Women Face Higher Insurance Costs Than Men, New Analysis Reveals
Table of Contents
- 1. Women Face Higher Insurance Costs Than Men, New Analysis Reveals
- 2. The Gender Premium Gap
- 3. Premiums by Age group
- 4. Understanding Insurance Premiums
- 5. Frequently Asked Questions About Insurance Costs
- 6. How have advancements in actuarial science and risk modeling shifted the reliance on individual leadership within insurance companies?
- 7. Unveiling the Multi-faceted Power Behind the Insurance Giant: More Than Just a Man’s Influence
- 8. The Evolution of a Financial Fortress: Beyond Individual Leadership
- 9. Core Pillars of Insurance Company Power
- 10. The Role of Technology & Data Analytics in Modern Insurance
- 11. The Impact of Macroeconomic Factors on Insurance Giants
- 12. Case Study: The Response to Hurricane ian (2022)
health-related policies.">
A recent extensive analysis reveals that Women are paying a important premium – literally – for insurance coverage compared to their male counterparts.The study, conducted by Habit Factory, examined the insurance coverage status of 10,000 men and women across various age groups, uncovering a consistent pattern of higher costs for women.
The data demonstrates that Women exhibit a stronger inclination towards securing coverage for critical areas like disease and cancer insurance. While this proactive approach to health is commendable,it appears to translate into increased premium burdens. Guaranteed Insurance,encompassing coverage for events such as hospitalization,accidents,and death,shows notable discrepancies between genders.
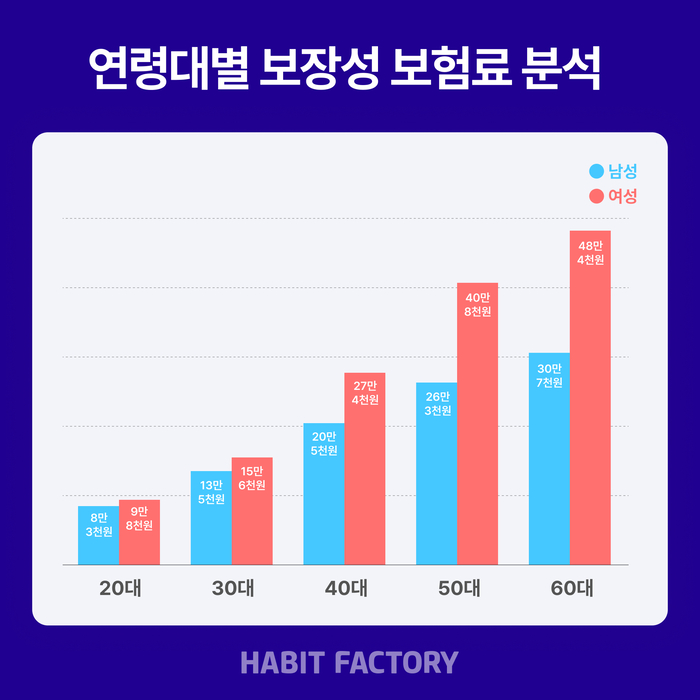
the disparity in premiums widens considerably with age. Individuals in their 60s face the largest gap, with men averaging 307,115 won in annual premiums, while women pay 484,636 won. This trend continues across other age brackets:
| Age Group | Average Male Premium (Won) | Average Female Premium (Won) | Difference (Won) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60s | 307,115 | 484,636 | 177,521 |
| 50s | 26,905 | 40,8490 | 13,9440 |
| 40s | 20,5927 | 27,4276 | 6,8349 |
| 30s | 13,553 | 15,6123 | 2,0593 |
| 20s | 8,3014 | 9,902 | 1,6006 |
As individuals age, the difference in insurance costs between men and women escalates. The gap was relatively small in the 20s at 15,5888 won, but expanded dramatically to 177,521 won in the 60s.
Officials at Habit Factory emphasize that while men may currently demonstrate lower engagement with insurance products, initiating coverage at a younger age can afford them more affordable premiums over time.
Did You Know? According to the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC), gender-based pricing in insurance is a complex issue, often justified by actuarial data reflecting differing risk profiles.
Pro Tip: Shop around and compare quotes from multiple insurance providers to ensure you’re receiving the best possible rate for your coverage needs.
Is this pricing fair, or does it reflect broader societal biases? What can be done to ensure equitable access to affordable insurance for all?
