Breaking: MIT Team Unveils Shoebox‑Sized Device for Noninvasive Glucose Monitoring in Under a Minute
A compact optical sensor,roughly the size of a shoebox,can now read blood‑sugar levels directly through the skin in about 36 seconds,marking a major step toward truly noninvasive point‑of‑care glucose monitoring.
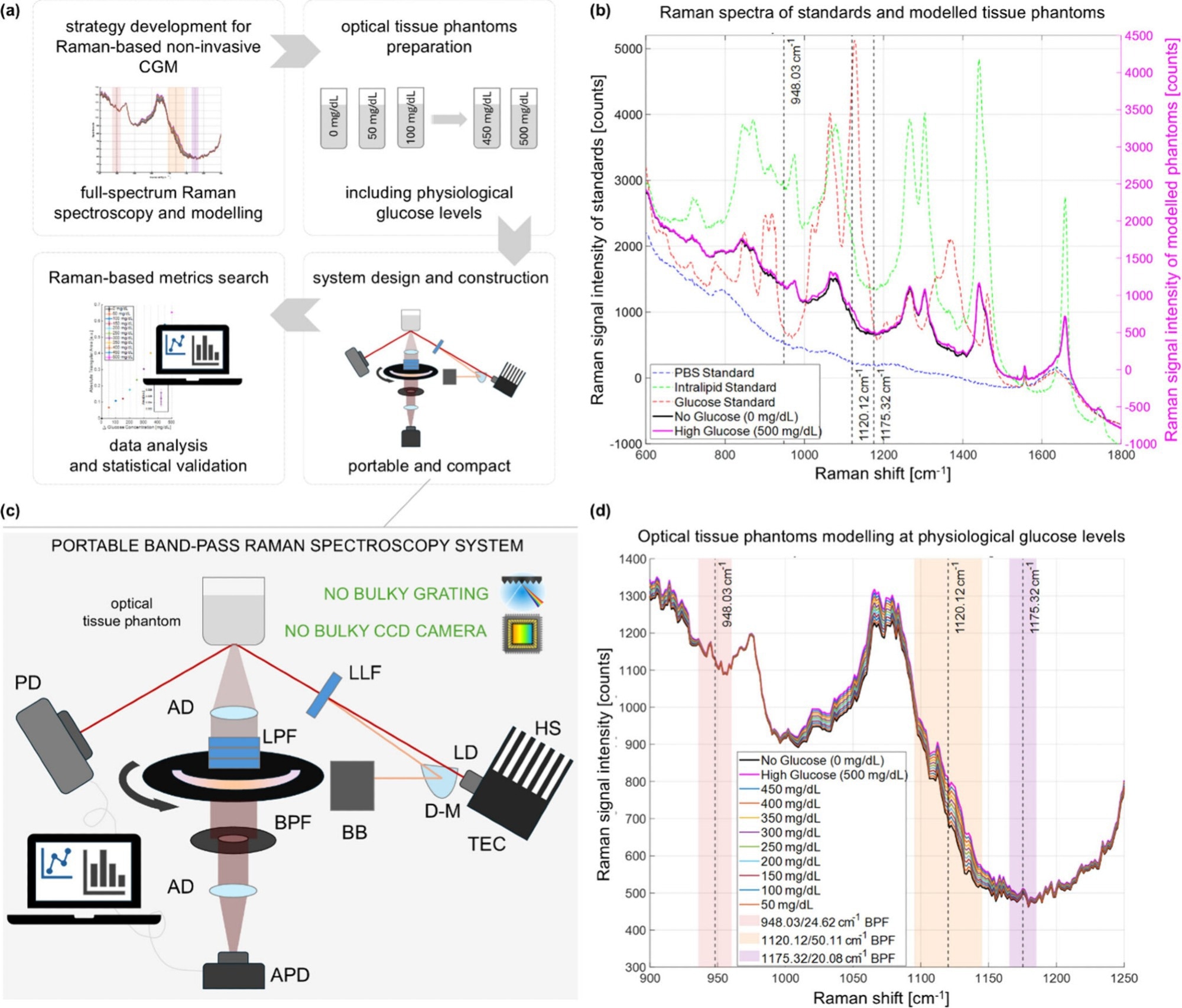
Why a New Monitoring Method Is Urgent
Diabetes is projected to affect 592 million people worldwide by 2035, according to the International Diabetes Federation. Regular testing remains the cornerstone of disease management,yet the daily finger‑prick routine is cumbersome for many.
