“`html
Expanded Breast Cancer Screening Planned for Women with Dense Tissue
Table of Contents
- 1. Expanded Breast Cancer Screening Planned for Women with Dense Tissue
- 2. Addressing a Critical Screening Gap
- 3. Previous Research and Current Challenges
- 4. Public Pressure and Petition Success
- 5. Implementation scenarios and Timelines
- 6. What are teh potential barriers to the rapid implementation of dedicated breast MRI across the UK’s NHS?
- 7. Urgent Call for Rapid Implementation of Close Breast Tissue MRI by outgoing cabinet
- 8. The Critical Need for High-Resolution Breast Imaging
- 9. Identifying the High-Risk Cohort: Who Benefits Most?
- 10. The Advantages of Dedicated Breast MRI
- 11. Addressing Implementation Challenges: A Multi-Faceted Approach
- 12. Real-World Impact: Case Studies & Emerging Data
- 13. Practical Tips for Healthcare Professionals
- 14. The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Breast MRI
- 15. Future Directions: Personalized Breast Cancer Screening
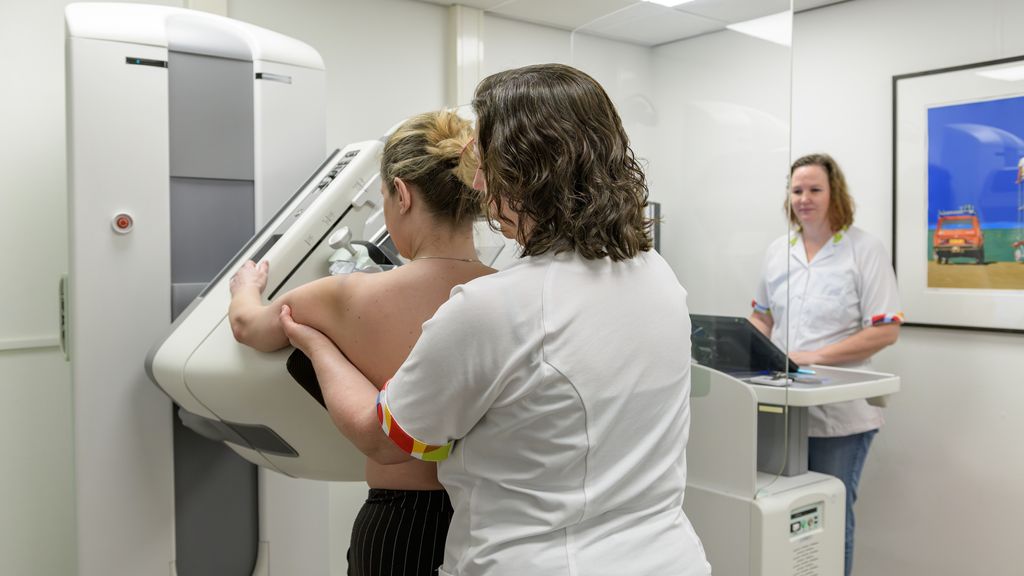
The Hague – The outgoing Dutch cabinet is prioritizing enhanced breast cancer screening for women with dense breast tissue, a population often facing challenges with customary mammography. the initiative follows a positive feasibility assessment by the National Institute for Public health and the Environment (RIVM).
Addressing a Critical Screening Gap
Approximately one in twelve women aged 50 to 75 participating in the national screening program exhibit very dense breast tissue. This density doubles their risk of developing breast cancer and can obscure tumor detection in standard mammograms. Early identification of tumors in this group leads to less intensive treatments and improved survival rates.
Previous Research and Current Challenges
While earlier research, known as the Dense examination, demonstrated the effectiveness of additional MRI scans, concerns regarding cost and screening efficiency led to a follow-up study (Dense-2) focused on shorter, more affordable alternatives, such as abbreviated MRIs and contrast mammography.The implementation of these findings has faced delays, prompting increased calls for immediate action.
Public Pressure and Petition Success
A petition launched by the Netherlands Breast Cancer Association garnered over 70,000 signatures, urging the government to prioritize additional screening for women with dense breast tissue. This public pressure, combined with a supportive motion in the Lower House led by State Secretary Tielen, prompted the RIVM to evaluate implementation strategies.
Implementation scenarios and Timelines
The RIVM has outlined four potential implementation scenarios, ranging from one to six years. The fastest path involves integrating density measurement during existing mammography screenings and leveraging hospitals and clinics for follow-up scans. This approach could be viable within one to three years.
A more comprehensive, quality-focused approach would prioritize centralized coordination and standardized protocols across the Netherlands, potentially extending the implementation timeline to four or five years. Experts emphasize that ensuring consistent quality and appropriate training for radiologists is paramount.
| Scenario | Implementation Timeline | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Fast Track | 1-3 years | Density measurement during mammograms, utilizing existing facilities. |
| Standardized Approach | 4-5 years | Centralized coordination, standardized protocols, and enhanced radiologist training. |
Did You Know? Despite advancements in screening, approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed by mammography,
What are teh potential barriers to the rapid implementation of dedicated breast MRI across the UK’s NHS?
