Amazon.com at 30: From Books to Everything, a Look Back at Its Humble Beginnings
Table of Contents
- 1. Amazon.com at 30: From Books to Everything, a Look Back at Its Humble Beginnings
- 2. Frequently Asked Questions
- 3. What was the importance of Amazon choosing the name “Amazon” over its initial name “Cadabra”?
- 4. Amazon at 30: A Journey from River Logo to Global Retail Giant
- 5. The Early Days: Books and Beyond (1994-1998)
- 6. Diversification and Expansion: Becoming the everything Store (1998-2005)
- 7. The Rise of Amazon Prime and Mobile (2005-2015)
- 8. Innovation and Global Dominance (2015-Present)
- 9. Amazon’s Impact on Retail and Beyond
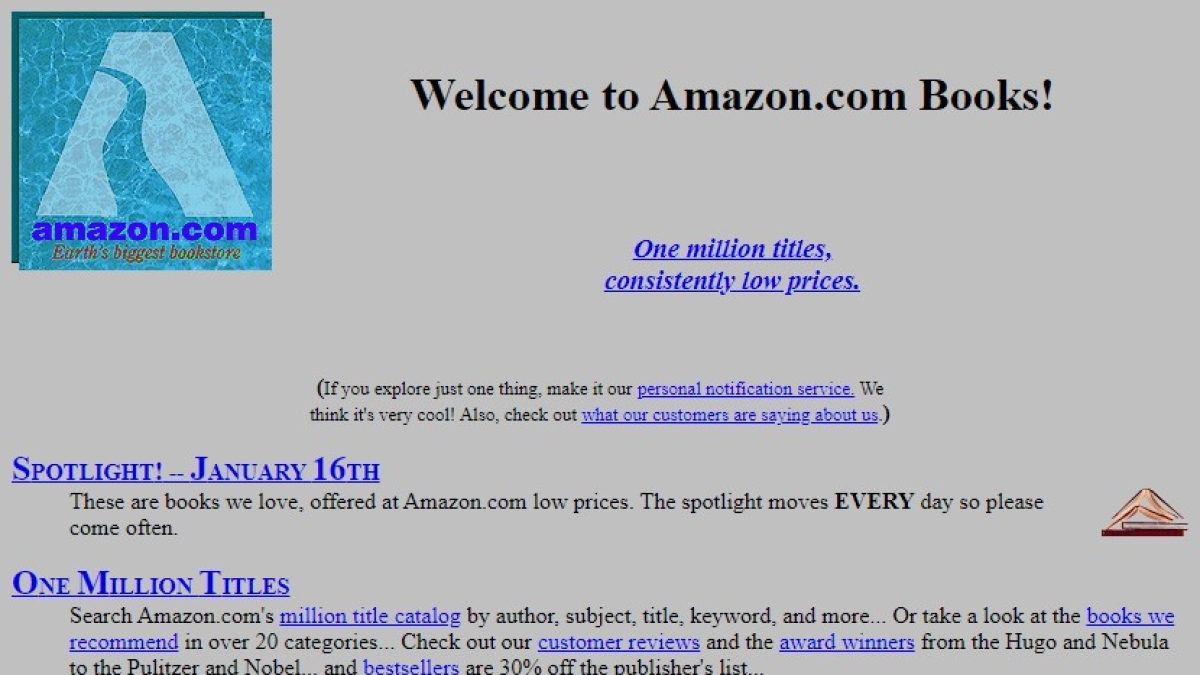
Thirty years ago, the online landscape looked vastly different. If you were to dig through digital archives today, you’d find a relic of what was once Amazon.com, a site almost unrecognizable from the e-commerce giant it is indeed now.
Its early design featured an indefinite gray background, a far cry from the iconic orange arrow logo that now graces its pages. The initial logo evoked the Amazon River, the world’s largest, with a water-like backdrop.
A cheerful, yet standard, black font welcomed visitors with the promise: “A million titles at consistently low prices.” Back then, Amazon sourced its books directly from publishers.
Launched on July 16, 1995, Amazon began its journey selling onyl books. CDs and videotapes arrived three years later, marking the start of its ascent to global success and a business model that would pivot from literature to virtually everything.