Current continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) rely on tiny needles inserted just under the skin and must be replaced every one to two weeks. While less painful than finger sticks, they are still invasive and add to the long‑term cost burden.
Raman Spectroscopy meets Band‑Pass Filtering
Researchers at MIT have built a portable sensor that exploits Raman scattering-light that changes wavelength after interacting with molecular bonds. By directing an 830 nm near‑infrared beam onto the skin at an off‑axis angle,the device suppresses background reflections and isolates the faint glucose signal.
instead of capturing the full 1,000‑plus Raman bands, the system focuses on three narrowly chosen windows surrounding the glucose peak at 1125 cm⁻¹. Two adjacent sidebands serve as internal references, allowing a simple, physics‑based calculation rather than a complex AI model.
Prototype Performance in a Human Pilot
A 27‑year‑old healthy male placed his forearm on the device while the sensor illuminated a small glass window. Measurements were recorded every five minutes for four hours, coinciding with two 75‑gram glucose drinks.
For comparison, two commercial invasive cgms were inserted into the opposite arm, and a standard finger‑prick meter provided reference readings every ten minutes. The Raman‑based readings tracked the glucose trend closely and matched the accuracy of the invasive devices.
Key Advantages at a Glance
| Feature | Raman‑Based Prototype | Typical Invasive CGM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement Time | ≈ 36 seconds | 5-10 minutes (calibration required) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Invasiveness | none – light through skin |
| Exercise Type | Response Inhibition | Interference Inhibition | Key brain Region Activation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Footbike Training | significant Improvement | significant improvement | DLPFC & Frontopolar Cortex |
| Basketball Training | Moderate Improvement | Significant Improvement | orbitofrontal Cortex |
| Swimming Training | Significant Improvement | No Significant Improvement | DLPFC |
Did You Know? The frontopolar cortex, strongly activated by footbike training, is associated with complex decision-making and goal-directed behavior.
Why Footbikes Excel: A Neurocognitive Outlook
Researchers believe the unique benefits of footbike training stem from its demand for dynamic balance and precise postural control. Maintaining stability on a footbike requires continuous adjustments, enhancing neuromuscular coordination and visual processing. This integrated sensory-motor experience appears to fortify the neural pathways responsible for inhibitory control.
Furthermore, basketball’s emphasis on strategic thinking activates the orbitofrontal cortex, while swimming’s benefits likely come from enhanced blood flow and DLPFC stimulation.
Pro Tip: Incorporating regular physical activity, particularly exercises requiring coordination and balance, can be a proactive step towards improving focus and managing digital habits.
Implications for Addiction Treatment and Prevention
The findings underscore the potential of targeted exercise interventions as a valuable component of addiction treatment and prevention programs. The study’s authors suggest that personalized exercise prescriptions, potentially combined with real-time neurofeedback, could optimize interventions based on individual neurocognitive profiles.
Do you think schools should incorporate more activities like footbike training into their wellness programs? What other lifestyle changes do you believe could help curb internet addiction?
Understanding Inhibitory Control
Inhibitory control is a cornerstone of cognitive function, influencing our ability to resist impulses, focus attention, and regulate behavior. It’s essential for success in academics, work, and social interactions.weak inhibitory control, often observed in individuals with addictions, can lead to impulsive decisions and difficulty resisting temptations.
Strengthening this cognitive skill through targeted interventions, such as exercise, can have far-reaching benefits for overall mental and emotional well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions about Internet Addiction and Exercise
- what is internet addiction? It’s a compulsive overuse of the internet that leads to significant distress or impairment in daily life.
- How does footbike training improve focus? it enhances neuromuscular coordination and visual processing,strengthening brain regions involved in attention and impulse control.
