Stay ahead with breaking tech news, gadget reviews, AI & software innovations, cybersecurity tips, start‑up trends, and step‑by‑step how‑tos.
Table of Contents
- 1. California Driver’s Homemade License Plate Fails to Fool Authorities
- 2. Ingenious Effort,Illegal Act
- 3. What To Do when A License Plate Is Lost Or Stolen
- 4. The Importance of Vehicle Registration
- 5. Frequently Asked Questions About License plates
- 6. What specific section of the California Vehicle Code addresses license plate regulations?
- 7. Custom License Plate Leads to Legal Trouble for California Driver
- 8. Understanding California’s License Plate Laws
- 9. What Constitutes an Illegal License Plate?
- 10. The Recent Case: A Costly Customization
- 11. The Process for Obtaining a Personalized License Plate
- 12. Common Reasons for Plate Application Rejection
- 13. Legal Consequences of Violating License Plate Laws
- 14. Protecting Yourself: Practical Tips
- 15. Resources for Further Details
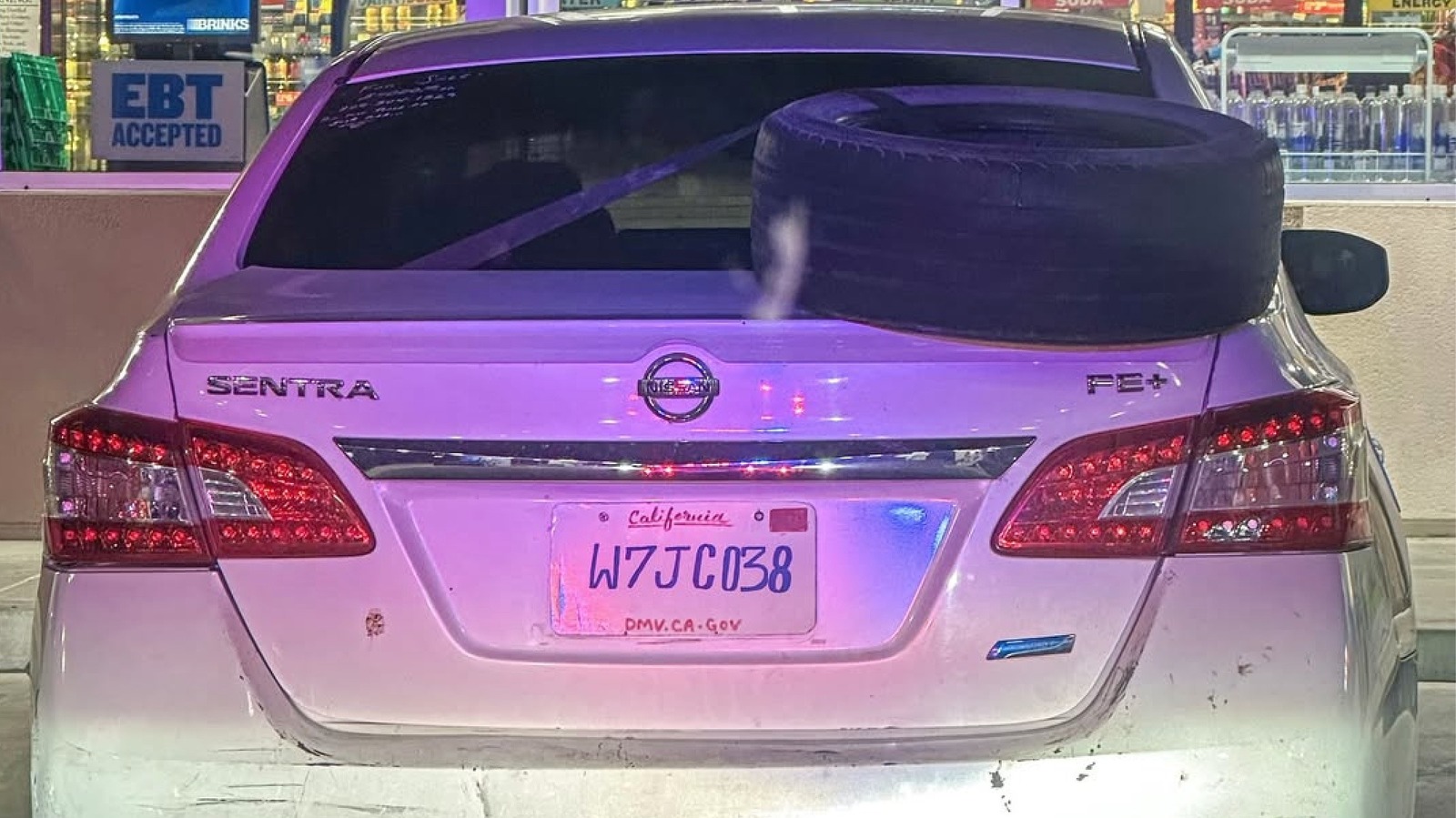
A Merced resident’s attempt to replicate a missing license plate with hand-drawn artistry proved unsuccessful, highlighting the legal risks of operating a vehicle without proper registration.
