Public Opinion Shifts on the Affordable Care Act: A New Landscape
Table of Contents
- 1. Public Opinion Shifts on the Affordable Care Act: A New Landscape
- 2. Persistent Partisan Divisions
- 3. Key Provisions Enjoy Broad Support
- 4. Pre-Existing Conditions: A Widespread Concern
- 5. Perceived Impact of the ACA
- 6. Looking Ahead
- 7. Understanding the ACA: A long-Term Perspective
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions About the ACA
- 9. How have major political events influenced public favorability of the ACA, as depicted in Chart 1?
- 10. Insights from Five Charts: Public sentiment on the Affordable Care Act
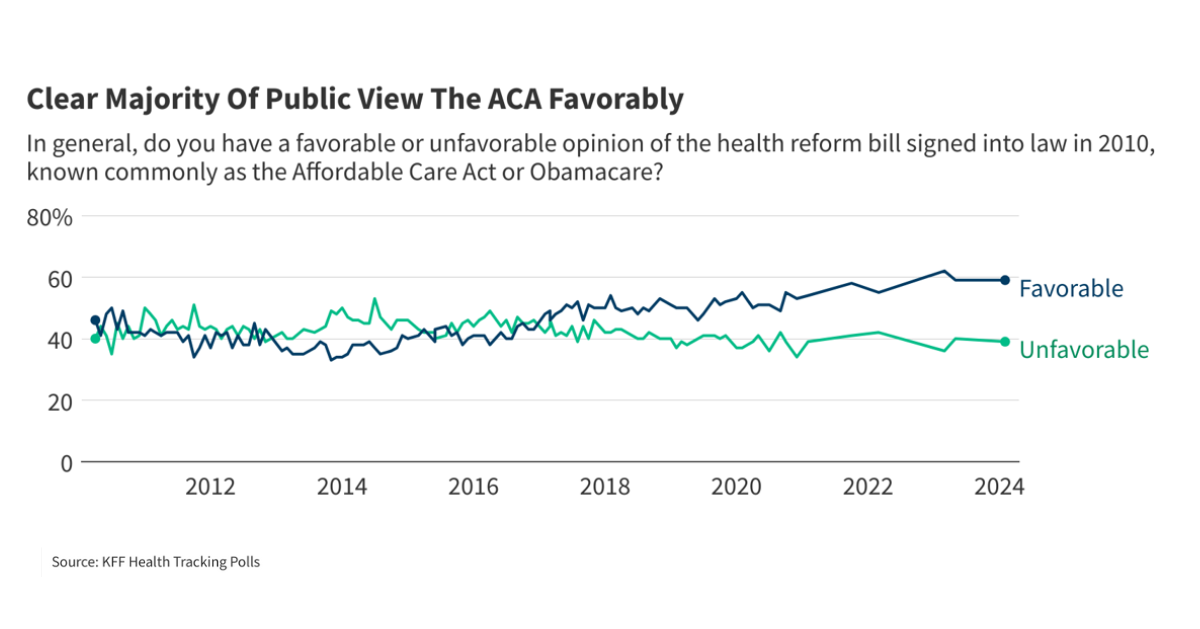
- 11. Chart 1: ACA Favorability Trends (2010-2025)
- 12. Chart 2: Demographic Breakdown of ACA Support
- 13. Chart 3: Impact of ACA on Uninsured Rates
- 14. chart 4: Consumer Satisfaction with Health Insurance Plans
- 15. Chart 5: Public Perception of ACA’s Key Provisions
- 16. Benefits of the Affordable Care Act: A Closer Look
- 17. Real-World Example: The Impact of Medicaid Expansion in Kentucky
Washington D.C. – As of Fall 2025, a majority of United States adults maintain a positive view of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), despite continuing political friction. Recent data indicates that approximately 64% of the population expresses favorability towards the healthcare law, while around 35% hold an unfavorable opinion, marking a notable trend sence the initial debates following its enactment in 2010.
Persistent Partisan Divisions
The Public’s assessment of the ACA remains deeply intertwined with political affiliation. An overwhelming 94% of Democrats report a favorable view, alongside 64% of Independents. conversely, nearly two-thirds of Republicans (64%) continue to view the law negatively. This stark contrast underscores the enduring partisan polarization surrounding healthcare policy in the United States.
