Soft Robotic Heart Breakthrough offers New Hope For Heart failure Patients
Table of Contents
- 1. Soft Robotic Heart Breakthrough offers New Hope For Heart failure Patients
- 2. the Hybrid Heart: A New Era In Cardiac Support
- 3. Addressing The Limitations Of Current Artificial Hearts
- 4. Hybrid Heart: Design And Functionality
- 5. Performance And Testing Of The Innovative Artificial Heart
- 6. Closed Fluidic System For Future Implants
- 7. Advantages Of The Hybrid Heart
- 8. Future Directions And Clinical Implications
- 9. The Future Of Heart Failure Treatment
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions About The Soft Robotic Heart
- 11. Soft Robotics Revolutionizes Artificial Hearts: A Leap Forward in Cardiac Care
- 12. Soft Robotics Revolutionizes Artificial Hearts: A Leap Forward in Cardiac Care
- 13. The Science of soft Robotics in Artificial Heart Design
- 14. Key features of Soft Robotic Artificial Hearts
- 15. Benefits of Soft Robotics for Artificial Hearts
- 16. List of Benefits:
- 17. Real-world Applications and Advancements
- 18. Case Study: The Zurich Artificial Heart
- 19. Table: Soft Robotic Artificial Heart Technologies
- 20. The Future of Artificial Hearts and Soft Robotics
A Groundbreaking Soft Robotic Heart Has Been Developed, Perhaps Revolutionizing The Treatment Of End-Stage Heart Failure. This Innovative Device brings Researchers Closer to Creating Fully Functional, Biocompatible Artificial Organs, Offering A Beacon Of Hope For Patients Awaiting Heart Transplants.
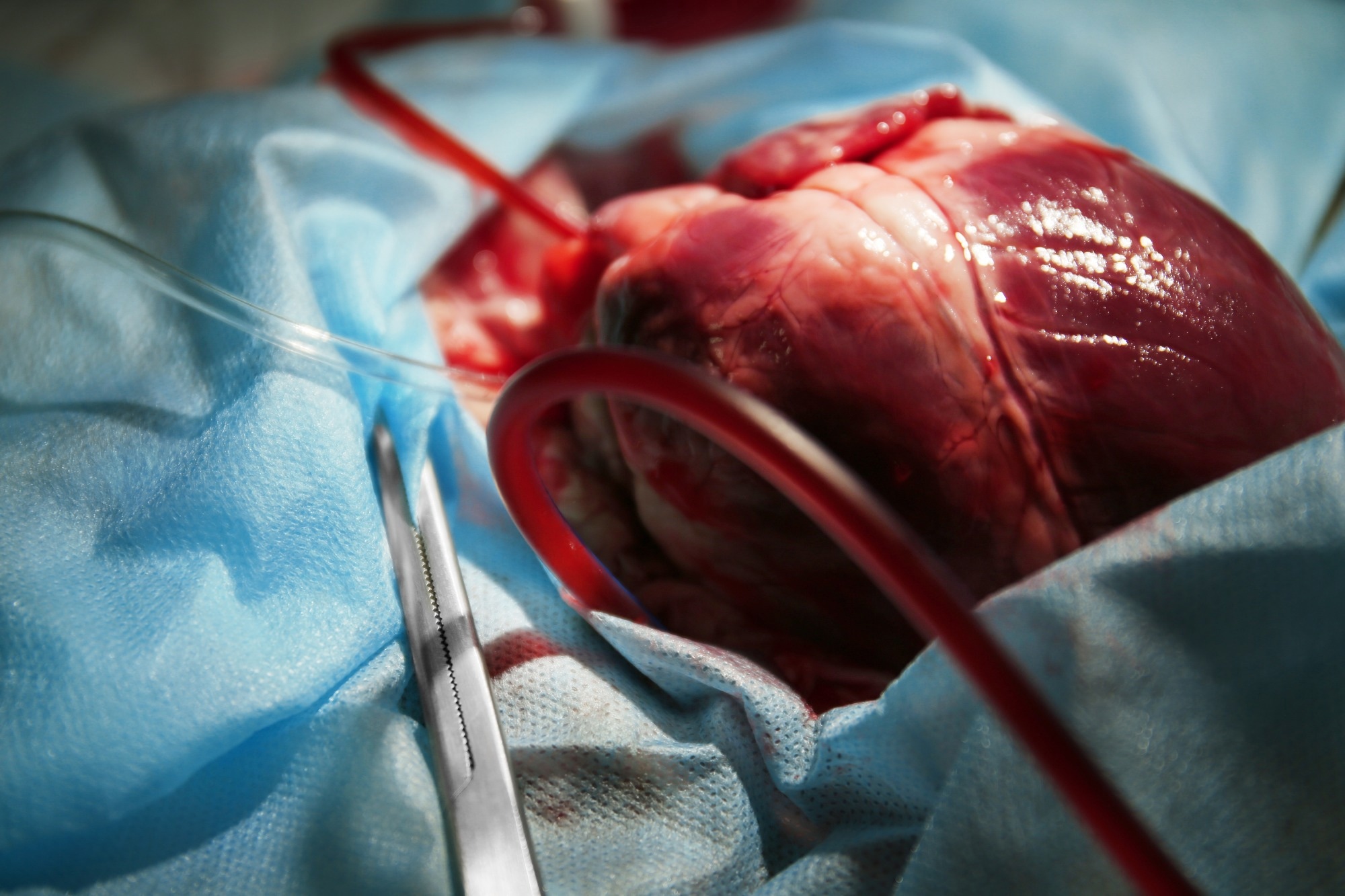
the Hybrid Heart: A New Era In Cardiac Support
The Hybrid Heart, A Total Artificial Heart Powered By Soft Robotics, Represents A Significant Leap Forward. Published In Nature Communications,The Research Details The Design And Functionality Of This Device,Opening Doors To New Possibilities In Heart Failure Treatment And Transplantation Medicine.
Addressing The Limitations Of Current Artificial Hearts
