Amazon.com at 30: From Books to Everything, a Look Back at Its Humble Beginnings
Table of Contents
- 1. Amazon.com at 30: From Books to Everything, a Look Back at Its Humble Beginnings
- 2. Frequently Asked Questions
- 3. What was the importance of Amazon choosing the name “Amazon” over its initial name “Cadabra”?
- 4. Amazon at 30: A Journey from River Logo to Global Retail Giant
- 5. The Early Days: Books and Beyond (1994-1998)
- 6. Diversification and Expansion: Becoming the everything Store (1998-2005)
- 7. The Rise of Amazon Prime and Mobile (2005-2015)
- 8. Innovation and Global Dominance (2015-Present)
- 9. Amazon’s Impact on Retail and Beyond
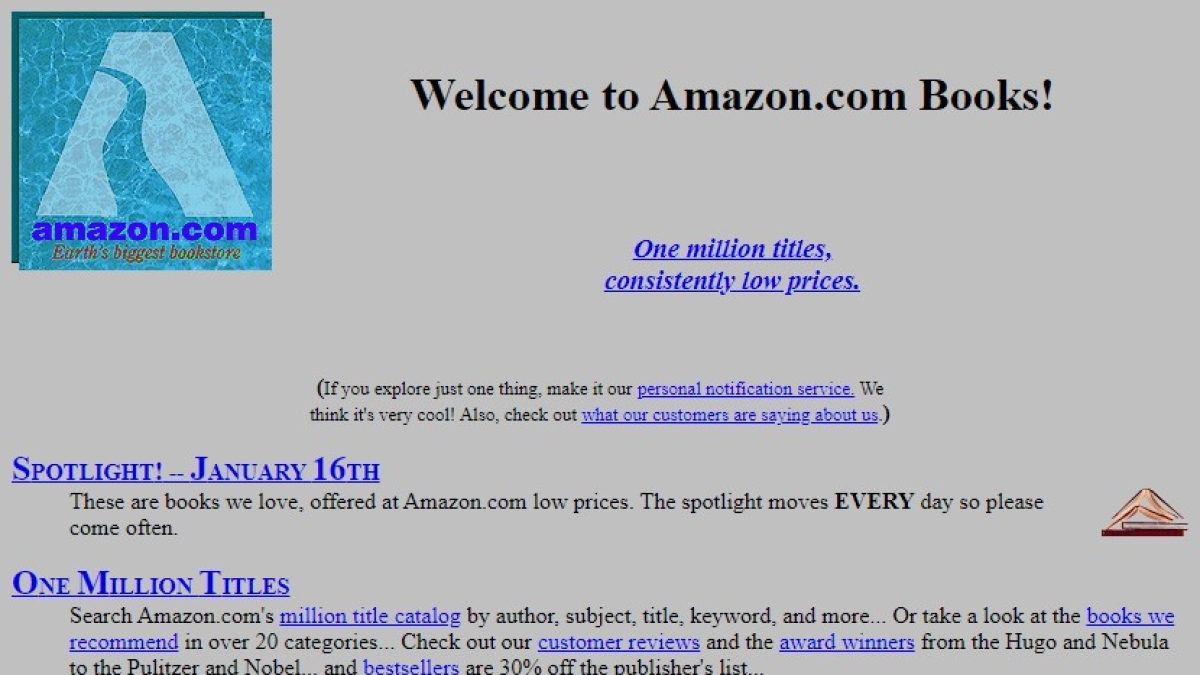
Thirty years ago, the online landscape looked vastly different. If you were to dig through digital archives today, you’d find a relic of what was once Amazon.com, a site almost unrecognizable from the e-commerce giant it is indeed now.
Its early design featured an indefinite gray background, a far cry from the iconic orange arrow logo that now graces its pages. The initial logo evoked the Amazon River, the world’s largest, with a water-like backdrop.