Key Provisions Enjoy Broad Support
Despite ongoing debate, specific components of the ACA resonate with a large segment of the population. Protections for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, including guaranteed issue adn community rating, are particularly popular. Approximately 67% of adults believe it is indeed “very critically important” to maintain the guaranteed issue provision, while 65% feel similarly about community rating. These provisions prevent insurers from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based on health status.
Did You Know? Awareness of the ACA’s pre-existing condition protections has actually declined in recent years. As of early 2024, only 39% of adults were aware of these protections, compared to 70% shortly after the ACA’s implementation in 2010.
Pre-Existing Conditions: A Widespread Concern
A meaningful portion of the U.S. population is directly impacted by pre-existing condition protections. An analysis estimates that 27% of adults aged 18-64 have a health condition that could have previously led to insurance denial. Furthermore, roughly half of all americans believe that thay or a family member have a pre-existing condition. This widespread relevance likely contributes to the strong support for maintaining these safeguards.
| ACA Provision | Percentage Saying “Very Important” to Keep |
|---|---|
| Guaranteed Issue | 67% |
| Community Rating | 65% |
Perceived Impact of the ACA
Around a quarter of Americans report that the ACA has positively impacted them or their families, primarily by enabling access to health coverage. Conversely, one in five feel the law has had a negative effect. For those who perceive a benefit, the ability to obtain or maintain coverage is the most frequently cited reason. However, among those who feel harmed, rising healthcare costs are the primary concern.
Pro Tip: Explore the Kaiser Family Foundation’s (KFF) interactive tools to delve deeper into public opinion on the ACA and its various provisions. KFF Interactive
The February 2024 Health Tracking Poll reveals that 39% of adults believe the ACA has made it easier to secure health insurance, while 23% believe it has made things more challenging. Importantly, Democrats are far more likely than Republicans to report a positive impact.
Looking Ahead
The Affordable Care Act continues to be a pivotal topic in American healthcare. Public sentiment, while generally favorable, remains very sensitive to political developments and economic factors. The ongoing debate highlights the complexities of providing affordable and accessible healthcare to all Americans.
Understanding the ACA: A long-Term Perspective
The ACA, signed into law in 2010, aimed to expand health insurance coverage and address long-standing issues within the U.S. healthcare system.Its core provisions include the expansion of Medicaid eligibility, the creation of health insurance marketplaces, and the aforementioned protections for individuals with pre-existing conditions. The law has undergone numerous legal challenges and legislative attempts at repeal, yet it remains a cornerstone of American healthcare policy. The future of the ACA is uncertain, contingent on ongoing political dynamics and potential legal rulings.
Frequently Asked Questions About the ACA
- what is the Affordable Care Act? The ACA is a thorough healthcare reform law enacted in 2010 to expand health insurance coverage and lower healthcare costs.
- Does the ACA protect people with pre-existing conditions? Yes, the ACA prohibits insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based on a person’s medical history.
- How has public opinion on the ACA changed over time? Public opinion has fluctuated, but currently, a majority of Americans hold a favorable view, even though partisan divides remain significant.
- What are the main criticisms of the ACA? common criticisms include rising premiums, limited provider networks, and government involvement in healthcare.
- Where can I find more facts about the ACA? The Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) provides in-depth analysis and data on the ACA: KFF Website.
- What is the role of the Supreme Court in the ACA’s future? The Supreme Court has previously ruled on the ACA and could potentially revisit its constitutionality in the future.
- How does the ACA impact different demographics? The ACA’s impact varies across different demographic groups, with lower-income individuals and those with pre-existing conditions benefiting the most.
What are your thoughts on the current state of the Affordable Care Act? Do you believe the benefits outweigh the costs, and what changes, if any, would you like to see implemented?
Share your perspective in the comments below!
How have major political events influenced public favorability of the ACA, as depicted in Chart 1?
Insights from Five Charts: Public sentiment on the Affordable Care Act
Chart 1: ACA Favorability Trends (2010-2025)
this chart illustrates the fluctuating public opinion of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), often referred to as Obamacare, since its inception. Initial favorability peaked shortly after the law’s passage in 2010, followed by a notable decline amidst political opposition and implementation challenges.
* Key Observation: Favorability ratings consistently correlate with political events – Supreme Court rulings, presidential elections, and legislative attempts at repeal.
