Federal Court Strikes Down Trump-Era Tariffs as Unlawful
Table of Contents
- 1. Federal Court Strikes Down Trump-Era Tariffs as Unlawful
- 2. Court Ruling and Potential Appeals
- 3. Impact on Trade Negotiations
- 4. Congressional Authority Over Tariffs
- 5. Implications for international Trade
- 6. The Historical context of U.S. tariffs
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions About the Trump Tariffs
- 8. What specific procedural failures led the court to rule Trump’s Section 232 tariffs unlawful?
- 9. Trump’s Tariff Policy Faces Legal Setback as Federal Court of Appeals rules It Illegal
- 10. The Ruling and Its Immediate Impact
- 11. Understanding the Legal Challenges to Trump’s Tariffs
- 12. Key Industries Affected by the Ruling
- 13. The Biden administration’s Response and Future Outlook
- 14. Case Study: The Impact on U.S. Steel Producers
- 15. Practical Tips for Businesses Navigating Trade Policy Changes
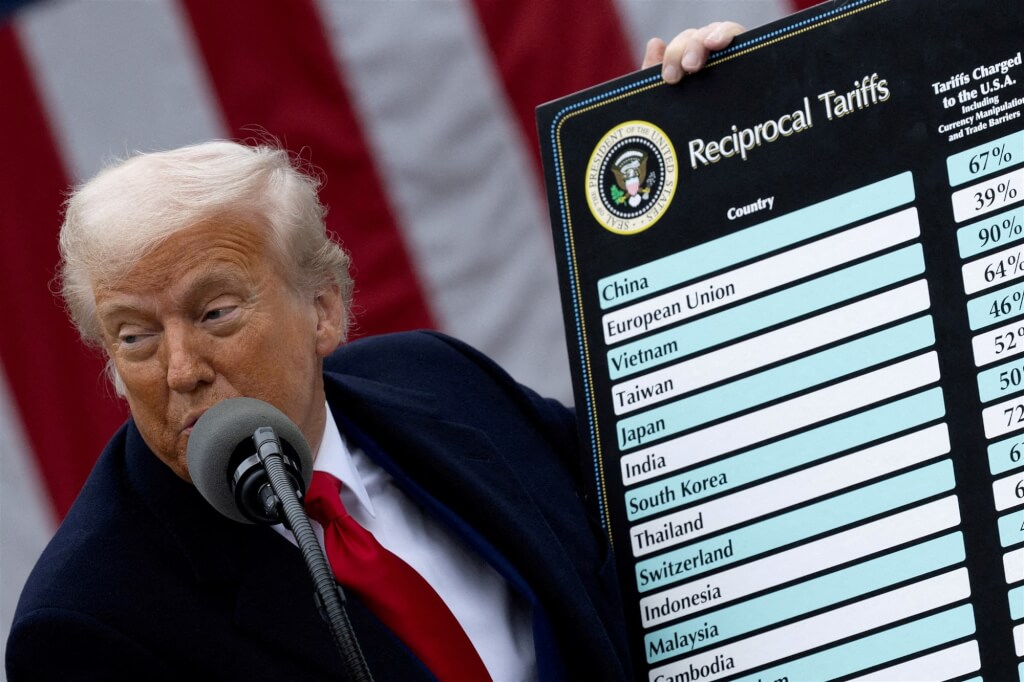
washington D.C. – A U.S. Federal Circuit Court of Appeals delivered a notable blow to former President Trump’s trade policies on Thursday,ruling that most of his globally imposed tariffs were enacted without legal justification. The Court steadfast that Trump exceeded the authority granted by the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA) of 1977 when utilizing executive orders to impose such tariffs.
Court Ruling and Potential Appeals
The appellate court’s decision, reached by a 7-4 vote, upholds a previous ruling from a lower court.Judges asserted that the IEEPA does not authorize the President to impose tariffs through executive action, specifically lacking the power to levy taxes without Congressional approval. Despite the ruling, the court has allowed the tariffs to remain in effect until mid-October, providing an opportunity for all parties involved to appeal to the Federal Supreme Court.