A cheerful, yet standard, black font welcomed visitors with the promise: “A million titles at consistently low prices.” Back then, Amazon sourced its books directly from publishers.
Launched on July 16, 1995, Amazon began its journey selling onyl books. CDs and videotapes arrived three years later, marking the start of its ascent to global success and a business model that would pivot from literature to virtually everything.
A curious anecdote highlights the company’s early days: a bell was rung in the office every time a book was sold.This cherished habit was short-lived; the bell’s frequent ringing soon led to its removal.
Within its first month, Amazon had already sold books across all American states and in 45 countries worldwide. This rapid expansion hinted at the immense potential of online retail.
Reflecting on the site’s conversion from its initial launch,just a year after the brand’s founding on July 5,1994,evokes a sense of nostalgia. Join us as we trace the evolution of the book e-commerce leader over three decades.
Frequently Asked Questions
- When was Amazon.com launched?
-
Amazon.com was launched on July 16, 1995, selling only books.
- What was Amazon’s initial product offering?
-
Initially, Amazon.com exclusively sold books, supplied directly by publishers.
- When did Amazon start selling CDs and videotapes?
-
Amazon began selling CDs and videotapes three years after its launch, in 1998.
- What was notable about early Amazon sales tracking?
-
In its early days, a bell was rung in the office each time a book was sold.
- How widespread was Amazon’s reach in its first month?
-
Within its first month, Amazon sold books in all American states and 45 countries.
Amazon at 30: A Journey from River Logo to Global Retail Giant
The Early Days: Books and Beyond (1994-1998)
Founded by jeff Bezos in 1994, Amazon began as an online bookstore, operating out of his garage in Bellevue, Washington. The initial name, “Cadabra,” was quickly scrapped for the more globally recognizable “Amazon,” inspired by the Amazon river – symbolizing vastness and scale. This early focus on e-commerce and a customer-centric approach were foundational.
July 5, 1994: Amazon.com officially launches.
1995: First order is placed – a copy of “Fluid Concepts and Creative Analogies.”
1997: Amazon goes public, raising $54 million.
Key Strategy: Bezos famously prioritized long-term growth over short-term profits, a strategy that would define Amazon’s trajectory. This involved aggressive investment in technology, infrastructure, and customer acquisition.
The initial success wasn’t just about selling books online. It was about offering a superior customer experience: personalized recommendations, easy ordering, and reliable delivery. This focus on customer experience became a core tenet of the Amazon philosophy.
Diversification and Expansion: Becoming the everything Store (1998-2005)
The late 90s and early 2000s saw Amazon aggressively diversify its product offerings. This period marked the conversion from an online bookstore to the “Everything Store.”
1998: Expansion into music and video sales.
1999: Launch of Amazon Auctions (later spun off as eBay). Introduction of Amazon Marketplace, allowing third-party sellers to list products. This was a pivotal moment, expanding selection exponentially.
2000: Introduction of Amazon Web Services (AWS), initially offering storage and computing power to developers. This seemingly unrelated venture would become a massive revenue driver.
2002: Launch of Amazon Fulfillment, offering warehousing and shipping services to third-party sellers.
2005: Introduction of Amazon Prime, a subscription service offering free two-day shipping and other benefits. Amazon Prime fundamentally changed consumer expectations around delivery speed and convenience.
This period was characterized by significant investment and,at times,skepticism from Wall Street. However,Bezos’s long-term vision continued to guide the company. The expansion into cloud computing with AWS proved particularly prescient.
The Rise of Amazon Prime and Mobile (2005-2015)
The introduction of Amazon Prime in 2005 was a game-changer. It fostered customer loyalty and encouraged more frequent purchases. Together,the rise of mobile technology presented new opportunities.
2007: Launch of the Kindle e-reader, disrupting the publishing industry.
2008: Amazon Appstore launches, entering the mobile app market.
2010: Introduction of Amazon Instant Video (now Prime Video), expanding into digital content streaming.
