Indonesian Nationals Increasingly Targeted by Trafficking Networks in Southeast Asia
Table of Contents
- 1. Indonesian Nationals Increasingly Targeted by Trafficking Networks in Southeast Asia
- 2. Recent Cases Highlight Escalating Crisis
- 3. Cambodia addresses Trafficking Ring
- 4. Key Facts: Indonesian Nationals affected
- 5. Understanding the Drivers of Human Trafficking
- 6. Frequently Asked Questions about Human Trafficking
- 7. How can international collaboration be strengthened to dismantle transnational criminal networks operating scam hubs and trafficking individuals in the Asia-Pacific region?
- 8. Rising Human Trafficking Cases Amid Escalating Regional Scam Operations in Asia & pacific
- 9. The Nexus of Online Scams and Modern Slavery
- 10. Understanding the Scam Operations
- 11. The Human Trafficking Connection: A Deeper Dive
- 12. Real-world Examples & Case Studies
- 13. The Role of Cryptocurrency & Digital Finance
- 14. Combating the Crisis: A Multi-faceted Approach
- 15. Benefits of increased Awareness &
As economic challenges intensify and legitimate employment opportunities dwindle, a growing number of indonesian Citizens are becoming victims of online scams and elegant human trafficking operations throughout Southeast Asia. Analysts predict this disturbing trend will continue unless effective prevention strategies and robust law enforcement measures are swiftly implemented.
Recent Cases Highlight Escalating Crisis
Over the weekend, the Indonesian Embassy in Yangon confirmed contact with 148 Indonesian Nationals who found themselves stranded in Myawaddy, Myanmar.This region, known for its conflict and proximity to Thailand, has emerged as a significant hub for fraudulent schemes and exploitative practices.
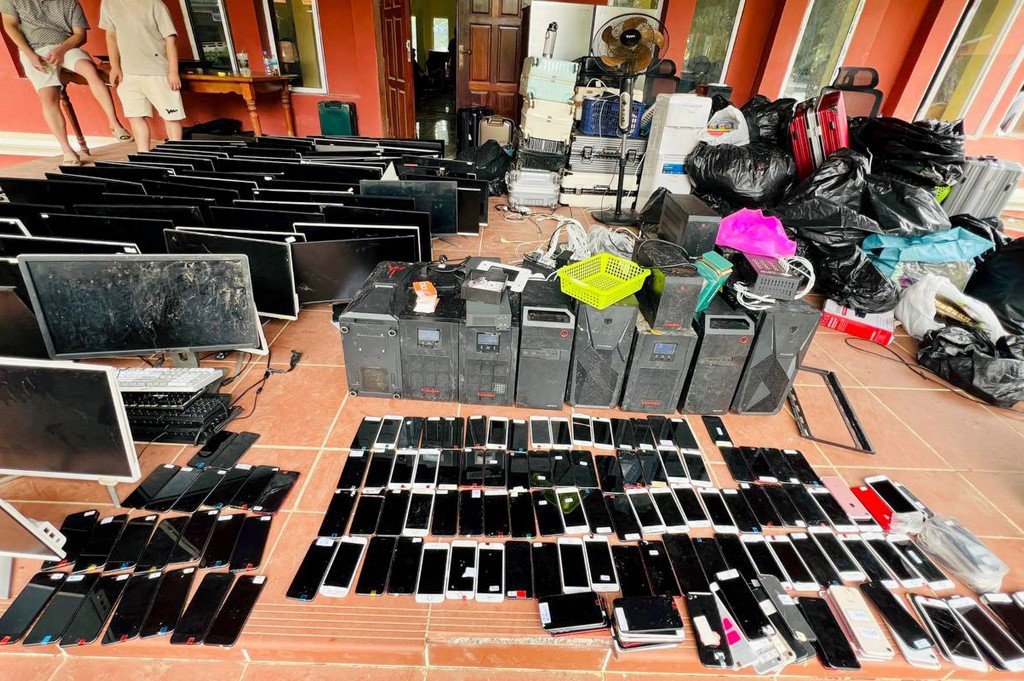
Embassy personnel responded to three separate reports detailing the plight of hundreds of Indonesian Citizens scattered throughout Myawaddy. Among those identified, 58 were reportedly located within the confines of the former KK Park complex, a notorious center for human trafficking which was recently dismantled by Myanmar’s military government.