Trump responded to the decision via his social media platform, Truth Social, maintaining his belief that the tariffs are valid and that the United States will ultimately prevail. he characterized the ruling as “highly partisan” and suggested the court was predisposed against him.
Impact on Trade Negotiations
In April of this year, Trump initiated what he termed “reciprocal tariffs” on imports from numerous U.S. trading partners, which initially caused market volatility and strong reactions internationally.He temporarily paused implementation to pursue negotiations, with adjusted tariff rates taking effect in early August. These negotiations with various nations remain ongoing.
The court’s ruling affects a broad range of tariffs implemented during Trump’s administration, including the 10% benchmark tariffs imposed on nearly all countries, retaliatory tariffs against nations deemed to have engaged in unfair trade practices, and additional tariffs on goods from Canada, China, and Mexico. Though, tariffs imposed on industries like automobiles, steel, aluminum, and copper, based on national security grounds, are not affected by this particular ruling.
The Court of Appeals emphasized that the power to impose tariffs rests with Congress. In their opinion, the IEEPA grants the President broad authority to act during national emergencies, but does not extend to levying taxes or tariffs without explicit Congressional authorization. “without the legal authorization of Congress, the president has no right to collect taxes,” the court stated.
The legal challenge was initiated by a coalition of Democratic states and small to medium-sized businesses shortly after Trump announced the tariffs. A previous ruling by the Court of International Trade in May had determined the tariffs were invalid, prompting the Trump administration’s appeal to the Federal Circuit Court of Appeals, which was heard by all 11 current judges.
Implications for international Trade
Analysts suggest that this ruling may prompt countries to reassess their trade negotiation strategies with the United States. With the legal basis for some trade agreements now in question, nations might potentially be less inclined to concede ground in ongoing talks.According to the U.S. Axios News Network, trade agreements reached with the European Union and Japan, predicated on the now-challenged legal framework, might potentially be subject to further scrutiny.
Did you know? The IEEPA was originally enacted in 1977 to address potential economic emergencies, but its interpretation regarding tariff authority has been a subject of ongoing debate.
| Tariff Type | Status after Ruling | Affected Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Reciprocal Tariffs | Ruled unlawful; subject to appeal | Broad range of imports |
| National Security Tariffs (Steel, Aluminum) | Unaffected by this ruling | Steel, Aluminum, Automobiles |
| Tariffs on Canada, China, Mexico | Ruled unlawful; subject to appeal | Various goods |
The Historical context of U.S. tariffs
The use of tariffs as a trade tool has a long history in the United States, dating back to the early days of the Republic. Alexander Hamilton, the first Secretary of the Treasury, advocated for protective tariffs to encourage domestic manufacturing. Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, tariffs have been used to protect American industries, raise revenue, and retaliate against unfair trade practices. The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930, widely criticized for exacerbating the Great Depression, remains a cautionary tale about the potential negative consequences of protectionist trade policies.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Trump Tariffs
- What are Trump tariffs? These are tariffs imposed by the Trump administration on imports from various countries,often in response to perceived unfair trade practices.
- Is the IEEPA a valid basis for imposing tariffs? The Court of Appeals has ruled that the IEEPA does not authorize the President to impose tariffs without Congressional approval.
- Will these tariffs be removed immediately? No, the tariffs will remain in effect pending potential appeals to the Supreme court.
- What is the impact of this ruling on trade negotiations? Countries may reconsider their negotiation strategies with the U.S. given the legal uncertainty.
- Are all of Trump’s tariffs affected by this ruling? No, tariffs imposed under national security authorizations are not affected.
- What does this ruling mean for businesses? Businesses may face changes in import costs and trade relationships depending on the outcome of potential appeals.
- what is the future of U.S. trade policy? The ruling may influence future trade negotiations and the balance of power between the President and Congress in trade matters.
What impact do you think this ruling will have on global trade relations? Will countries adjust their trade strategies considering this decision?
Share your thoughts in the comments below and help us continue the conversation!
What specific procedural failures led the court to rule Trump’s Section 232 tariffs unlawful?