A curious anecdote highlights the company’s early days: a bell was rung in the office every time a book was sold.This cherished habit was short-lived; the bell’s frequent ringing soon led to its removal.
Within its first month, Amazon had already sold books across all American states and in 45 countries worldwide. This rapid expansion hinted at the immense potential of online retail.
Reflecting on the site’s conversion from its initial launch,just a year after the brand’s founding on July 5,1994,evokes a sense of nostalgia. Join us as we trace the evolution of the book e-commerce leader over three decades.
Frequently Asked Questions
- When was Amazon.com launched?
-
Amazon.com was launched on July 16, 1995, selling only books.
- What was Amazon’s initial product offering?
-
Initially, Amazon.com exclusively sold books, supplied directly by publishers.
- When did Amazon start selling CDs and videotapes?
-
Amazon began selling CDs and videotapes three years after its launch, in 1998.
- What was notable about early Amazon sales tracking?
-
In its early days, a bell was rung in the office each time a book was sold.
- How widespread was Amazon’s reach in its first month?
-
Within its first month, Amazon sold books in all American states and 45 countries.
Amazon at 30: A Journey from River Logo to Global Retail Giant
The Early Days: Books and Beyond (1994-1998)
Founded by jeff Bezos in 1994, Amazon began as an online bookstore, operating out of his garage in Bellevue, Washington. The initial name, “Cadabra,” was quickly scrapped for the more globally recognizable “Amazon,” inspired by the Amazon river – symbolizing vastness and scale. This early focus on e-commerce and a customer-centric approach were foundational.
July 5, 1994: Amazon.com officially launches.
1995: First order is placed – a copy of “Fluid Concepts and Creative Analogies.”
1997: Amazon goes public, raising $54 million.
Key Strategy: Bezos famously prioritized long-term growth over short-term profits, a strategy that would define Amazon’s trajectory. This involved aggressive investment in technology, infrastructure, and customer acquisition.
The initial success wasn’t just about selling books online. It was about offering a superior customer experience: personalized recommendations, easy ordering, and reliable delivery. This focus on customer experience became a core tenet of the Amazon philosophy.
Diversification and Expansion: Becoming the everything Store (1998-2005)
The late 90s and early 2000s saw Amazon aggressively diversify its product offerings. This period marked the conversion from an online bookstore to the “Everything Store.”
1998: Expansion into music and video sales.
1999: Launch of Amazon Auctions (later spun off as eBay). Introduction of Amazon Marketplace, allowing third-party sellers to list products. This was a pivotal moment, expanding selection exponentially.
2000: Introduction of Amazon Web Services (AWS), initially offering storage and computing power to developers. This seemingly unrelated venture would become a massive revenue driver.
2002: Launch of Amazon Fulfillment, offering warehousing and shipping services to third-party sellers.
2005: Introduction of Amazon Prime, a subscription service offering free two-day shipping and other benefits. Amazon Prime fundamentally changed consumer expectations around delivery speed and convenience.
This period was characterized by significant investment and,at times,skepticism from Wall Street. However,Bezos’s long-term vision continued to guide the company. The expansion into cloud computing with AWS proved particularly prescient.
The Rise of Amazon Prime and Mobile (2005-2015)
The introduction of Amazon Prime in 2005 was a game-changer. It fostered customer loyalty and encouraged more frequent purchases. Together,the rise of mobile technology presented new opportunities.
2007: Launch of the Kindle e-reader, disrupting the publishing industry.
2008: Amazon Appstore launches, entering the mobile app market.
2010: Introduction of Amazon Instant Video (now Prime Video), expanding into digital content streaming.
2011: Amazon achieves greater sales than Barnes & Noble for the first time.
2014: Amazon acquires Twitch, a live streaming platform for gamers.
The focus shifted towards creating an ecosystem of products and services, seamlessly integrated to enhance the customer experience. Digital transformation was in full swing. The Kindle demonstrated Amazon’s willingness to disrupt established industries.
Innovation and Global Dominance (2015-Present)
The last decade has seen Amazon continue to innovate at a rapid pace,expanding into new markets and technologies.