End-Stage Heart Failure Carries A High Mortality Rate, and While Heart Transplantation Remains A Viable Treatment, The Scarcity Of Donor Hearts Is A Critical Challenge. Existing Total Artificial Hearts And Left Ventricular Assist Devices Frequently enough Suffer From Poor Biocompatibility Due To Non-Biological Materials, Leading To Blood Clot Formation And Other Complications.
Moreover, Percutaneous drivelines, Necessary For Powering These Devices, Increase The Risk Of Infection And Diminish The PatientS Quality Of Life. These Drawbacks Limit The Widespread Clinical application Of Current Artificial Heart Technologies. The Newly Developed Hybrid Heart Aims To Alleviate These Issues By Mimicking The Natural Physiology Of The Human Heart.
Hybrid Heart: Design And Functionality
The Hybrid Heart Is Engineered To Replicate The Structure And Function Of A Natural Human Heart. It Features Two Chambers, Similar To The Left And Right Ventricles, Separated By A Soft Pneumatic Muscle Acting As A Septum.
The Ventricles And Septum Are Constructed From Nylon Coated Wiht Thermoplastic Polyurethane. This Design Incorporates Inextensible Wires Arranged In A Closed Loop, Distributing forces Across Both Ventricles to Mimic The heart’s Coordinated Contractions.
To Enhance Biocompatibility, Supramolecular Coatings Are Applied To The Thermoplastic polyurethane-Coated Nylon Material. Air Pressure Controls The Inflation And Deflation Of The Septum, Squeezing The Ventricles During Systole To eject Blood, Emulating A Natural Heartbeat. During Diastole, The Ventricles passively Refill.
By Adjusting The Length And Number Of Wires Around Each Ventricle, The Cardiac Output Of Each chamber Can Be Tailored.This Adaptability Is Crucial for Meeting Individual Patient Needs, Especially In Conditions Like Pulmonary Hypertension.
The Device’s Soft Robotic Actuation Mechanism Converts A Constant Air Pump Flow Into pressure Pulses, Driving The Hybrid Heart Without Relying Heavily On Electronics. While Electronic Components Are Present for Power And Control, Especially In The Implantable Versions, The Core Mechanics Are Pneumatically Driven.