Trump’s Tariff Policy Faces Legal Setback as Federal Court of Appeals rules It Illegal
The Ruling and Its Immediate Impact
A recent decision by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit has dealt a significant blow to former President Donald Trump’s trade policy. The court ruled that a key component of his tariff strategy – specifically, the imposition of tariffs on steel and aluminum imports under Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act of 1962 – was unlawful. This ruling stems from challenges brought by several foreign governments and domestic businesses impacted by the tariffs. The core issue wasn’t the ability to impose tariffs, but how they were implemented, specifically the lack of adherence to established administrative procedures.
Section 232: This act allows the President to impose tariffs on imports deemed a threat to national security.
The Ruling’s Focus: The court found that the Trump administration failed to adequately justify the national security basis for the tariffs and didn’t follow proper rulemaking procedures.
Immediate Consequences: While the ruling doesn’t automatically eliminate all tariffs, it opens the door for further legal challenges and possibly requires the Biden administration to revisit the justification and implementation of existing Section 232 tariffs.
Understanding the Legal Challenges to Trump’s Tariffs
The legal battles surrounding Trump’s tariffs were multifaceted. Several plaintiffs argued that the tariffs:
- Exceeded Presidential Authority: Critics contended that the broad request of the tariffs stretched the definition of “national security” beyond its intended scope.
- Violated Administrative Procedure Act (APA): The APA requires federal agencies to follow specific procedures when making rules, including providing notice and prospect for public comment. Plaintiffs argued the Trump administration bypassed these requirements.
- Caused Economic Harm: Businesses reliant on imported steel and aluminum demonstrated significant cost increases and disruptions to their supply chains. This included manufacturers in the automotive, construction, and energy sectors.
The court largely sided with these arguments, emphasizing the importance of procedural regularity in the exercise of presidential power. The case hinged on the principle that even when acting within statutory authority, the executive branch must adhere to established legal processes. Trade disputes and international trade law were central to the arguments presented.
Key Industries Affected by the Ruling
The impact of the tariffs,and now the potential for their rollback,is far-reaching. Here’s a breakdown of key industries:
Automotive Industry: Steel and aluminum are crucial components in vehicle manufacturing. Tariffs increased production costs, potentially leading to higher car prices for consumers.
Construction: Rising steel prices impacted construction projects, potentially delaying or increasing the cost of infrastructure progress.
Energy Sector: Steel is used in pipelines and other energy infrastructure. Tariffs added to the expense of energy projects.
Manufacturing: Downstream manufacturers relying on steel and aluminum as inputs faced increased costs and supply chain disruptions. Supply chain management became a critical concern.
Agriculture: Retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries in response to the U.S. tariffs significantly harmed American farmers,particularly soybean and pork producers. Agricultural trade suffered.
The Biden administration’s Response and Future Outlook
The Biden administration faces a complex situation.While generally more supportive of multilateral trade agreements than the Trump administration, it has been hesitant to immediately remove all Section 232 tariffs, citing concerns about protecting domestic steel and aluminum production.
Here’s what to expect:
Review of Existing Tariffs: The administration is likely to review the existing Section 232 tariffs to ensure they are justified under the national security standard and implemented according to proper procedures.
Negotiations with Allies: The ruling could create opportunities for the U.S. to negotiate with allies to address trade imbalances and concerns about unfair trade practices. Trade negotiations will be crucial.
Potential for Further Litigation: The Trump administration could appeal the ruling,potentially prolonging the legal battle.
Impact on USMCA: The ruling could indirectly influence the implementation of the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) by setting a precedent for how trade disputes are resolved.
Case Study: The Impact on U.S. Steel Producers
While the tariffs were intended to benefit U.S. steel producers, the results were mixed. While some companies saw increased profits initially, others struggled with higher input costs and reduced demand from downstream manufacturers. nucor Corporation, a major U.S.steel producer, initially supported the tariffs but later expressed concerns about the negative impact on its customers. This illustrates the complex and often unintended consequences of protectionist trade policies. Steel industry analysis reveals a nuanced picture.
For businesses impacted by these trade policy shifts,here are some practical steps:
Diversify Supply Chains: Reduce reliance on single suppliers or countries.
monitor Trade Developments: Stay informed about changes in tariffs, trade agreements, and regulations.