2015: Amazon surpasses Walmart as the most valuable retailer in the US.
2017: Acquisition of Whole Foods Market, marking a significant entry into the grocery industry.
2018: Amazon reaches a market capitalization of $1 trillion.
2020: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerates e-commerce growth, benefiting Amazon considerably.
2023: Amazon invests heavily in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
current Focus: artificial intelligence (AI),logistics innovation (drones,robotics),and expansion into healthcare.
amazon’s dominance extends beyond retail. AWS is now a leading provider of cloud services, powering countless businesses worldwide. the company’s influence spans logistics, artificial intelligence, digital advertising, and entertainment.
Amazon’s Impact on Retail and Beyond
Amazon’s impact on the retail landscape is undeniable. It has forced conventional retailers to adapt to the demands of the digital age.
Price Transparency: Amazon’s competitive pricing has driven down prices across the board.
convenience: amazon Prime and fast shipping have raised consumer expectations for convenience
Spotify Could Pull Out of Turkey Amidst Content Row & Antitrust Probe – Breaking News
ISTANBUL, TURKEY – Spotify is weighing a complete exit from the Turkish market as tensions with the Turkish government reach a boiling point. The streaming giant faces accusations of hosting content deemed offensive to national and religious values, alongside a formal investigation into potential anti-competitive practices. This breaking news development, reported Friday by The Times (United Kingdom), signals a significant escalation in the ongoing struggle between global tech platforms and increasing regulatory scrutiny in Turkey.
Government Accusations & The Competition Investigation
The Turkish Competition Authority launched an investigation on July 4th, examining whether Spotify has engaged in practices that disadvantage competitors in the online music streaming space and unfairly impact fee distribution to artists and content creators. Specifically, the authority is looking into potential discrimination in platform visibility. Adding fuel to the fire, Turkish Vice Minister of Culture and Tourism, Batuhan Mumcu, publicly criticized Spotify for hosting playlists he described as “insidious and provocative,” singling out lists referencing President Erdoğan’s wife, Emine Erdoğan, and even the Prophet Muhammad. Mumcu also voiced concerns about Spotify’s perceived lack of support for local Turkish music genres like folk and arabesque.
Controversial Playlists Spark Outrage
The playlists cited by Mumcu – including “Emine Ergodan Hotgirl Playlist” and “Songs Emine Erdogan listened to when his golden tap broke out” – have become a focal point of the controversy. These lists, circulating on the platform, clearly struck a nerve with government officials, highlighting the challenges faced by streaming services in navigating cultural sensitivities and content moderation in diverse markets. Mumcu also criticized Spotify’s algorithms for promoting content he deemed inappropriate, including slang, violence, and references to prohibited substances.
Spotify’s Response & The Broader Context
Spotify acknowledged the investigation, stating through a spokesperson to MBW last week, “We cooperate with the investigation, we actively seek to understand it and will work towards a rapid and constructive resolution with the Turkish competition. We respect all the laws applicable in all our operations, but we are unable to comment more because we lack details on the scope or concentration of the inspection.” However, the company is reportedly considering all options, including a complete withdrawal from the Turkish market.
This isn’t an isolated incident. In 2021, Turkey’s media watchdog warned Spotify to “regulate its content” or face removal from the country. The Turkish government has been increasingly assertive in its attempts to control online content, reflecting a broader trend of digital sovereignty and content regulation globally. This situation underscores the delicate balance streaming services must strike between upholding freedom of expression and complying with local laws and cultural norms.
The Rise of Local Music & Spotify’s Turkish Footprint
Ironically, Spotify’s own data reveals a significant increase in the popularity of Turkish artists on its platform. The company reports that streams of local artists have surged from 11% in 2013 to 65% in 2025 (projected), and the number of Turkish artists appearing in the Top 100 annual Spotify charts has grown from 11 in 2013 to 93 in 2024. This growth demonstrates a clear demand for local content within the Turkish market, making a potential exit even more complex.
