“`html
Astronomers Discover ‘Teenage Vampire’ White Dwarf, Key to Stellar Evolution
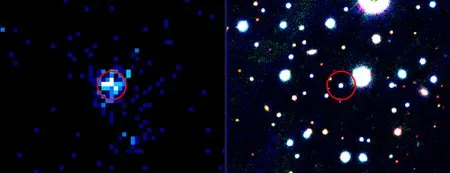
A Revolutionary discovery has been made by astronomers: a “teenage vampire” white dwarf star. This celestial body represents the missing link between the death of sun-like stars and the birth of white dwarf stellar remnants. The white dwarf, named Gaia22ayj, is located approximately 8,150 light-years away from Earth and is actively consuming stellar plasma from a nearby companion star.
Gaia22ayj: A Cosmic Vampire Unveiled
observed using the Zwicky transient Facility (ZTF) at the Palomar Observatory in California, Gaia22ayj initially stood out due to its rapidly pulsing signal. This led to its initial classification as a detached double white dwarf binary-a system of two white dwarf stars orbiting one another.However, further observations revealed a different, more intriguing reality.
The star exhibited brightness increases of up to 700% in a mere two minutes, marking it as one of the most extreme pulsating objects ever observed. The clarification? Gaia22ayj is a white dwarf actively feeding off a companion star,placing it in a rare and fleeting phase of stellar evolution.

Stellar Death and Rebirth: Understanding White Dwarf evolution
The life cycle of stars is dictated by their mass. Stars considerably larger than our Sun meet a dramatic end in supernova explosions, eventually becoming neutron stars or black holes. Stars similar in mass to our Sun, however, transform more quietly into white dwarfs after shedding their outer layers as red giants.
In binary systems, where two stars orbit a common center, white dwarfs can experience a resurgence by drawing material from their companion star. This vampiric process is precisely what’s occurring with Gaia22ayj.

Unraveling the Mystery of Gaia22ayj
Initially, astronomers were puzzled by Gaia22ayj’s unusual light curve.Tony Rodriguez, a graduate student at the California Institute of Technology, discovered that Gaia22ayj is likely orbited by a low-mass star instead of another white dwarf. Furthermore,the white dwarf component is highly magnetic and spins rapidly.
This discovery led to the realization that Gaia22ayj represents a missing link in the evolution of white dwarf pulsars, showcasing an early, short-lived phase where the star develops a strong magnetic field and begins to siphon matter from its companion.
The Meaning of the “Teenage” Phase
This “teenage” phase in a white dwarf‘s life lasts approximately 40 million years. While seemingly long, it constitutes a mere 0.4% of a star’s total lifespan. This discovery provides invaluable insights into a critical, yet brief, period in stellar evolution.
Data from the W. M.Keck Observatory confirmed the presence of a strong magnetic field and the funneling of matter onto the white dwarf. Additional data from the Palomar Observatory revealed the system is slowing down remarkably.
the research findings were published in February in the journal Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific.
key Differences in Stellar remnants
Here’s a swift look at the different types of stellar remnants, and their characteristics:
| Stellar Remnant | Formation | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| White Dwarf | Stars similar to the Sun | Small, dense, hot; gradually cools over billions of years |
| Neutron Star | Supernova explosions of massive stars | Extremely dense, strong magnetic fields, rapid rotation |
| Black Hole | Supernova explosions of very massive stars | region of spacetime with gravity so strong that nothing can escape |
Did you know?
White dwarfs can sometimes reignite through thermonuclear events if they accrete enough mass from a companion star, leading to a Type Ia supernova.
Pro tip
Amateur astronomers can contribute to white dwarf research by participating in citizen science projects that analyze light curves from telescopes like ZTF and Pan-STARRS.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