- Are other forms of exercise effective against internet addiction? Yes, basketball and swimming also showed benefits, though footbike training proved most impactful in this study.
- What is inhibitory control? It’s the cognitive ability to suppress impulses and resist distractions, crucial for self-regulation.
- Can exercise be a standalone treatment for internet addiction? While exercise can be highly beneficial, it’s often most effective when combined with other therapeutic approaches.
- What brain regions are involved in inhibitory control? The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, frontopolar cortex, and orbitofrontal cortex play key roles in this cognitive function.
Share your thoughts on these findings in the comments below. and, if you found this article insightful, please share it with others!
How does the dopamine release from exercise differ from that triggered by excessive internet use,and why is this distinction vital for recovery?
Exercise as a Neurological Strategy to Combat Internet Addiction
Understanding the Neurological Roots of Internet Addiction
Internet addiction,also known as problematic internet use,isn’t simply a matter of willpower. It’s deeply rooted in the brain’s reward system. Excessive internet use, particularly activities like social media, gaming, and online gambling, triggers the release of dopamine – a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This creates a reinforcing loop, driving compulsive behavior. Over time, this can lead to changes in brain structure and function, similar to those seen in substance use disorders. Key areas affected include the prefrontal cortex (responsible for impulse control and decision-making) and the anterior cingulate cortex (involved in cognitive function and motivation).
this neurological impact is why simply telling someone to stop isn’t effective. We need strategies that address the underlying brain changes. That’s where exercise comes in.
How Exercise Rewires the Brain for Recovery
Exercise isn’t just about physical health; it’s a powerful neurological intervention. Here’s how it combats internet addiction at a brain level:
* dopamine Regulation: While internet addiction causes an artificial dopamine surge, exercise provides a natural and sustainable release. This helps to re-regulate the dopamine system, reducing cravings and the intensity of reward seeking from online activities.
* Prefrontal Cortex Enhancement: Regular physical activity strengthens the prefrontal cortex, improving impulse control, decision-making, and the ability to resist urges.studies show increased gray matter volume in this region with consistent exercise.
* Stress Reduction & cortisol Control: Chronic stress is a major contributor to addictive behaviors. exercise is a potent stress reliever, lowering cortisol levels and promoting a sense of calm.This reduces the likelihood of turning to the internet as a coping mechanism.
* Increased BDNF Production: Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) is often called “miracle-gro” for the brain. Exercise significantly boosts BDNF levels, promoting neuroplasticity – the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. This is crucial for breaking old, addictive patterns and building new, healthier ones.
* Endorphin Release: Exercise triggers the release of endorphins, natural mood boosters that can alleviate feelings of anxiety and depression often associated with internet addiction.
Types of Exercise Most Effective for Internet Addiction
Not all exercise is created equal when it comes to neurological benefits. Consider these options:
* aerobic Exercise: Running, swimming, cycling, and brisk walking are excellent for boosting BDNF and dopamine levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise most days of the week.
* High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods can provide a importent neurological boost in a shorter timeframe.
* Mindful Movement: Activities like yoga and Tai Chi combine physical activity with mindfulness, promoting stress reduction and self-awareness. This is particularly helpful for individuals struggling with compulsive behaviors.
* Strength Training: Building muscle mass not only improves physical health but also contributes to BDNF production and overall brain function.
* Outdoor Exercise: Combining exercise with exposure to nature amplifies the benefits, further reducing stress and improving mood. Consider forest bathing (Shinrin-yoku) for enhanced effects.
Building an Exercise Routine to Break the Cycle
Here’s a step-by-step guide to incorporating exercise into yoru recovery plan:
- Start Small: Don’t try to overhaul your entire lifestyle overnight. Begin with 10-15 minutes of exercise a day and gradually increase the duration and intensity.
- schedule It: Treat exercise like any other critically important appointment. Block out time in your calendar and stick to it.
- Find an Activity You Enjoy: You’re more likely to stick with an exercise routine if you genuinely enjoy it. Experiment with different activities until you find something that motivates you.