The situation in Turkey is a crucial case study for the future of digital streaming. It highlights the growing power of governments to regulate online platforms and the potential for conflict between global tech companies and local cultural values. For investors and industry watchers, this is a Google News alert worth following closely. Understanding the nuances of these regulatory battles is key to navigating the evolving landscape of the digital music industry and optimizing SEO strategies for global reach.
As Spotify navigates this challenging situation, the future of music streaming in Turkey hangs in the balance. The outcome will undoubtedly set a precedent for other platforms operating in markets with similar regulatory pressures, and will be a key indicator of how successfully global tech companies can adapt to an increasingly localized digital world. Stay tuned to Archyde.com for further updates on this developing story and in-depth analysis of the global streaming landscape.
Northland Building Reforms: A Climate-Specific Shift and What It Means for New Zealand Housing
A staggering 31% drop in Northland building consents year-on-year – the largest decrease in New Zealand – underscored a critical issue: building costs were spiraling out of control, effectively pricing many out of the dream of homeownership. Now, a significant policy shift is underway, promising to alleviate some of that pressure by tailoring building codes to the region’s unique subtropical climate. The removal of the H1 schedule, coupled with potential for a dedicated Northland climate zone, isn’t just about saving builders money; it’s a potential blueprint for a more regionally-responsive approach to construction across the country.
The Burden of a ‘One-Size-Fits-All’ Approach
For years, builders in Northland have argued that national building standards, particularly those related to insulation and glazing, were overly stringent for the region’s milder winters. Matt Hatchard, Far North NZ Certified Builders Association president, succinctly put it: the existing rules were adding unnecessary cost. “Removing the H1 schedule will cut through the cost burden,” he stated, echoing the sentiment of many in the industry. The previous regulations, implemented in May 2023, significantly increased framing sizes and doubled glazing standards, adding substantial expense to every build.
The core of the problem, as highlighted by A1 Homes Northland manager Steve Hart, was the assumption of a “neat little house on a flat, easy-access site” – a scenario rarely reflective of Northland’s terrain and building conditions. The reality is more complex, often involving challenging sites and a strong desire among homeowners for designs that maximize views and natural light, even in smaller dwellings. This desire for expansive glazing, combined with the higher costs of thermally broken joinery required by the previous standards, created a significant affordability barrier.
Cost Savings and the Transition Ahead
The immediate impact of removing the H1 schedule is projected to be a reduction in building costs. Estimates suggest potential savings of up to $15,000 simply by allowing for standard double glazing. However, the extent of these savings remains dependent on how quickly the industry adapts. Some joinery factories have already invested in new equipment to meet the previous, higher standards, and a transition period is crucial. The government has acknowledged this, outlining a phased approach with the schedule method being removed by the end of the year, followed by a 12-month transition period.
Crucially, the changes aren’t simply about reducing standards. The prospect of a dedicated Northland climate zone, currently under consultation with the Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment (MBIE), represents a more nuanced and sustainable solution. This would acknowledge the region’s specific climatic conditions and allow for building practices tailored to maximize energy efficiency without imposing unnecessary costs. This is a significant step towards recognizing the diversity of New Zealand’s climate and the need for regionally-appropriate building codes.
Beyond Northland: A National Conversation?
The Northland situation isn’t unique. Other regions of New Zealand with milder climates have also voiced concerns about the applicability of national building standards. The success of the Northland reforms could pave the way for a broader national conversation about climate-specific building codes. This could involve creating multiple climate zones across the country, each with its own set of regulations tailored to local conditions.
This shift aligns with growing global trends in sustainable building design, which emphasize the importance of adapting building practices to local climates and resources. A report by the International Energy Agency highlights the crucial role of building efficiency in achieving net-zero emissions targets, but stresses the need for tailored solutions that consider regional variations.
Affordability and the Future of Housing Stock
The ultimate goal of these reforms is to address the growing housing affordability crisis in Northland and beyond. Mortgage advisor Sarah Curtis notes that the post-Covid cost increases have made building increasingly challenging for many. Easing the financial burden through more appropriate building standards could stimulate construction activity and help to replenish dwindling housing stock. The recent dip in building consents underscores the urgency of this situation.