Performance And Testing Of The Innovative Artificial Heart
Laboratory Testing Under Physiological conditions Showed The Hybrid Heart Mimics The Human Heart’s Pumping Action. The Left Ventricle Achieved A Cardiac Output Of 5.7 Liters Per Minute At 60 Beats Per Minute. The Right ventricle Was Adjusted To 5 liters Per Minute To Reflect Natural Physiological Differences.
The Device Was Surgically Implanted In Animals’ Pericardial Space For Short-Term Testing (50 Minutes), Demonstrating Initial proof-of-Concept For Blood Flow Regulation.
Animal Testing Validated The Improved Biocompatibility And Anti-Thrombogenic Properties Of The Thermoplastic Polyurethane-Coated nylon Material With Supramolecular Coatings, reducing Platelet Adhesion And Thrombosis Compared To Uncoated Materials.
Closed Fluidic System For Future Implants
For A Fully Implantable Version, A Closed Fluidic System Has Been Developed, Comprising A Continuous-flow Air Pump And A Soft Robotic Actuation System. This System Is Integrated With A Transcutaneous energy Transfer (TET) System, Powering The Pump Wirelessly Through The skin.
This Wireless Power Transfer Reduces The Risk Of Infection And Improves patient Quality Of Life. Early Testing Of The Closed Fluidic System Showed Lower cardiac Output Due To Initial Limitations In the TET system’s Power Output, An Area Under Ongoing Enhancement.
Advantages Of The Hybrid Heart
The Hybrid Heart Offers Several Key Advantages Over Existing Artificial Hearts:
- Biocompatibility: The Materials Used Are Non-Toxic And Designed To Integrate With The Body’s Tissues.
- Physiological Mimicry: The Device Adapts To Changing Blood Pressure And Volumes, Behaving Like A Natural Heart.
- Customization: The Device Can Be Configured To Meet Individual Patient Needs.
| Feature | Hybrid Heart | Traditional Artificial Hearts |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Soft Robotics, Pneumatic | Electronic, Mechanical |
| Biocompatibility | High, Supramolecular Coatings | Lower, Risk Of Clotting |
| Physiological Response | Adaptive, Mimics natural heart | Less Adaptive, Fixed Output |
Future Directions And Clinical Implications
Despite Promising results, The Hybrid Heart Is Still In Early Stages Of Development. Further Long-Term Animal Studies Are Needed To Confirm Its Safety, Durability, And Overall Performance.
Critical components, The Implantable Version, And Tissue Engineering Coatings Require Extensive Testing Before Clinical Application. If Successful,The Hybrid Heart Could offer Safer,more Functional,And Adaptable Solutions For End-Stage heart Failure.
The Future Of Heart Failure Treatment
Advancements In Soft Robotics And Biomimetic Engineering Are Paving The Way For A New Generation Of Artificial Hearts. The Hybrid Heart Represents A Significant Step Towards Devices That Not Only Replace The Function Of A Failing Heart But Also Integrate Seamlessly With The Body.
Ongoing Research Is Focused On Improving The Biocompatibility Of Materials, Enhancing The Efficiency Of Wireless Power Transfer, And Developing more Elegant Control Systems. The Ultimate Goal Is To Create Fully Implantable, Long-Lasting artificial Hearts That Can Restore Patients’ Quality Of Life.
Frequently Asked Questions About The Soft Robotic Heart
- What is a Soft Robotic Heart? A Soft Robotic Heart is an innovative artificial heart that uses soft robotics technology to mimic the natural pumping action of a human heart.
- How Does The Soft Robotic Heart Work? The Soft Robotic Heart utilizes pneumatic muscles and air pressure to inflate and deflate chambers, creating a pumping action similar to a biological heart.
- What Are The Advantages Of A Soft Robotic Heart Over Traditional Artificial Hearts? Soft Robotic Hearts offer improved biocompatibility, reduced risk of blood clots, and the ability to mimic the natural physiological responses of a human heart, providing more adaptable cardiac support.
- Is The Soft Robotic Heart Ready For Clinical Use? No, The Soft Robotic Heart is still in the early stages of development and requires extensive further testing, including long-term animal studies, before it can be considered for clinical use.