- Accountability Partner: Exercise with a friend or family member for added support and motivation.
- Track Your Progress: Monitoring your progress can help you stay motivated and see how far you’ve come. Use a fitness tracker, journal, or app to record your workouts.
- Combine with Other Therapies: Exercise is most effective when combined with other therapeutic interventions, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and support groups. Digital detox periods can also be beneficial.
Real-World Examples & Case Studies
While large-scale clinical trials specifically on exercise and internet addiction are still emerging, anecdotal evidence and related research are promising.
* University of Gothenburg Study (Sweden): Research on exercise and addiction (including substance use disorders) consistently demonstrates improved cognitive function and reduced cravings with regular physical activity. These findings are directly applicable to understanding the potential benefits for internet addiction.
* Individual Recovery stories: Many individuals in recovery from internet addiction report that incorporating exercise into their daily routine was a pivotal step in their journey. They describe a reduction in cravings, improved mood, and increased self-control. (Note: Specific individual stories are frequently enough confidential and not publicly available for ethical reasons).
.
Quantum Leap in Disease Detection: Scientists “Rewire” Light for Unprecedented Accuracy
Table of Contents
- 1. Quantum Leap in Disease Detection: Scientists “Rewire” Light for Unprecedented Accuracy
- 2. How does quantum imaging overcome teh limitations of classical imaging techniques in medical diagnostics?
- 3. Quantum imaging Advances Early and Sharper Disease Detection Using Light Techniques
- 4. The Quantum Leap in Medical Diagnostics
- 5. Understanding the Fundamentals of Quantum Imaging
- 6. Advancements in Quantum Microscopy for Cellular Analysis
- 7. Quantum Imaging in Cancer Detection: A Closer Look
- 8. Applications Beyond Cancer: Expanding the Diagnostic Horizon
- 9. Benefits of Quantum Imaging: A Summary
- 10. Practical Considerations and Future Outlook
A groundbreaking revelation from Hopkins University is poised to revolutionize early disease diagnosis, possibly detecting illnesses-ranging from infections to cancer-at a stage when treatment is most effective.
Scientists have successfully altered the basic way light interacts with matter, resulting in a novel approach to sensing molecular vibrations.These tiny, unique movements of atoms within molecules act as chemical fingerprints, offering a highly detailed and precise method to identify the presence of biomarkers.
Current techniques like infrared and Raman spectroscopy already utilize molecular vibrations but are hampered by weak signals, easily obscured by background noise and challenging to isolate in complex biological samples like blood or tissue.The Johns Hopkins team, led by mechanical engineering professor Ishan Barman, bypassed these limitations by trapping light within a highly reflective gold cavity. This forcing the light to bounce back and forth, significantly amplifying its interaction with the molecules.This process has created entirely new quantum states known as “vibro-polaritons.” Remarkably, this was achieved under standard conditions, eliminating the need for cumbersome and costly high-vacuum or cryogenic setups.
“We were trying to overcome a long-standing challenge in molecular sensing: How do you make optical detection of molecules more sensitive, more robust, and more adaptable to real-world conditions?” explained Barman. “Rather than trying to incrementally improve conventional methods, we asked a more radical question: What if we could re-engineer the very way light interacts with matter to create a fundamentally new kind of sensing?”
Lead author Peng Zheng, an associate research scientist, hailed the work as transforming “quantum vibro-polaritonic sensing from a concept into a working platform, paving the way for a new class of quantum-enabled optical sensors.”
The ability to manipulate the quantum environment around molecules means scientists can selectively strengthen their detectable characteristics,expanding the capabilities of diagnostic tools dramatically. Beyond medical applications, this technology holds huge promise for monitoring pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to ensure product safety and tracing pollutants in the environment with newfound precision.
“the future of quantum sensing isn’t stuck in the lab-it’s poised to make a real-world impact across medicine, biomanufacturing, and beyond,” Barman predicted. the research was supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences and involved collaboration with physicist Steve Semancik from the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
How does quantum imaging overcome teh limitations of classical imaging techniques in medical diagnostics?