However, it’s important to remember that building costs are influenced by a multitude of factors, including interest rates, material prices, and labor availability. While the changes to the H1 schedule are a positive step, they are unlikely to solve the affordability crisis on their own. A comprehensive approach that addresses all these factors will be necessary to ensure that all New Zealanders have access to safe, affordable, and sustainable housing.
What impact will these changes have on the quality and longevity of Northland homes? The answer lies in striking a balance between affordability and performance, and ensuring that builders have the knowledge and resources to implement climate-appropriate building practices. The next 12 months will be critical as the industry adapts and MBIE consults on the potential for a dedicated Northland climate zone. Stay informed and engaged – the future of housing in Northland, and potentially across New Zealand, is being shaped now.
Explore more insights on New Zealand’s housing market in our dedicated section.
MSD Signals major Overhaul in Technology and Advancement Functions Amidst Budget Investment
Breaking News: New Zealand’s Ministry of Social Growth (MSD) is embarking on a notable transformation of its improvement, Systems, and Technology functions, as confirmed by a departmental spokesperson. This strategic move is underpinned by a substantial investment of $67.59 million allocated in Budget 2025 to the “Services for the Future” program, signaling a clear commitment to modernizing the ministry’s operational capabilities.
The consultation process, currently underway, aims to equip this crucial area with advanced technologies and streamlined work methodologies. While the specifics of the proposed changes remain under discussion and final decisions are yet to be made, the initiative is poised to reshape how MSD delivers essential services to the public.
This development follows a period of workforce adjustments for MSD, which last year announced plans to reduce its headcount by 712 positions, a figure representing 7.5% of its total workforce. This reduction was part of a wider government directive for departments and agencies to achieve spending cuts between 6.5% and 7.5%.
A representative from the PSA (Public Service Association), Fitzsimons, attributed these ongoing cuts to government pressure on public services to achieve more with fewer resources. Social Development Minister Louise Upston has directed inquiries regarding these matters to MSD.
Evergreen Insights:
The MSD’s proactive investment in its “Services For the Future” programme highlights a critical trend in public sector management: the imperative to adapt and innovate through technology. As governments worldwide grapple with increasing demands and finite resources, strategic allocation of funds towards technological advancement and process improvement becomes paramount.This approach mirrors the broader evolution of how public services are delivered, moving towards more efficient, data-driven, and citizen-centric models. Investing in the capabilities to harness modern technologies not only addresses current operational challenges but also builds resilience for future needs and evolving societal expectations. The success of such transformations often hinges on effective change management, clear communication, and a sustained focus on empowering staff with the skills and tools necessary to navigate these shifts. The ongoing consultation process at MSD underscores the principle that significant organizational change requires thoughtful dialog and consideration of all stakeholder perspectives.
How can organizations mitigate the risk of losing critical institutional knowledge when experienced tech staff are laid off?
Table of Contents
- 1. How can organizations mitigate the risk of losing critical institutional knowledge when experienced tech staff are laid off?
- 2. Social Advancement Tech Team Facing Significant Staff Reductions
- 3. Understanding the Impact on International Development
- 4. Key Drivers Behind the Reductions
- 5. The Specific Roles Affected: A Breakdown
- 6. The Consequences for Social Impact
- 7. Case Study: A Women’s Rights Organization’s Experience
- 8. Benefits of Maintaining a Strong Tech Team (Despite Challenges)
- 9. Practical Tips for Tech Professionals in the Social Development Sector
Understanding the Impact on International Development
Recent months have seen a worrying trend: significant staff reductions within the technology teams of social development organizations. This isn’t isolated to one region or type of NGO; it’s a global phenomenon impacting organizations working on critical issues like women’s rights, gender equality, poverty alleviation, and humanitarian aid. These cuts aren’t simply about downsizing; they represent a strategic shift with potentially far-reaching consequences for the effectiveness of international development programs. The core issue revolves around funding models, evolving technological landscapes, and a re-evaluation of priorities within the sector.
Key Drivers Behind the Reductions
Several interconnected factors are contributing to these tech team layoffs. Understanding these drivers is crucial for both those affected and the organizations navigating these changes.