2011: Amazon achieves greater sales than Barnes & Noble for the first time.
2014: Amazon acquires Twitch, a live streaming platform for gamers.
The focus shifted towards creating an ecosystem of products and services, seamlessly integrated to enhance the customer experience. Digital transformation was in full swing. The Kindle demonstrated Amazon’s willingness to disrupt established industries.
Innovation and Global Dominance (2015-Present)
The last decade has seen Amazon continue to innovate at a rapid pace,expanding into new markets and technologies.
2015: Amazon surpasses Walmart as the most valuable retailer in the US.
2017: Acquisition of Whole Foods Market, marking a significant entry into the grocery industry.
2018: Amazon reaches a market capitalization of $1 trillion.
2020: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerates e-commerce growth, benefiting Amazon considerably.
2023: Amazon invests heavily in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
current Focus: artificial intelligence (AI),logistics innovation (drones,robotics),and expansion into healthcare.
amazon’s dominance extends beyond retail. AWS is now a leading provider of cloud services, powering countless businesses worldwide. the company’s influence spans logistics, artificial intelligence, digital advertising, and entertainment.
Amazon’s Impact on Retail and Beyond
Amazon’s impact on the retail landscape is undeniable. It has forced conventional retailers to adapt to the demands of the digital age.
Price Transparency: Amazon’s competitive pricing has driven down prices across the board.
convenience: amazon Prime and fast shipping have raised consumer expectations for convenience
 Cloud Intelligence International President Selina Yuan”>
Cloud Intelligence International President Selina Yuan”>Alibaba Cloud Bets on AI and Open Source for Global Expansion
Table of Contents
- 1. Alibaba Cloud Bets on AI and Open Source for Global Expansion
- 2. What specific investments is Alibaba Cloud making to support the expansion of digital infrastructure in emerging markets, and how do these investments contribute to the predicted “perpetual globalization” trend?
- 3. Alibaba Cloud Executive Predicts Perpetual Globalization Trend
- 4. The Resurgence of Interconnectedness: A New Era of Globalization
- 5. The Driving Forces Behind Perpetual Globalization
- 6. Alibaba Cloud’s Role in Facilitating Global Connectivity
- 7. Impact on Businesses: Adapting to a Perpetual Globalization Model
- 8. Case Study: Cross-Border E-commerce Success with Alibaba Ecosystem
- 9. The Future of Globalization: Beyond Borders
Alibaba Cloud Intelligence International views globalization not as a short-term project but as a continuous evolution, especially as it navigates the burgeoning wave of artificial intelligence (AI) and seeks to capture overseas markets. Selina Yuan, President of Alibaba Cloud Intelligence International and Vice President of Alibaba Group Holding, detailed the companyS expansive strategies in a recent interview.
With a decade of growth, Alibaba Cloud has established a significant global footprint, boasting 89 availability zones across 29 regions worldwide. The company serves approximately 5 million clients, including high-profile organizations like the International Olympic Committee, BMW Group, SAP, and LVMH. Over 200 of its cloud computing and AI products and solutions are now available in international markets.
To accelerate the development of its global cloud computing network, which already spans China, Japan, South Korea, Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Europe, and the Americas, Alibaba Cloud has been actively building new data centers. This year alone, new facilities have been established in Mexico, Thailand, South Korea, and Malaysia, driven by increasing demand.
The rapid deployment of AI applications globally is a key driver for this expansion, constantly elevating customer demand for cloud resources, AI products, and services. Yuan emphasized the necessity for the company to bolster its local response capabilities to meet these evolving needs.
Looking ahead, Alibaba Cloud anticipates a new era of high-speed development for cloud computing and AI over the next three to five years, or even longer. A core element of its AI strategy is a commitment to open source. The company’s large language model, Qwen, has seen over 200 models open-sourced, leading to more than 140,000 derivative models, positioning it as one of the world’s most extensive open-sourced model series.