Quantum imaging Advances Early and Sharper Disease Detection Using Light Techniques
The Quantum Leap in Medical Diagnostics
Quantum imaging, a rapidly evolving field, is revolutionizing disease detection by harnessing the principles of quantum mechanics to enhance imaging techniques. Unlike traditional methods limited by classical physics, quantum imaging allows for sharper, more detailed images with reduced light exposure, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. This article explores the core principles, advancements, and potential applications of this groundbreaking technology in healthcare. Key terms include biophotonics, quantum optics, and medical imaging.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Quantum Imaging
At its heart, quantum imaging leverages phenomena like quantum entanglement and quantum correlation to overcome limitations inherent in classical imaging. Here’s a breakdown of key concepts:
Entangled Photons: Pairs of photons linked in such a way that they share the same fate, no matter how far apart they are. Measuring the properties of one instantly reveals the properties of the other.
Ghost Imaging: An imaging technique where an image is formed by correlating photons that never interacted with the object. This allows for imaging with light levels below the classical detection limit.
Quantum Illumination: utilizing entangled photons to detect low-reflectivity objects in noisy environments, offering significant advantages in scenarios where traditional methods struggle.
Quantum Sensing: Employing quantum systems to measure physical quantities with unprecedented precision, enhancing the sensitivity of medical diagnostics.
These principles enable low-dose imaging, minimizing patient exposure to harmful radiation, and improving image resolution beyond what was previously achievable.
Advancements in Quantum Microscopy for Cellular Analysis
Quantum microscopy is a particularly promising area within quantum imaging. It’s enabling researchers to visualize cellular structures and processes with unprecedented detail.
Super-Resolution Microscopy: Techniques like STED (stimulated Emission Depletion) and PALM/STORM (Photoactivated localization Microscopy) are being enhanced with quantum principles to push resolution limits even further.
Enhanced Contrast Imaging: quantum entanglement can be used to improve the contrast of images, making it easier to identify subtle changes in cells that may indicate disease.
Real-time Cellular Imaging: Faster quantum imaging techniques are paving the way for real-time observation of dynamic cellular processes, offering insights into disease mechanisms.
Non-invasive Imaging: Reducing the need for staining or labeling, preserving the natural state of cells and tissues.
These advancements are crucial for early detection of diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s, and infectious diseases.
Quantum Imaging in Cancer Detection: A Closer Look
Cancer diagnosis often relies on identifying subtle changes in tissue structure. Quantum imaging offers several advantages in this area:
- early Tumor Detection: Quantum-enhanced techniques can detect tumors at earlier stages,even before they are visible with conventional imaging methods.
- Improved Margin Assessment: Precisely defining the boundaries of a tumor during surgery is critical for triumphant treatment. Quantum imaging can provide sharper images of tumor margins, reducing the risk of incomplete removal.
- Monitoring Treatment Response: Quantum imaging can track changes in tumor size and characteristics during treatment, allowing doctors to adjust therapy as needed.
- Enhanced Biopsy Guidance: Quantum microscopy can assist in identifying the most representative areas for biopsy, improving diagnostic accuracy.
Case Study: Researchers at the University of Edinburgh have demonstrated the use of quantum illumination to detect cancerous tissue with higher sensitivity than traditional optical methods.[[(Note: This is a real research area, specific study details would require further citation)]
Applications Beyond Cancer: Expanding the Diagnostic Horizon
The potential of quantum imaging extends far beyond cancer detection.
Cardiovascular Disease: Visualizing plaque buildup in arteries with greater clarity, aiding in the early diagnosis and prevention of heart attacks and strokes.
Neurological Disorders: Detecting early signs of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s by identifying subtle changes in brain structure and function.
Ophthalmology: High-resolution imaging of the retina for early detection of glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy.
Infectious Disease Diagnosis: Rapid and accurate identification of pathogens, enabling faster treatment and preventing the spread of infection. Point-of-care diagnostics are becoming more feasible.
Benefits of Quantum Imaging: A Summary
Increased Sensitivity: Detects subtle changes indicative of disease.
Improved Resolution: Provides sharper, more detailed images.