Ingenious Effort,Illegal Act
Recent events in Merced,California,demonstrate that even the most creative solutions aren’t always legal ones.A California Highway Patrol Officer initiated a traffic stop after observing an anomaly with a vehicle’s rear license plate. A subsequent inspection revealed the plate was a meticulously crafted forgery, with the driver having attempted to recreate a standard-issue California plate entirely by hand, including the distinctive cursive lettering.
While the officer acknowledged the driver’s dedication, the Highway patrol emphasized that displaying a non-official license plate constitutes a violation of the law. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, approximately 1.2 million vehicles are stolen in the United States annually, and fraudulent license plates frequently enough facilitate these crimes.
Law enforcement agencies utilize Automatic License Plate Readers (ALPRs) that scan plates and cross-reference them with databases containing details about vehicle registration, warrants, and stolen vehicles. These systems can instantly reveal a vehicle’s status, making it difficult to operate an unregistered or fraudulently plated vehicle undetected.
What To Do when A License Plate Is Lost Or Stolen
Facing a missing or stolen license plate can be stressful, but there are established procedures to follow that prevent legal ramifications. Authorities recommend reporting the incident promptly to the local police department. Creating a police report provides documentation for your state’s Department of Motor Vehicles and can protect you from liability if the plate is used in illegal activities.
Contacting the DMV is the next crucial step. Many states offer online or mail-in options for requesting a replacement plate, streamlining the process for vehicle owners. however, in-person visits may be required in some jurisdictions.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Report the loss/theft to local police. |
| 2 | File a report with your state’s DMV. |
| 3 | Gather required documentation (ID, registration, proof of insurance). |
| 4 | Pay the replacement fee. |
Did You Know? Replacing a lost or stolen license plate typically incurs a fee, varying by state, ranging from $20 to $100.
Pro Tip: Keep a record of your license plate number in a safe place, such as with your vehicle registration and insurance documents.
The Importance of Vehicle Registration
Maintaining valid vehicle registration is more then just a legal requirement. It ensures that vehicles on public roads meet safety standards and are properly insured. Regular vehicle inspections, frequently enough tied to registration renewal, help identify and address potential mechanical issues, contributing to safer roadways for everyone.
Furthermore,registration fees contribute to funding for road maintenance and infrastructure improvements. By ensuring vehicles are properly registered, drivers actively participate in supporting the transportation system they rely on.
Frequently Asked Questions About License plates
- What happens if I drive with a missing license plate? Driving without a valid license plate is generally illegal and can result in fines, vehicle impoundment, or even arrest.
- Can I make a temporary license plate myself? No, creating a temporary license plate is illegal. You must obtain an official replacement from your state’s DMV.
- What information do I need to replace a lost license plate? Typically, you will need a valid driver’s license, vehicle registration, proof of insurance, and a police report (if applicable).
- How long does it take to get a replacement license plate? Processing times vary by state,but it generally takes between one to three weeks to receive a replacement plate.