Beyond open-sourcing, Alibaba Cloud is actively collaborating with clients to create impactful AI applications. As an example, the company assisted UK consumer healthcare giant Haleon in launching an AI nutrition assistant, which has notably reduced response times for nutritionists.
Geographically, Asia remains a cornerstone market for Alibaba Cloud, with robust data centre presence in Indonesia, Japan, Hong Kong, Singapore, and Malaysia. The company is also keenly observing the growth and potential within Latin American markets, recognizing the burgeoning digitization, cloud computing, and AI trends.
For the Middle East and European markets, Alibaba Cloud plans to implement flexible and diverse market strategies to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
A crucial aspect of Alibaba Cloud’s localization efforts involves its workforce. On average, over 60 percent of its overseas team members are hired locally, with this figure reaching 70 to 80 percent in certain countries. This strategy enhances the company’s ability to provide tailored local services. Through AI technologies, the company is continually improving its support for local languages, with Qwen currently supporting 119 languages. Furthermore, Alibaba Cloud is investing in future talent by collaborating with 120 overseas universities to co-develop systems for training and empowering local professionals.
What specific investments is Alibaba Cloud making to support the expansion of digital infrastructure in emerging markets, and how do these investments contribute to the predicted “perpetual globalization” trend?
Alibaba Cloud Executive Predicts Perpetual Globalization Trend
The Resurgence of Interconnectedness: A New Era of Globalization
Recent statements from an Alibaba Cloud executive signal a firm belief in the continuation – and even acceleration – of globalization, despite geopolitical tensions and recent disruptions to global supply chains. this perspective, diverging from narratives of “deglobalization,” centers on the evolving nature of global trade and the critical role of digital infrastructure. The prediction hinges on the idea that globalization isn’t simply about physical goods, but increasingly about the flow of data, technology, and digital services – areas where Alibaba Cloud is a major player. This shift represents a move towards digital globalization.
The Driving Forces Behind Perpetual Globalization
Several key factors underpin this prediction of sustained globalization. These aren’t simply economic forces, but also technological and societal shifts:
Digital Infrastructure Expansion: The continued build-out of cloud computing, 5G networks, and high-speed internet access globally is lowering barriers to entry for businesses of all sizes. Alibaba Cloud’s own expansion into new markets exemplifies this trend.
E-commerce Growth: The explosive growth of e-commerce platforms, like Alibaba’s own marketplaces (Taobao, Tmall, AliExpress), facilitates cross-border trade and connects consumers and businesses directly, bypassing customary intermediaries. Cross-border e-commerce is a meaningful driver.
Remote Work & distributed Teams: the normalization of remote work, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, allows companies to access talent globally and operate with greater adaptability. This fosters international collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Demand for Global Supply Chain Resilience: Recent disruptions have highlighted the need for diversified and resilient supply chains. Companies are actively seeking to reduce reliance on single sources and build more agile networks, often spanning multiple countries. Supply chain diversification is paramount.
Rise of the Digital Economy: the increasing importance of the digital economy – encompassing areas like fintech, artificial intelligence, and data analytics – necessitates global collaboration and data flows.
Alibaba Cloud’s Role in Facilitating Global Connectivity
Alibaba Cloud isn’t simply observing this trend; it’s actively shaping it. The company’s investments in global data centers, cloud services, and digital infrastructure are designed to facilitate seamless cross-border operations for businesses.
Global Data Center Network: Alibaba Cloud operates a growing network of data centers across the globe, providing businesses with localized cloud services and reducing latency. This is crucial for applications requiring real-time data processing.
Cloud-Native Technologies: The promotion and support of cloud-native applications and technologies like Kubernetes and serverless computing enable businesses to build and deploy scalable, resilient applications globally.
Security and Compliance: Addressing concerns around data security and compliance is critical. Alibaba Cloud invests heavily in security measures and certifications to meet the regulatory requirements of different countries. Data sovereignty is a key consideration.