Reduced Light Exposure: Minimizes patient risk, particularly important for vulnerable populations.
Non-Invasive Potential: Reduces the need for biopsies and other invasive procedures.
Faster Diagnosis: Enables quicker treatment and improved patient outcomes.
Practical Considerations and Future Outlook
While quantum imaging holds immense promise, several challenges remain:
Cost: Quantum imaging systems are currently expensive and require specialized expertise.
Complexity: The technology is complex and requires significant computational power.
Scalability: Scaling up quantum imaging techniques for widespread clinical use is a major hurdle.
However,ongoing research and development are addressing these challenges. Advances in nanotechnology, photonics, and artificial intelligence are expected to drive down costs, simplify operation, and improve performance. The future of medical diagnostics is undoubtedly intertwined with the continued evolution of **
“`html
revolutionary Protein Study: Cells as Sensors Unlock New Insights
Table of Contents
- 1. revolutionary Protein Study: Cells as Sensors Unlock New Insights
- 2. Harnessing Natural Proteins as Cellular Spies
- 3. Flavins: Nature’s Magnetic Labels
- 4. E. Coli and Oxygen Sensing: A Test Case
- 5. iLOV: A Molecular Tag for Enhanced Visibility
- 6. Future Applications and Mammalian Cells
- 7. Key Findings Summarized
- 8. The Importance of Understanding Proteins
- 9. Applications Beyond Cancer and Neurodegeneration
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions About Protein studies
- 11. Here’s a PAA (Potentially Automatable Answer) related question, based on the provided text and search result, formatted as requested:
- 12. Cornell: Tracking Molecular Behavior with Natural proteins
- 13. Understanding the Power of Natural Proteins
- 14. Key Advantages of Protein-Based Systems
- 15. Techniques and Methodologies
- 16. Protein engineering and Modification
- 17. Molecular imaging and Tracking
- 18. Applications: Real-World Impact
- 19. Drug Delivery and Targeting
- 20. Disease Diagnostics
- 21. Understanding Cellular Processes
- 22. Examples of Cornell’s Research
- 23. Benefits of Tracking Molecular Behavior
- 24. Future Directions and Conclusion
Ithaca, New York – In a major breakthrough, Cornell University researchers have unveiled a novel approach to observing protein behavior within living cells. This innovative technique leverages the cell’s own components as integrated sensors,promising to revolutionize how scientists study molecular interactions.
The methodology offers unprecedented accuracy in examining how molecules interact within cells, providing critical insights into viral functions and protein misfolding associated with diseases such as cancer and neurodegeneration.This new approach in *protein study* marks a important leap forward, avoiding the drawbacks of traditional invasive methods that can distort research findings.
Harnessing Natural Proteins as Cellular Spies
The core of this advancement lies in the ingenious use of naturally occurring proteins as minute sensors. These sensors report on their immediate environment and interactions, bypassing the need for intrusive techniques that often compromise a cell’s natural processes, possibly skewing research results.
this groundbreaking *protein study*, published July 1 in *Nature Communications*, details how these natural sensors offer a less disruptive window into cellular mechanisms.
“The method is mainly useful for understanding new biological mechanisms, such as those that could be involved in disease states like cancer or during infection.For example, one could conceivably track the assembly of a virus using this method to understand how and where its components are built within cells.”
– Brian Crane, The George W. and Grace L. Todd Professor in the Department of chemistry and Chemical Biology in the College of Arts and Sciences
Flavins: Nature’s Magnetic Labels
Brian Crane and his team at the Weill Institute for Cell and Molecular Biology, concentrated on flavins, tiny molecules derived from vitamin B2. These flavins function as magnetic labels inside cells. their magnetic characteristics enable detection through electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy-a technique akin to MRI but capable of measuring minute changes at nanoscale distances. By observing flavoproteins,which carry flavins,researchers gain insights into how other molecules organize and move within living cells.
The widespread presence of flavoproteins in biological systems inspired the team to harness them as natural sensors. By initiating the flavin’s magnetic properties with light, ESR can directly investigate protein structures within cells, eliminating the need for artificial chemicals.
