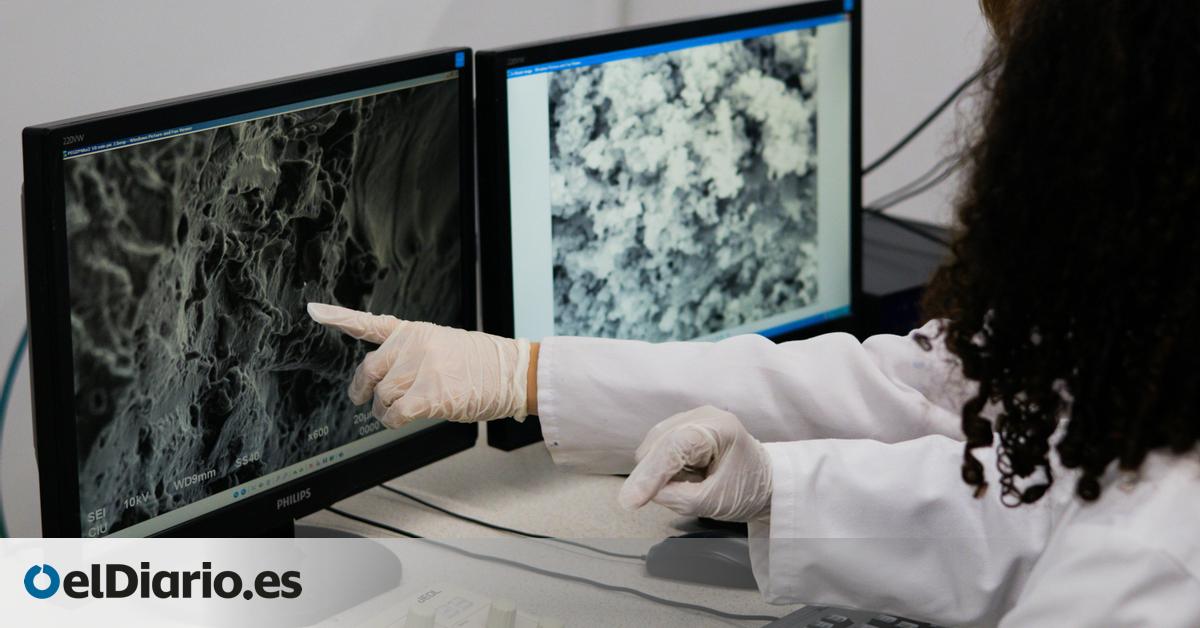
The research team, led by Professor Birgit Schilling at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging, employed cutting-edge techniques – spatial matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI MSI) and synovial fluid proteomics – to analyze human knee joint tissues. This innovative approach allowed them to map the location of hundreds of proteins within both bone and cartilage with extraordinary precision. Their inquiry revealed that specific alterations in collagen fragments and other proteins within the subchondral bone appeared even when overlying cartilage appeared healthy.
Fluid-Based Biomarkers: A less Invasive Approach
Remarkably, manny of these bone-derived protein signatures were also present in synovial fluid – the lubricating fluid within joints. This is significant because synovial fluid can be easily sampled through minimally invasive procedures like joint aspiration. Current diagnostic methods frequently enough rely on analyzing cartilage-associated markers, which tend to decrease as the disease progresses. The study highlights that tracking changes in bone remodeling offers a more sensitive and earlier indication of Osteoarthritis progression.
Understanding Osteoarthritis As A Whole-Joint Disease
these findings reinforce the emerging understanding of Osteoarthritis not as solely a cartilage disease, but as a complex condition affecting the entire joint. Altered cellular activity in the subchondral bone, particularly involving osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes, appears to play a considerable role in the advancement and progression of the disease. Further research is underway to unravel the intricate interplay between these cellular processes and their impact on cartilage health.
Key Findings at a Glance
| Aspect | Conventional View | New research Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Early Detection focus | Cartilage Damage | Subchondral Bone Changes |
| Biomarker Source | Cartilage-associated Proteins | Bone-Derived proteins in Synovial fluid |
| Disease Understanding | Primarily Cartilage disease | Whole-Joint Condition |
implications for Treatment and Prevention
The implications of this research extend beyond improved diagnostics. By identifying early molecular events in bone,scientists hope to develop targeted therapies that can slow or even prevent the progression of Osteoarthritis before permanent damage occurs. Current treatments are primarily focused on managing symptoms, with joint replacement surgery remaining the ultimate solution for advanced cases.
according to a report from the Arthritis Foundation, approximately 37 million U.S. adults live with Osteoarthritis.Developing new early detection methods and innovative therapies could significantly reduce this number and improve the quality of life for countless individuals.
What role do you believe early detection will play in transforming Osteoarthritis care? and how might a shift towards bone-targeted therapies impact the future of joint health?
This study represents a significant step forward in our understanding of Osteoarthritis. By focusing on the molecular landscape of subchondral bone, researchers are paving the way for earlier diagnoses, more effective monitoring, and ultimately, more personalized treatment approaches.