Digital Payment Solutions: Alipay and other digital payment solutions facilitate secure and efficient cross-border transactions, removing friction from international trade.
Impact on Businesses: Adapting to a Perpetual Globalization Model
For businesses, this prediction of perpetual globalization means adapting to a more interconnected and dynamic world. Here’s how:
- Embrace Digital Conversion: Invest in digital technologies to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and expand into new markets.
- develop a Global mindset: Cultivate a culture of international collaboration and understanding within your institution.
- Diversify supply Chains: Reduce reliance on single suppliers and build more resilient supply chains that span multiple geographies.
- Prioritize Cybersecurity: Protect your data and systems from cyber threats, especially as you expand your global footprint.
- Understand Local Regulations: Navigate the complex web of regulations governing international trade and data privacy. international trade law expertise is valuable.
Case Study: Cross-Border E-commerce Success with Alibaba Ecosystem
A notable example is the success of numerous small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) leveraging Alibaba’s ecosystem to reach global customers. As an example, a French wine producer, previously limited to domestic sales, saw a 300% increase in international revenue after listing its products on AliExpress. This demonstrates the power of digital platforms to democratize access to global markets.the key was adapting product descriptions and marketing materials to resonate with Chinese consumers, highlighting the importance of localization.
The Future of Globalization: Beyond Borders
The executive’s prediction isn’t about a return to the pre-pandemic status quo. It’s about a new form of globalization* – one driven by digital technologies, characterized by greater resilience, and focused on the flow of data and ideas. This perpetual globalization trend presents both opportunities and challenges for businesses,governments,and individuals alike. Successfully navigating this evolving landscape will require adaptability, innovation, and a commitment to global
Microsoft Exchange Online Outages: A Harbinger of Cloud Reliability Concerns?
The recent, multi-day disruptions to Microsoft Exchange Online services, impacting both personal and business users, aren’t just a temporary inconvenience. They’re a stark reminder of the inherent risks of relying on centralized cloud infrastructure – and a potential preview of escalating challenges as organizations increasingly migrate critical communications to these platforms. While Microsoft assures users that 71% of the affected infrastructure has been corrected, the lingering access issues and the underlying complexity of the problem demand a closer look at the future of cloud reliability and the strategies businesses need to adopt to mitigate potential fallout.
The Anatomy of a Cloud Outage
The current outage, initially reported on Thursday and continuing into the week, stems from a “multi-layered problem within the processing infrastructure” at Microsoft, leading to excessive backend resource consumption. This isn’t a simple server failure; it’s a systemic issue impacting mailbox access across multiple connection methods. The fact that Microsoft initially downplayed the impact, categorizing it as a problem solely affecting private customers, highlights a critical challenge in cloud service transparency. Businesses rely on accurate and timely information to make informed decisions, and a delayed or incomplete assessment can exacerbate the consequences of an outage.
The incident, documented in Microsoft’s admin center under ticket EX1113110, underscores the fragility of even the most robust cloud systems. The sheer scale of Microsoft 365 – serving hundreds of millions of users – means that even minor disruptions can have a cascading effect. This incident isn’t isolated; recent years have seen a growing number of high-profile cloud outages affecting major providers like Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud, raising serious questions about the resilience of the modern digital infrastructure.
Beyond Band-Aids: The Rise of Infrastructure Complexity
Microsoft’s approach of “slowing down the distribution” of fixes, while prudent to avoid further disruption during peak hours, is essentially a temporary workaround. The root cause – a complex interplay of backend components overwhelmed by inquiries – points to a fundamental issue: the increasing complexity of cloud infrastructure. As cloud providers add layers of abstraction and automation, they also introduce new potential points of failure.
Cloud infrastructure is becoming increasingly intricate, making it harder to pinpoint and resolve issues quickly. This complexity is driven by the demand for scalability, feature richness, and cost optimization. However, it comes at the expense of simplicity and predictability.