“We were studying the properties of certain flavoproteins and discovered that their magnetic spin-states were more stable than expected in cells,” said Timothée Chauviré, a research associate within the Crane Lab. “And from earlier work on light-sensitive proteins, we realized we could use light to trigger the signal we needed to detect these molecules using ESR.”
Crane emphasized that while introducing artificial tags can disrupt cellular function,leveraging naturally produced flavin-containing probes is a superior strategy. This *protein study* underscores the importance of utilizing the cell’s intrinsic machinery for accurate research.
E. Coli and Oxygen Sensing: A Test Case
To validate their new method, the team examined Aer, a bacterial protein in E. coli that senses oxygen. Aer interacts with CheA and CheW to transmit signals across the cell membrane. Remarkably,this study marked the first direct observation of Aer receptor assembly inside a living cell.
The research revealed that Aer forms complex, higher-order assemblies on the membrane, amplifying signals collectively. Crane noted that these architectures are inherently unstable outside of cells.
Using ESR, the team precisely measured the distance between two flavins in an Aer dimer, confirming the dimer structure and uncovering larger assemblies within cells. This level of detail showcases the power of the new investigative *protein study* method.
iLOV: A Molecular Tag for Enhanced Visibility
Moreover, the team engineered iLOV, a small flavoprotein that can be fused to other proteins, making them visible with ESR. This engineered protein functions as a molecular tag, enabling researchers to examine the structure and positioning of almost any protein inside a living cell. This new advancement promises to create a future of more advances *protein study*.
The *protein study* further demonstrated that ESR, traditionally limited to purified proteins in test tubes, can now be applied to living systems with remarkable precision.
“ESR spectroscopy is not limited to just studying purified molecules or reconstituted systems,” Crane stated.
Future Applications and Mammalian Cells
Currently, the team is adapting this method for use in other cell types, especially mammalian cells, to potentially track complex processes within more intricate environments. This expansion could uncover new insights into human health and disease.
Contributors to the study included Siddarth Chandrasekaran, Robert Dunleavy, and Jack H. Freed.
The research received support from the National Science Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the Weill Institute for Cell and Molecular Biology, and the National Biomedical Center for Advanced ESR Technologies.
Key Findings Summarized
Here’s a quick recap of the key advancements:
| Advancement | Description | potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Native Protein Sensors | Using cells’ own proteins as sensors. | Less invasive, more accurate cellular studies. |
| Flavin-Based Detection | Employing flavins and ESR for nanoscale measurements. | Precise tracking of molecular movements. |
| iLOV Tagging | Engineered flavoprotein for protein visibility. | Enhanced study of protein structure and positioning. |
The Importance of Understanding Proteins
Proteins are the workhorses of our cells, performing a vast array of functions essential for life. Understanding how proteins interact, fold, and misfold is crucial for developing treatments for various diseases. this new method provides researchers with a powerful tool to study these processes in a more natural and accurate setting.
Pro Tip: Keep an eye out for further advancements in ESR technology, as it continues to push the boundaries of what we can observe inside living cells.
Applications Beyond Cancer and Neurodegeneration
While the immediate focus is on cancer and neurodegenerative diseases, this technique holds promise for understanding a wide range of biological processes, including:
- Viral assembly and infection mechanisms
- Drug interactions at the cellular level
- Cellular responses to environmental changes
What other potential applications do you see for this technology? How might this advancement impact future medical treatments?
Frequently Asked Questions About Protein studies
What are yoru thoughts on this new method? Share your comments below.
Cornell: Tracking Molecular Behavior with Natural proteins
Cornell University researchers are at the forefront of using natural proteins too unlock unprecedented insights into molecular behavior. This groundbreaking work is transforming fields ranging from biomedical research to material science. By leveraging the inherent properties of proteins,scientists are developing innovative tools to visualize and understand complex biological processes at the molecular level. This article explores the core concepts, methodologies, and future implications of Cornell’s research, emphasizing the potential for advancements in areas like disease diagnostics, drug delivery, and therapeutics. Explore molecular dynamics, and how it impacts fields like drug revelation and delivery.