* Data Point (2024): A Kaiser Family Foundation poll showed 53% of Americans held a favorable view of the ACA, a high point in recent years, largely attributed to increased enrollment during the pandemic and expanded subsidies.
* Related Keywords: ACA approval ratings, Obamacare public opinion, healthcare reform sentiment, health insurance favorability.
Chart 2: Demographic Breakdown of ACA Support
This chart segments ACA support by key demographic groups – age, income, race/ethnicity, and political affiliation. Understanding these nuances is crucial for targeted policy discussions and outreach efforts.
* Young Adults (18-34): Consistently demonstrate higher levels of support,benefiting significantly from provisions allowing dependents to stay on parents’ plans until age 26.
* Low-Income Individuals: show strong support due to expanded medicaid eligibility and premium subsidies,making health insurance more accessible.
* Minority Groups: Experience disproportionately higher rates of uninsurance and therefore exhibit greater support for the ACA’s coverage expansions.
* Political Affiliation: A stark divide exists, with Democrats overwhelmingly supporting the ACA and Republicans largely opposing it. Independents often fall in between, influenced by specific policy details.
* LSI Keywords: Healthcare disparities, health insurance access, demographic health trends, political polarization healthcare.
Chart 3: Impact of ACA on Uninsured Rates
This chart tracks the national uninsured rate before and after the ACA’s implementation. A primary goal of the ACA was to reduce the number of Americans without health insurance.
* Pre-ACA (2013): The uninsured rate stood at 16%.
* Post-ACA (2025): The uninsured rate has fallen to approximately 8%, representing a significant reduction. Tho, rates have fluctuated based on economic conditions and policy changes.
* State-Level Variations: States that expanded Medicaid under the ACA experienced more ample reductions in uninsured rates compared to non-expansion states.
* Relevant Search Terms: Uninsured population statistics,ACA coverage rates,Medicaid expansion impact,healthcare access statistics.
chart 4: Consumer Satisfaction with Health Insurance Plans
This chart measures consumer satisfaction with their health insurance plans, differentiating between those obtained through the ACA marketplaces and other sources (employer-sponsored, direct purchase).
* marketplace Plans: Satisfaction levels are generally lower for those enrolled in ACA marketplace plans, often citing concerns about high deductibles, limited provider networks, and rising premiums.
* Employer-Sponsored Plans: Typically exhibit higher satisfaction rates due to more comprehensive coverage and lower out-of-pocket costs.
* Factors Influencing Satisfaction: Plan type (HMO, PPO), cost-sharing arrangements, and access to preferred providers all play a role in consumer satisfaction.
* Keywords: Health insurance satisfaction, ACA marketplace reviews, healthcare plan quality, consumer healthcare experience.
Chart 5: Public Perception of ACA’s Key Provisions
This chart assesses public opinion on specific provisions of the ACA, such as the individual mandate (now repealed), pre-existing condition protections, and essential health benefits.
* Pre-Existing Condition Protections: Enjoy overwhelmingly strong public support,with over 90% of Americans agreeing that individuals with pre-existing conditions should not be denied coverage.
* Essential Health Benefits: Also receive broad support, ensuring that all plans cover a comprehensive range of services, including preventive care, maternity care, and mental health services.
* Individual Mandate: Was the most controversial provision, facing significant opposition and ultimately being repealed in 2017.
* Practical Tip: Understanding public perception of these provisions is vital for crafting effective messaging and advocating for policies that address consumer concerns.
* Related Terms: ACA provisions, healthcare policy analysis, public health law, health insurance regulations.
Benefits of the Affordable Care Act: A Closer Look
Beyond reducing the uninsured rate, the ACA has delivered several key benefits:
* Preventive Care Access: Expanded access to preventive services, such as screenings and vaccinations, leading to improved health outcomes.
* Financial Security: Protected millions of Americans from medical debt by limiting out-of-pocket expenses and prohibiting discriminatory practices.
* Innovation in Healthcare Delivery: Encouraged the progress of new healthcare delivery models, such as Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs), aimed at improving quality and reducing costs.
Real-World Example: The Impact of Medicaid Expansion in Kentucky
Kentucky’s early and aggressive expansion of Medicaid under the ACA provides a compelling case study. The state saw a dramatic reduction in its uninsured rate – from 20.5% in 2013 to 5.7% in 2025 – and significant improvements in access to care and health outcomes. This example demonstrates