Urgent Call for Rapid Implementation of Close Breast Tissue MRI by outgoing cabinet
The Critical Need for High-Resolution Breast Imaging
The outgoing cabinet has issued a strong and urgent call for the accelerated implementation of close breast tissue MRI – specifically,dedicated breast MRI protocols – across the UK’s National Health Service (NHS). This isn’t simply a procedural recommendation; it’s a response to mounting evidence demonstrating the superior diagnostic capabilities of MRI in specific high-risk patient populations and the potential to significantly improve early breast cancer detection rates. Breast MRI,dedicated breast MRI,and high-risk breast cancer screening are key terms driving this initiative.
Identifying the High-Risk Cohort: Who Benefits Most?
Current national screening programs, while effective, primarily rely on mammography. However, mammography’s sensitivity is reduced in women with dense breast tissue. This is where dedicated breast MRI proves invaluable. The primary groups who stand to benefit most from rapid access to this technology include:
* BRCA1/2 Gene Mutation Carriers: Individuals with known mutations in these genes have a significantly elevated lifetime risk of developing breast cancer.Annual BRCA screening with MRI is now considered standard of care.
* Li-Fraumeni Syndrome Patients: This rare genetic condition predisposes individuals to a range of cancers, including breast cancer, at a young age.
* Women with a Strong Family History: Those with a substantial family history of breast or ovarian cancer, even without identified gene mutations, may benefit from supplemental MRI screening.
* Individuals with Prior Chest Radiation: Radiation therapy to the chest, particularly during childhood, increases breast cancer risk.
* Dense Breast Tissue: As mentioned, mammographic sensitivity is lower in women with dense breasts. Dense breast tissue MRI can definitely help overcome this limitation.
The Advantages of Dedicated Breast MRI
Dedicated breast MRI offers several key advantages over conventional mammography and even whole-body MRI for breast cancer detection:
* Superior Sensitivity: MRI detects smaller tumors and subtle abnormalities that might potentially be missed by mammography, particularly in dense breasts.
* No Ionizing Radiation: Unlike mammography and CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for frequent screening.
* Improved Characterization of Lesions: MRI can frequently enough differentiate between benign and malignant lesions with greater accuracy, reducing the need for needless biopsies. breast lesion characterization is a crucial aspect of diagnosis.
* Detection of Multifocal Disease: MRI excels at identifying multiple tumors within the same breast or in both breasts simultaneously.
Addressing Implementation Challenges: A Multi-Faceted Approach
The outgoing cabinet acknowledges that rapid implementation isn’t without its challenges. Key hurdles include:
- MRI Availability: Not all hospitals currently have dedicated breast MRI scanners or the necessary expertise to interpret the images.Investment in infrastructure and training is paramount.
- Radiologist Training: specialized training in breast MRI interpretation is essential to ensure accurate diagnoses.A national training program is being proposed.
- Cost Considerations: MRI is more expensive than mammography. However, the potential for earlier detection and reduced treatment costs justifies the investment. Breast cancer cost-effectiveness studies support this argument.
- Workflow Integration: Integrating MRI into existing screening pathways requires careful planning and coordination. Breast screening pathways need to be adapted.
- Patient Access & Equity: Ensuring equitable access to breast MRI for all eligible women, irrespective of location or socioeconomic status, is a critical priority.
Real-World Impact: Case Studies & Emerging Data
Several studies have demonstrated the clinical benefits of supplemental MRI screening in high-risk women. Such as, research published in Radiology (2023) showed that annual MRI screening in BRCA mutation carriers led to a 60% reduction in interval cancers (cancers detected between scheduled screenings). Furthermore, the UK’s National Breast Cancer Screening Programme is currently evaluating the feasibility of incorporating MRI into its screening protocols for women with extremely dense breasts.
Practical Tips for Healthcare Professionals
* Referral Guidelines: familiarize yourself with the latest national referral guidelines for breast MRI.
* Patient Education: Clearly explain the benefits and limitations of MRI to patients.
* Collaboration: Work closely with radiologists and other specialists to ensure optimal patient care.
* Stay Updated: Keep abreast of the latest research and advancements in breast MRI technology. Breast imaging updates are frequently published in medical journals.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Breast MRI
The integration of AI in breast MRI is rapidly evolving. AI algorithms are being developed to:
* Improve Image Quality: Reducing noise and artifacts in MRI images.
* Automate Lesion Detection: Assisting radiologists in identifying potential tumors.
* enhance Characterization: Predicting the likelihood of malignancy based on image features.
* Streamline Workflow: prioritizing cases based on risk.
Future Directions: Personalized Breast Cancer Screening
The ultimate goal is to move towards personalized breast cancer screening strategies, tailored to each woman’s individual risk factors. This will likely involve a combination of mammography, MRI, genetic testing, and possibly other emerging technologies. Personalized breast cancer screening represents the