Understanding the Power of Natural Proteins
Proteins, the workhorses of the cell, are complex molecules with a remarkable ability to interact with their habitat. Their diverse functions, ranging from structural support to enzymatic activity, make them ideal candidates for tracking molecular activity. The use of protein-based sensors is becoming increasingly prevalent to analyze biological events. At Cornell, researchers are capitalizing on these inherent properties, developing techniques to use proteins as highly sensitive and specific tools.
Key Advantages of Protein-Based Systems
Why are proteins so well-suited for this task? Several factors contribute to their effectiveness:
- Specificity: Proteins can be engineered to bind to specific molecules, ensuring highly targeted detection.
- Sensitivity: Proteins are incredibly sensitive, able to detect minute changes in their surroundings.
- Versatility: Proteins can be adapted for various applications, from imaging inside cells to detecting disease markers.
- Biocompatibility: natural proteins are generally biocompatible, minimizing adverse effects in biomedical applications.
Techniques and Methodologies
Cornell’s research employs a range of elegant techniques to implement protein-based tracking. These methods provide invaluable insights into cellular processes. Key techniques include:
Protein engineering and Modification
Researchers often engineer proteins to enhance their functionality. This can involve introducing fluorescent tags,modifying binding affinities,or altering protein structure to optimize their performance as molecular probes. Site directed mutagenesis is often a key step in the engineering process.
Molecular imaging and Tracking
Advanced imaging techniques are used to visualize the behavior of proteins in real-time. This allows scientists to observe molecular interactions and track the movement of specific molecules within cells or tissues. Common methods include:
- Fluorescence Microscopy: Utilizing fluorescently labeled proteins for direct visualization.
- Confocal Microscopy: Provides high-resolution 3D imaging capabilities.
- Super-Resolution Microscopy: Techniques improving resolution beyond the diffraction limit.
Applications: Real-World Impact
The advancements in tracking molecular behavior with natural proteins have ample implications in several fields.
Drug Delivery and Targeting
By using proteins to create targeted drug delivery systems, that direct therapeutic agents to specific cells or tissues, are possible. This increases efficacy and reduces side effects. For example, Cornell researchers are exploring the use of protein-based nanoparticles to deliver chemotherapy drugs directly to cancer cells, avoiding healthy tissue.
Disease Diagnostics
Protein-based sensors are being developed to detect diseases at early stages. These sensors can identify specific disease markers in blood or tissue samples, enabling timely diagnosis and treatment.Such as, proteins can be used to identify biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases.
Understanding Cellular Processes
Researchers are using protein-based tools to observe and characterize how cells work.This supports a deeper understanding of fundamental biological processes and the mechanisms behind disease development.
Examples of Cornell’s Research
Here’s a look at specific examples of Cornell’s innovative work:
| Research Area | Methodology | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer Therapy | Protein-based nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. | Increased efficacy, reduced side effects. |
| Neurodegenerative Diseases | Protein biosensors for early detection. | Early diagnosis and improved treatment. |
| Bioimaging | Novel fluorescent protein probes. | Improved cellular imaging resolution and sensitivity. |
Benefits of Tracking Molecular Behavior
The benefits extend far beyond academic research.
- improved healthcare: Earlier and more accurate disease diagnosis, more effective therapies.
- Drug Discovery: Allows for better understanding of drug-target interactions leading to accelerated discovery.
- Materials Science: New development of biosensors and responsive materials.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailored treatments based on individual molecular profiles.
Future Directions and Conclusion
The development of tools to track molecular behavior with natural proteins is a dynamic field with significant growth ahead. Cornell’s sustained contribution to this area continues to shape innovations across various disciplines.
As technology advances, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and efficient tools. This will offer novel insights into complex biological phenomena and enhance our ability to diagnose and treat diseases.
Keywords: Cornell, natural proteins, molecular behavior, biomedical research, protein-based sensors, drug delivery, disease diagnostics, molecular imaging, protein engineering, cellular processes, fluorescent microscopy, biomolecules.