Funding Shifts: A major driver is the changing landscape of donor funding. Traditional donors are increasingly prioritizing direct program delivery over investment in internal technological infrastructure. This ofen leads to tech roles being seen as “overhead” rather than essential components of program success.
Economic Downturn & Global Uncertainty: The current global economic climate, marked by inflation and geopolitical instability, is forcing many organizations to tighten their belts. Tech teams, often perceived as costly, are vulnerable during these periods.
Rise of Low-Code/No-Code Solutions: The emergence of accessible low-code and no-code development platforms is leading some organizations to believe they can reduce their reliance on specialized tech staff. While these tools offer benefits, they frequently enough lack the scalability and customization needed for complex development challenges.
Focus on AI & Automation: Paradoxically,investment in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation technologies is also contributing to staff reductions. While AI can enhance efficiency, it’s often implemented with the goal of reducing headcount.
Digital Change Challenges: Many organizations initiated ambitious digital transformation projects during the pandemic. However, a lack of clear strategy, insufficient change management, and unrealistic expectations have lead to project failures and subsequent cost-cutting measures, including staff reductions.
The Specific Roles Affected: A Breakdown
The impact isn’t uniform across all tech roles. Certain specializations are proving more vulnerable than others.
Data Engineers & Scientists: While data remains crucial, some organizations are streamlining their data operations, leading to cuts in these roles.
Software Developers (Especially Custom request Developers): The shift towards off-the-shelf solutions and low-code platforms is reducing the demand for developers building bespoke applications.
IT Support & Infrastructure Specialists: Cloud migration and managed IT services are reducing the need for in-house IT support staff.
GIS (Geographic Details Systems) Specialists: While GIS remains valuable, budget constraints are impacting the ability to maintain dedicated GIS teams in some organizations.
Cybersecurity Professionals: Surprisingly, despite increasing cyber threats, some smaller NGOs are reducing cybersecurity staff due to cost concerns.This is a significant risk.
These staff reductions have serious implications for the effectiveness of social development work.
Reduced Innovation: A smaller tech team means less capacity for innovation and the development of new solutions to complex problems.
slower Program Implementation: Without adequate tech support, program implementation can be delayed and hampered by technical glitches.
Data Quality Issues: Cuts to data engineering and science roles can lead to poor data quality,undermining the ability to monitor and evaluate program impact.
Increased Security Risks: Reduced cybersecurity staffing leaves organizations vulnerable to data breaches and cyberattacks, potentially compromising sensitive beneficiary information.
Digital Divide Exacerbation: A lack of investment in technology can widen the digital divide, hindering efforts to reach marginalized communities.
Loss of Institutional knowledge: Experienced tech staff leaving organizations take valuable institutional knowledge with them, making it harder to maintain and improve existing systems.
Case Study: A Women’s Rights Organization’s Experience
Kate Bishop, Co-Director of Technical Team at Social Development (as per LinkedIn data), highlights a common scenario. “We saw a 20% reduction in our tech team last quarter. While the organization remains committed to gender equality, the funding landscape shifted. donors wanted to see more direct impact on the ground, and investment in our data analytics platform – crucial for measuring that impact – was deemed ‘non-essential’ by some.” This resulted in the loss of key data scientists and a slowdown in the organization’s ability to track progress towards its goals.
Benefits of Maintaining a Strong Tech Team (Despite Challenges)
Despite the pressures, organizations that do prioritize their tech teams stand to gain significant advantages.
Improved Program Efficiency: Technology can automate tasks, streamline workflows, and reduce administrative burdens, freeing up staff to focus on core program activities.
Enhanced Data-Driven Decision Making: Robust data analytics capabilities enable organizations to make informed decisions based on evidence, leading to more effective programs.
Increased Openness & Accountability: technology can improve transparency and accountability by providing real-time data on program performance.
Greater Scalability: Well-designed technology solutions can enable organizations to scale their programs more effectively.
* Stronger Security Posture: A dedicated cybersecurity team can protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of organizational systems.
For those working in social development tech, navigating this challenging landscape requires proactive steps.
- Upskill in High-Demand Areas: Focus on developing skills in areas like data science, cybersecurity, cloud computing,