Embassy staff are currently working to verify the identities of those affected, collaborating with local authorities to ensure their safe relocation and facilitate the necessary permits for repatriation. This action follows a previous intervention just one week prior, where the embassy assisted 83 Indonesian Nationals escaping the KK Park complex, bringing the total number of newly reported trafficking cases to 231 in under ten days.
Cambodia addresses Trafficking Ring
Simultaneously, a coordinated operation in Cambodia led to the arrest of 106 Indonesian Citizens, including 36 women, in Phnom penh’s Tuol Kork district. The arrests were connected to allegations of involvement in online scam activities following a raid conducted by Cambodian authorities.
Did You know? The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) reports that human trafficking generates an estimated $150 billion in profits annually worldwide. UNODC on Human Trafficking
Key Facts: Indonesian Nationals affected
| Location | Number of Nationals | Nature of Incident |
|---|---|---|
| Myawaddy, myanmar | 148 | Stranded victims of human trafficking due to online scams |
| KK Park Complex, Myanmar | 58+ | Victims of a known human trafficking hub |
| Phnom Penh, Cambodia | 106 | Arrested on online scam charges |
Understanding the Drivers of Human Trafficking
Several factors contribute to the rising vulnerability of Indonesian Citizens to these exploitative schemes. Limited economic opportunities at home, coupled with deceptive online recruitment practices promising lucrative employment abroad, create a fertile ground for traffickers. These schemes frequently lure individuals with false promises of jobs in areas like customer service or data entry, only to trap them in forced labor or online scam operations.
Pro Tip: Be cautious of job offers received through social media or unfamiliar channels, especially those promising high salaries for minimal qualifications. always verify the legitimacy of the employer and the job conditions before accepting any offer.
Frequently Asked Questions about Human Trafficking
- What is human trafficking? human trafficking involves the recruitment, transportation, transfer, harbouring, or receipt of persons, by means of the threat or use of force, or other forms of coercion, for the purpose of exploitation.
- What are the common signs of human trafficking? These include debt bondage, restrictions on movement, confiscation of identity documents, and isolation from family and friends.
- What can be done to prevent human trafficking? Raising awareness, strengthening law enforcement, and addressing the root causes of vulnerability, such as poverty and lack of chance, are crucial preventive measures.
- What should I do if I suspect someone is being trafficked? Report your suspicions to the authorities or a relevant anti-trafficking organization.
- What resources are available for Indonesian Citizens abroad? Contact the nearest Indonesian Embassy or Consulate for assistance.
How can international collaboration be strengthened to dismantle transnational criminal networks operating scam hubs and trafficking individuals in the Asia-Pacific region?
Rising Human Trafficking Cases Amid Escalating Regional Scam Operations in Asia & pacific
The Nexus of Online Scams and Modern Slavery
The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing a disturbing surge in human trafficking, inextricably linked to the proliferation of sophisticated online scam operations. What initially appears as a digital crime wave – romance scams, fake job offers, cryptocurrency fraud – is increasingly revealed as a front for large-scale human exploitation. This isn’t simply about financial loss; it’s about the systematic enslavement of vulnerable individuals. The term “scam hubs” is now commonly used to describe locations where victims are held against their will and forced to participate in these fraudulent schemes.
Understanding the Scam Operations
These aren’t amateur endeavors.Organized criminal groups, often transnational in nature, are establishing complex networks. Key characteristics include:
* Targeted Recruitment: Scammers actively recruit individuals, often from impoverished backgrounds, with promises of legitimate employment – data entry, customer service, even marketing roles.