- What Is The Significance Of This Soft Robotic heart Development? This development shows that soft robotic techniques can create a biocompatible artificial heart; this offers an effective cardiac output, and overcomes shortcomings of now available artificial hearts.
What do you think about this innovation? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Soft Robotics Revolutionizes Artificial Hearts: A Leap Forward in Cardiac Care
Soft Robotics Revolutionizes Artificial Hearts: A Leap Forward in Cardiac Care
The field of artificial hearts is undergoing a dramatic conversion, thanks to the innovative advancements in soft robotics. This technology, which utilizes pliable, flexible materials mimicking biological tissues, is paving the way for more biocompatible, efficient, and life-saving devices. This article delves into how soft robotics artificial hearts are changing the landscape of cardiac care, offering fresh hope for patients with heart failure . Key topics covered include soft robot heart technology, advantages of soft robotics in medicine, and the future of artificial heart design.
The Science of soft Robotics in Artificial Heart Design
Conventional artificial hearts frequently enough involve rigid components that can trigger complications like blood clotting, tissue damage, and immune responses. Soft robots, on the other hand, are engineered from malleable materials such as silicon, polymers, and elastomers. This flexibility allows these devices to more closely mimic the natural movement of the heart. This is a critical aspect of the development of next-generation artificial hearts. The goal is to minimize stress on the body, reduce device-related complications, and extend patient lifespan.
Key features of Soft Robotic Artificial Hearts
- Biocompatibility: Soft materials are inherently more compatible with the human body,reducing the risk of immune rejection and clotting.
- Mimicking Natural Heart Function: They can replicate the heart’s natural pumping action more closely, reducing hemodynamic issues.
- Reduced Risk of Trauma: The compliant nature of soft robots minimizes damage to surrounding tissues.
Benefits of Soft Robotics for Artificial Hearts
The integration of soft robotics into artificial heart development offers a multitude of advantages over customary designs. Some main benefits include:
Research shows the many advantages
List of Benefits:
- Enhanced Biocompatibility :Minimizes the risk of blood clots and immune system reactions.
- Improved Hemodynamics : Replicates the heart’s natural pumping action.
- Lower Risk of Tissue Damage : Reduced stress on surrounding tissues.
- Increased Device Longevity : Soft materials make for more robust and lasting implants.
- Potential for Personalization : Customizable designs tailored to individual patient needs.
Real-world Applications and Advancements
Several research teams and companies are actively working on soft robotics artificial hearts. These innovations range from prototypes undergoing laboratory testing to devices successfully implanted in animal models. Here are some examples:
Case Study: The Zurich Artificial Heart
the Zurich Artificial Heart, developed at ETH Zurich and the University Hospital Zurich, is an excellent example of the possibilities in the soft robotics world. Unlike traditional artificial hearts that use mechanical pumps, this device relies on electrically driven artificial muscles, mimicking the heart’s natural motion. The design is intended to closely simulate the human natural heart, aiming to reduce the strain on the body. This design focuses on reducing the risk for clot in the pumping chambers and make it efficient and gentle, while making sure that the pump can be used for many more years.
Learn more about the Zurich Artificial Heart
Table: Soft Robotic Artificial Heart Technologies
| Technology | Key Features | Current Status |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle-Powered Heart (Zurich) | Electrically driven soft actuators mimic human heart muscles. | Animal trials and ongoing improvement. |
| Fluid-Driven Devices | uses fluid pressure to drive flexible heart chambers. | Prototyping with promising results for enhanced biocompatibility. |
| Integrated Sensor Systems | Includes embedded sensors to measure pressure and flow. | Enhancing device responsiveness and patient monitoring in trials. |
The Future of Artificial Hearts and Soft Robotics
The future of artificial hearts is intricately linked with the advancement of soft robotics. Future innovations will likely center on:
- Improved Materials: Development of even more biocompatible and durable materials.
- Advanced Control Systems: Integrating complex control systems that ensure optimal performance, reacting to the needs of the patient.
- Personalization: Custom-designing devices to meet an individual patient’s anatomy and physiology.
- Miniaturization: Reducing the size of the mechanisms.
soft robotics is poised to revolutionize the field of artificial hearts,providing improved options for patients suffering from heart failure and ushering in a new era of cardiac care.