Disclaimer: This article provides general data and should not be considered medical advice. Consult with a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
share this article with anyone who may benefit from this vital research. Let’s start a conversation about Osteoarthritis and the promise of early detection!
what are the most promising bone‑derived biomarkers that can detect osteoarthritis before cartilage loss occurs?
early Bone‑Derived Biomarkers Uncover Osteoarthritis Before Cartilage Loss
Osteoarthritis (OA) is often considered a “wear and tear” disease, focusing on cartilage degradation.Though, emerging research reveals a far more complex picture.Increasingly, scientists are recognizing that changes in the subchondral bone – the bone beneath the cartilage – are not just a consequence of OA, but often precede cartilage damage and play a crucial role in disease initiation and progression. This shift in understanding has led to intense examination into early bone biomarkers as potential tools for diagnosis and intervention before irreversible cartilage loss occurs.
The Subchondral Bone’s Role in Osteoarthritis
For years,the focus was almost exclusively on cartilage. While cartilage breakdown is a hallmark of OA, it’s now understood that the subchondral bone undergoes significant remodeling in the early stages of the disease.This remodeling isn’t simply reactive; it actively contributes to the OA process.
Here’s how:
* Microfractures: Increased stress on the bone can lead to microfractures, triggering repair mechanisms. Though, these repairs aren’t always perfect, leading to altered bone structure.
* Bone Marrow Lesions (BMLs): Visible on MRI, BMLs are areas of edema and altered bone marrow signal. They are strongly associated with pain and disease progression, frequently enough appearing before significant cartilage loss.
* Subchondral bone Sclerosis: The bone becomes denser and harder, altering joint biomechanics and perhaps accelerating cartilage wear.
* Osteophyte Formation: Bone spurs develop at joint margins, contributing to pain and limited range of motion.
Identifying Early Biomarkers: What Are We Looking For?
Traditional methods for diagnosing OA, like X-rays, often only detect changes after substantial cartilage damage has occurred. This is were bone-derived biomarkers offer a promising choice. These biomarkers are measurable indicators of bone remodeling activity, detectable in synovial fluid or blood, potentially signaling OA risk years before symptoms manifest.
key biomarkers under investigation include:
- CTx-II (C-terminal Crosslinking Telopeptide of Type II Collagen): While traditionally associated with cartilage breakdown, CTx-II levels can also be influenced by subchondral bone remodeling.
- PINP (Procollagen Type II N-terminal Peptide): Reflects new collagen formation, potentially indicating bone repair attempts.
- Bone Sialoprotein (BSP): Involved in bone matrix mineralization and remodeling. Elevated levels suggest increased bone turnover.
- Receptor Activator of NF-κB Ligand (RANKL): A key regulator of osteoclast activity (cells that break down bone). Increased RANKL levels indicate increased bone resorption.
- Osteoprotegerin (OPG): Acts as a decoy receptor for RANKL, inhibiting osteoclast activity. The RANKL/OPG ratio is a crucial indicator of bone remodeling balance.
- MicroRNAs (miRNAs): Small non-coding RNA molecules that regulate gene expression. Specific miRNAs found in synovial fluid show promise as early OA indicators, reflecting changes in both cartilage and bone.
The Promise of Synovial Fluid Analysis
Synovial fluid, the lubricant within joints, is emerging as a notably rich source of biomarkers. Analyzing synovial fluid allows for a more localized assessment of joint health, potentially detecting subtle changes that wouldn’t be apparent in blood tests.
* Proteomics: Analyzing the entire protein content of synovial fluid can identify patterns of protein expression associated with early OA.
* Metabolomics: Studying the small molecule metabolites in synovial fluid can reveal alterations in metabolic pathways linked to bone and cartilage metabolism.
* miRNA Profiling: Identifying specific miRNA signatures in synovial fluid can provide a highly sensitive and specific diagnostic tool.
Clinical Applications & Future Directions
The progress of reliable bone-derived biomarkers has the potential to revolutionize OA management.
* Early Diagnosis: Identifying individuals at risk before they develop symptoms allows for proactive interventions.
* personalized Treatment: Biomarker profiles can help tailor treatment strategies to individual patients, maximizing effectiveness.
* Monitoring Disease Progression: Tracking biomarker levels can assess the effectiveness of treatments and adjust them accordingly.
* Drug Development: Biomarkers can be used to evaluate the efficacy of new OA drugs in clinical trials.
Case Study: The framingham Osteoarthritis Study
The ongoing Framingham Osteoarthritis Study has been instrumental in identifying risk factors for OA and validating potential biomarkers. Longitudinal data from this study has demonstrated that individuals with elevated levels of certain bone turnover markers are more likely to develop OA, even in the absence of radiographic evidence of cartilage loss.
Practical Tips for Joint Health
While biomarker testing isn’t yet widely available, there are steps you can take to support joint health and potentially delay the onset of OA:
* Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts increased stress on weight-bearing joints.
* Regular Exercise: Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and walking strengthen muscles around joints and improve joint stability.
* Proper Nutrition: A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods (fruits, vegetables, omega-3 fatty acids) can help protect joints.
* Injury Prevention: Protect your joints from injury by using proper form during exercise and avoiding activities that put excessive stress on them.
* Early Intervention: If you experience joint pain or stiffness, seek medical attention promptly.