“Did you know?” A recent report by Gartner estimates that the cost of cloud outages to businesses exceeded $50 billion globally in 2023, a figure expected to rise significantly in the coming years.
The Future of Cloud Resilience: A Multi-Pronged Approach
The Microsoft Exchange Online outage serves as a wake-up call for organizations to proactively address cloud resilience. Simply relying on a single provider’s assurances is no longer sufficient. Here’s how businesses can prepare for a future where cloud disruptions are increasingly common:
1. Diversification and Multi-Cloud Strategies
The most effective way to mitigate risk is to avoid putting all your eggs in one basket. Adopting a multi-cloud strategy – distributing workloads across multiple providers – can provide redundancy and ensure business continuity in the event of an outage. This doesn’t necessarily mean completely abandoning Microsoft 365, but rather supplementing it with alternative solutions for critical functions like email and collaboration.
2. Robust Backup and Disaster Recovery Plans
Regular, automated backups are essential, but they’re only part of the equation. Organizations need comprehensive disaster recovery plans that outline specific procedures for restoring services in the event of an outage. These plans should be regularly tested and updated to ensure they remain effective. Consider utilizing immutable storage for backups to protect against ransomware and data corruption.
3. Enhanced Monitoring and Alerting
Proactive monitoring of cloud services is crucial for detecting potential issues before they escalate into full-blown outages. Organizations should implement robust monitoring tools that track key performance indicators (KPIs) and generate alerts when anomalies are detected. This allows IT teams to respond quickly and minimize the impact of disruptions.
“Pro Tip:” Invest in a third-party cloud monitoring solution that provides independent visibility into the health and performance of your cloud services. Don’t rely solely on the provider’s own monitoring tools.
4. Embrace Hybrid Cloud Architectures
A hybrid cloud approach, combining on-premises infrastructure with cloud services, can offer the best of both worlds. Critical applications and data can be kept on-premises, providing greater control and resilience, while less sensitive workloads can be migrated to the cloud for scalability and cost savings.
The Impact on Data Sovereignty and Compliance
Cloud outages also raise concerns about data sovereignty and compliance. Organizations operating in regulated industries may be required to maintain control over their data and ensure its availability at all times. A prolonged outage can jeopardize compliance efforts and expose businesses to legal and financial penalties.
“Expert Insight:” “The increasing reliance on cloud services necessitates a re-evaluation of data sovereignty and compliance strategies. Organizations must understand their obligations and implement appropriate safeguards to protect their data, regardless of where it’s stored.” – Dr. Anya Sharma, Cloud Security Analyst.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the root cause of the Microsoft Exchange Online outage?
Microsoft attributes the outage to a “multi-layered problem within the processing infrastructure” leading to excessive resource consumption. It’s not a single point of failure, but a systemic issue impacting backend components.
How can businesses protect themselves from future cloud outages?
Diversification through multi-cloud strategies, robust backup and disaster recovery plans, enhanced monitoring, and embracing hybrid cloud architectures are key steps to mitigate risk.
Is a multi-cloud strategy expensive?
While implementing a multi-cloud strategy can involve initial costs, the long-term benefits of increased resilience and reduced downtime often outweigh the expenses. Careful planning and optimization are crucial.
What role does data sovereignty play in cloud resilience?
Data sovereignty regulations require organizations to maintain control over their data. Cloud outages can jeopardize compliance, making it essential to choose providers and architectures that meet these requirements.
The Microsoft Exchange Online outage is a critical reminder that cloud services, while offering numerous benefits, are not immune to disruption. Organizations must proactively address cloud resilience, adopting a multi-pronged approach that prioritizes diversification, backup, monitoring, and compliance. The future of business continuity depends on it. What steps will your organization take to prepare for the inevitable next cloud disruption?