* Debt bondage: Victims are frequently lured with loans to cover travel expenses, promptly placing them in debt bondage upon arrival.
* Confiscation of Documents: Passports and other identification are routinely confiscated, rendering victims unable to leave.
* Forced Participation in Scams: Individuals are compelled to create fake online profiles,engage in romance scams,or operate fraudulent investment schemes. Failure to meet quotas results in severe punishment – physical abuse, starvation, and threats against family members.
* Geographic Hotspots: Cambodia, Myanmar (especially the Shwe Kokko Special Economic Zone), Laos, and the Philippines have emerged as major hubs for these operations.Thailand and Indonesia also see significant activity.
The Human Trafficking Connection: A Deeper Dive
The link between online scams and human trafficking is becoming increasingly clear. Victims aren’t just employees; they are the exploited.
* Definition of Trafficking: According to the Palermo Protocol, human trafficking involves the recruitment, transportation, transfer, harbouring or receipt of persons, by means of the threat or use of force, or other forms of coercion, for the purpose of exploitation. This definition directly applies to the situation unfolding in scam hubs.
* Forms of Exploitation: Beyond forced participation in scams, victims are subjected to:
* Sexual Exploitation: While not universal, reports of sexual abuse within these compounds are rising.
* Forced Labor: Victims work long hours under brutal conditions.
* Organ Harvesting: Though less common, credible reports suggest the potential for organ harvesting in some locations.
* Vulnerable Populations: Individuals from China, Taiwan, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia are disproportionately affected. Though, citizens from Western countries are also being targeted and trafficked.
Real-world Examples & Case Studies
* Shwe kokko, Myanmar: This Special Economic Zone has become notorious as a haven for scam operations and human trafficking. Reports detail widespread abuse and the presence of armed groups protecting the compounds. Investigations have revealed sophisticated infrastructure designed to facilitate criminal activity.
* Sihanoukville, Cambodia: Once a burgeoning tourist destination, sihanoukville has been overrun by scam hubs. Numerous reports document the horrific conditions faced by trafficked individuals, including torture and forced confinement.
* The Philippines – ALABEL Compound: In 2023, a large-scale raid in Alabel, Sarangani province, Philippines, uncovered a scam operation involving hundreds of Filipino and foreign nationals. The operation was linked to human trafficking and forced labor.
The Role of Cryptocurrency & Digital Finance
Cryptocurrency plays a crucial role in facilitating these scams and laundering the proceeds.
* Anonymity: Cryptocurrencies offer a degree of anonymity, making it difficult to trace funds.
* cross-Border Transactions: Digital currencies enable seamless cross-border transactions, bypassing traditional banking systems.
* Investment Scams: Many scams involve fraudulent cryptocurrency investment schemes, attracting victims with promises of high returns.
* Money Laundering: Illicit profits are often converted into cryptocurrency and laundered through complex networks.
Combating the Crisis: A Multi-faceted Approach
Addressing this complex issue requires a coordinated international effort.
* Enhanced Law Enforcement Cooperation: Increased collaboration between law enforcement agencies across the Asia-Pacific region is essential. This includes intelligence sharing, joint investigations, and extradition treaties.
* Victim Identification & Rescue: Prioritizing the identification and rescue of victims is paramount. This requires specialized training for law enforcement and social workers.
* Disrupting Scam Networks: Targeting the financial infrastructure supporting these operations – cryptocurrency exchanges, money laundering networks – is crucial.
* public Awareness Campaigns: Raising public awareness about the risks of online scams and human trafficking can definitely help prevent individuals from falling victim.
* Strengthening Border Security: Improved border security measures can definitely help prevent the trafficking of individuals.
* International Pressure: Diplomatic pressure on countries harboring scam hubs is necessary to compel them to take action.
* Support for Victims: Providing comprehensive support services to victims – medical care, psychological counseling, legal assistance, and repatriation – is vital.