- What if I suspect someone is using a fake license plate? Report your suspicions to your local law enforcement agency.
What specific section of the California Vehicle Code addresses license plate regulations?
Custom License Plate Leads to Legal Trouble for California Driver
Understanding California’s License Plate Laws
California Vehicle Code (CVC) Section 5200 outlines strict regulations regarding license plates.While personalized or custom license plates are popular, they must adhere to specific guidelines. A recent case highlights the potential legal ramifications of failing to comply with these rules. The core issue isn’t personalization itself,but obscuring readability or displaying offensive content. This applies to both standard-issue plates and vanity plates.
What Constitutes an Illegal License Plate?
Several factors can render a california license plate illegal, leading to fines, vehicle impoundment, and even court appearances. These include:
* Obscured Numbers/Letters: Any alteration that makes the plate challenging to read, such as covering it with a clear cover, mud, or damage.
* Reflective Materials: Adding reflective tape or materials that alter the plate’s visibility.
* Unauthorized Modifications: Changing the plate’s shape, size, or colour.
* Offensive or Misleading Content: Plates deemed offensive, vulgar, or that misrepresent official law enforcement or government agencies. The DMV has a extensive list of prohibited combinations.
* Incorrect Spacing or Font: Altering the spacing between characters or using a different font.
The Recent Case: A Costly Customization
In September 2025, a driver in Los Angeles County was cited after a California Highway Patrol officer noticed their custom license plate was intentionally designed to resemble a different, official-looking plate. While the driver claimed it was a harmless aesthetic choice, the officer resolute it violated CVC 5200, specifically regarding misrepresentation.
The driver faced:
- A fine of over $250.
- Mandatory court appearance.
- Requirement to replace the plate with a standard-issue California license plate.
- Potential for increased insurance premiums due to the traffic violation.
This case serves as a stark reminder that license plate regulations are taken seriously in California.
The Process for Obtaining a Personalized License Plate
California offers a variety of personalized license plate options through the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV).Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Check Availability: Use the DMV’s online plate availability tool to see if yoru desired combination is available. (https://www.dmv.ca.gov/portal/personalized-license-plates/)
- Application: Complete the online application or visit a DMV office.
- Fees: Pay the required application and annual renewal fees. Fees vary depending on the plate type.
- Approval: The DMV reviews the application to ensure it complies with all regulations.
- Plate Issuance: Onc approved, the DMV will issue your personalized plate.
Common Reasons for Plate Application Rejection
The DMV frequently rejects applications for:
* Profanity or Offensive Language: Any combination deemed inappropriate.
* similarity to existing Plates: Avoiding confusion with existing standard or personalized plates.
* Political Statements: Plates expressing strong political views are often rejected.
* References to Illegal Activities: any implication of illegal behavior.
Legal Consequences of Violating License Plate Laws
Beyond the case mentioned above, violations of California’s license plate laws can lead to meaningful consequences. These include:
* Fix-It Tickets: Often issued for minor infractions, requiring the driver to correct the issue and provide proof of compliance to the court.
* Traffic Citations: Resulting in fines and points on your driving record.
* Vehicle Impoundment: In severe cases, the vehicle may be impounded until the issue is resolved.
* Criminal Charges: intentional obstruction of a license plate or fraudulent use of a plate can lead to criminal charges.
Protecting Yourself: Practical Tips
* Keep Your Plate Clean: Regularly clean your license plate to ensure it’s visible.
* Avoid Covers: Do not use clear covers or any materials that obscure the plate.
* Report Damaged Plates: If your plate is damaged, replace it instantly at the DMV.
* Review DMV Guidelines: Familiarize yourself with the DMV’s regulations regarding license plates.
* Choose Wisely: when applying for a vanity plate, carefully consider your chosen combination to avoid potential rejection.
Resources for Further Details
* California DMV: https://www.dmv.ca.gov/
* California Vehicle Code: [https://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/codes_displaySection.xhtml?lawCode=VEH§ionNum=5200](https://leg