Google Poised for Major Cloud Discounts with U.S. Government
Table of Contents
- 1. Google Poised for Major Cloud Discounts with U.S. Government
- 2. Understanding Government Cloud Contracts
- 3. Frequently Asked Questions About Government Cloud Computing
- 4. What are the main benefits of cloud computing for government agencies?
- 5. Why would Google offer discounts on cloud services to the U.S. government?
- 6. Are discounts from Amazon and Microsoft expected to follow Google’s offer?
- 7. What is the significance of the GSA in government cloud procurements?
- 8. How does Oracle’s 75% software discount compare to cloud service pricing?
- 9. What specific GCP services are included in the discount program, and how might these services address common challenges faced by government agencies?
- 10. Google too Offer Cloud Service Discounts to U.S. Government
- 11. Expanding Government Access to Secure Cloud Solutions
- 12. Details of the Discount Program
- 13. Why this Matters: Benefits for Government agencies
- 14. Google Cloud for Government: A deeper Dive
- 15. Real-world Applications & Case Studies
- 16. Navigating the Discount Program: Practical Tips
- 17. Related Search Terms
Google is reportedly preparing to significantly reduce its cloud computing service prices for the U.S. government. The information stems from a senior official at the General Services Management (GSA), as reported by the Financial Times.
This potential agreement is anticipated to be finalized within the coming weeks. It signals a strategic move to capture a larger share of the government’s burgeoning cloud infrastructure needs.
Industry watchers expect similar discount offers from major cloud providers like Microsoft’s Azure and Amazon Web Services to follow swiftly. These competitive pricing strategies underscore the critical importance of government contracts in the cloud market.
google has officially declined to comment on the specifics of the pending cloud deal. Representatives for Microsoft also issued no comment, while Amazon did not respond to the Financial Times’ earlier requests for information.
A spokesperson for the GSA likewise stated they could not comment on the ongoing negotiations. This silence from all parties involved is typical during sensitive government contract discussions.
Meanwhile, Oracle has been offering U.S. government agencies substantial discounts, reportedly as high as 75% on its software, according to The Wall Street Journal. This highlights a broader trend of aggressive pricing within the sector.
Understanding Government Cloud Contracts
Government agencies are increasingly migrating their digital infrastructure to the cloud for enhanced security, scalability, and cost-efficiency. These transitions involve complex procurement processes and often lead to significant, long-term agreements.
Cloud providers compete fiercely for these contracts, offering specialized services and pricing structures tailored to the unique requirements of public sector entities. The potential discounts from Google and its competitors suggest a heightened competition for government cloud spending.
Frequently Asked Questions About Government Cloud Computing
What are the main benefits of cloud computing for government agencies?
Government agencies benefit from enhanced data security, greater scalability, improved operational efficiency, and potential cost savings through cloud computing services.
Why would Google offer discounts on cloud services to the U.S. government?
Google likely offers discounts to secure a significant share of the U.S. government’s cloud market, establishing long-term partnerships and driving adoption of its cloud platform.
Are discounts from Amazon and Microsoft expected to follow Google’s offer?
Yes, reports suggest that equivalent discounts from Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure are expected to follow, indicating a competitive pricing landscape.
What is the significance of the GSA in government cloud procurements?
the General Services Administration (GSA) plays a crucial role in facilitating IT procurements for federal agencies, including cloud services, frequently enough negotiating master agreements and setting pricing benchmarks.
How does Oracle’s 75% software discount compare to cloud service pricing?
Oracle’s reported 75% discount on software is a significant price reduction for specific products, while Google’s discounts are
What specific GCP services are included in the discount program, and how might these services address common challenges faced by government agencies?
Google too Offer Cloud Service Discounts to U.S. Government
Expanding Government Access to Secure Cloud Solutions
Google is considerably expanding its commitment to the U.S. government by offering considerable discounts on its Google Cloud Platform (GCP) services. This move aims to accelerate the adoption of secure, scalable, and innovative cloud technologies across federal, state, and local government agencies. The initiative focuses on providing cost-effective solutions for critical missions, including data analytics, cybersecurity, and citizen services. this builds upon existing government cloud offerings like Google Cloud for Government.
Details of the Discount Program
The new discount structure, announced in July 2025, provides tiered pricing based on usage volume. Key features include:
Usage-Based Discounts: Agencies will receive increasing discounts as their consumption of GCP services grows. This incentivizes broader adoption and allows agencies to scale their cloud infrastructure efficiently.
Committed Use Discounts (CUDs): Similar to existing enterprise programs, CUDs offer significant savings in exchange for a commitment to a specific level of resource usage over a one- or three-year term. This is particularly beneficial for predictable workloads.
Special Pricing for high-Impact Projects: Google is offering customized pricing for projects deemed critical to national security or public welfare.This demonstrates a willingness to partner with the government on high-priority initiatives.
Focus on Key Services: Discounts apply to a wide range of GCP services, including:
Compute Engine: Virtual machines for running diverse workloads.
Cloud storage: Scalable and durable object storage.
BigQuery: Serverless, highly scalable, and cost-effective multi-cloud data warehouse designed for business agility.
Cloud SQL: Fully-managed relational database services.
Chronicle: Google’s cloud-native security analytics platform.
Why this Matters: Benefits for Government agencies
These discounts translate into tangible benefits for government agencies:
Reduced IT Costs: Lower cloud service costs free up budget for other critical priorities. This is especially critically important for state and local governments with limited resources.
Accelerated Innovation: Access to advanced cloud technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) enables agencies to develop innovative solutions to complex challenges.
Enhanced Cybersecurity: Google Cloud’s robust security infrastructure and advanced threat detection capabilities help protect sensitive government data. google’s commitment to FedRAMP compliance is a key factor.
Improved Citizen Services: Cloud-based solutions can improve the delivery of citizen services, making them more accessible, efficient, and user-kind.
Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud infrastructure allows agencies to quickly scale resources up or down as needed, responding to changing demands and unexpected events.
Google Cloud for Government: A deeper Dive
Google Cloud for Government is specifically designed to meet the stringent security and compliance requirements of the U.S. public sector. it offers:
FedRAMP Authorization: Full FedRAMP High authorization ensures that GCP meets the highest standards for security and data protection.
Impact Level 6 (IL6) Environments: dedicated IL6 environments provide the highest level of security for unclassified sensitive details.
Regional Cloud Availability: Geographically dispersed data centers offer redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities.
Dedicated Support: Specialized support teams provide expert assistance to government agencies.
Real-world Applications & Case Studies
While specific details of agency implementations are frequently enough confidential,several examples illustrate the potential of Google Cloud in the public sector:
City of Los Angeles: Utilizing Google Cloud for data analytics to improve traffic flow and reduce congestion.
National Institutes of Health (NIH): Leveraging GCP for genomic research and data analysis, accelerating scientific discovery.
Department of Defense (DoD): Exploring the use of AI and ML on GCP for predictive maintenance and logistics optimization. (Publicly announced pilot programs).
Government agencies interested in taking advantage of these discounts should:
- Assess Cloud Readiness: Evaluate existing IT infrastructure and identify workloads suitable for migration to the cloud.
- Develop a Cloud Strategy: Define clear objectives and a roadmap for cloud adoption.
- Engage with Google Cloud: Contact Google Cloud’s government sales team to discuss specific needs and explore available discount options.
- Understand CUD Requirements: Carefully review the terms and conditions of Committed Use Discounts to ensure they align with agency usage patterns.
- Prioritize Security and compliance: Ensure that all cloud deployments meet relevant security and compliance standards, including FedRAMP.
Government cloud computing
FedRAMP authorized cloud providers
Google Cloud pricing
Cloud migration for government
Public sector cloud solutions
GCP discounts
Cloud security for government
Data analytics in government
AI in government
* Digital change in the public sector