Insurance premiums are calculated based on a variety of factors, including age, gender, health status, lifestyle, and the type of coverage sought. Insurers use actuarial science – the assessment and management of risk – to determine these rates.
While gender-based pricing is permissible in many jurisdictions, it is subject to increasing scrutiny due to concerns about fairness and potential discrimination. Several states are actively considering regulations to address these disparities.
External Link: National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC)
Frequently Asked Questions About Insurance Costs
- Why do women generally pay more for insurance? Women often pay higher premiums due to statistical differences in health and longevity,leading insurers to perceive them as a higher risk group overall.
- What is actuarial science and how does it impact insurance rates? Actuarial science involves the assessment of risk and the calculation of appropriate insurance premiums based on statistical data.
- Can I negotiate my insurance premium? While direct negotiation is frequently enough limited, you can explore discounts, adjust your coverage, and compare quotes from different providers.
- Is gender-based insurance pricing legal? The legality of gender-based pricing varies by jurisdiction, with increasing debate around fairness and potential discrimination.
- What steps can men take to lower their insurance premiums? Starting coverage at a younger age and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can definitely help lower premiums for men.
How have advancements in actuarial science and risk modeling shifted the reliance on individual leadership within insurance companies?
Unveiling the Multi-faceted Power Behind the Insurance Giant: More Than Just a Man’s Influence
The Evolution of a Financial Fortress: Beyond Individual Leadership
For decades, the narrative surrounding major insurance companies frequently enough centered on a charismatic leader – the face of the brand. However,attributing success solely to a single individual drastically underestimates the complex interplay of factors that propel these institutions. Today’s insurance giants, like Prudential, New York Life, and State Farm, are built on robust systems, data-driven strategies, and a deeply ingrained culture of risk management. Understanding this shift is crucial for investors, industry professionals, and anyone seeking to comprehend the stability – and potential vulnerabilities – of these financial powerhouses. This article delves into the core components that define their enduring strength, moving beyond the “man at the helm” trope.
Core Pillars of Insurance Company Power
The strength of a major insurance provider isn’t simply about premium collection; it’s a refined operation built on several key pillars:
Actuarial Science & Risk modeling: This is the bedrock. Accurate risk assessment,predicting mortality rates,and forecasting claims are paramount. Advanced algorithms and data analytics are now integral, moving beyond customary statistical methods.
Investment Portfolio Management: Insurance companies are massive institutional investors. Their ability to generate returns on premiums collected directly impacts profitability and policyholder dividends (where applicable). Diversification across asset classes – stocks, bonds, real estate, and increasingly, alternative investments – is key.
regulatory Compliance & Capital Adequacy: The insurance industry is heavily regulated. Maintaining sufficient capital reserves to meet future claims is non-negotiable. Solvency ratios and stress tests are constant concerns.
Distribution Networks: Whether through independent agents, brokers, or direct sales channels, a robust distribution network is vital for reaching target markets and securing new buisness. Digital change is reshaping these networks.
Claims Processing Efficiency: A smooth, fair, and efficient claims process builds trust and customer loyalty.Technology, including AI-powered claims assessment, is streamlining this process.
The Role of Technology & Data Analytics in Modern Insurance
The insurance landscape is undergoing a rapid digital transformation. Insurtech – the application of technology to improve insurance processes – is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a present-day reality.
AI and Machine Learning: Used for fraud detection, personalized pricing, and automated claims processing. This leads to reduced operational costs and improved customer experience.
Big Data Analytics: Analyzing vast datasets to identify trends, assess risk more accurately, and develop new insurance products. Data-driven decision making is now standard practice.
Telematics & IoT: In auto insurance, telematics devices track driving behavior, enabling usage-based insurance (UBI) and personalized premiums.The Internet of Things (IoT) is expanding into home and health insurance, offering proactive risk mitigation.
Blockchain Technology: potential applications include secure data storage, fraud prevention, and streamlined claims processing. While still in early stages, blockchain offers long-term promise.
The Impact of Macroeconomic Factors on Insurance Giants
Insurance companies aren’t immune to broader economic forces. Several macroeconomic factors considerably influence their performance:
Interest Rate Environment: Low interest rates can squeeze investment yields, impacting profitability. Conversely, rising rates can boost investment income.
Inflation: Increased claims costs due to inflation (e.g., medical expenses, repair costs) can erode margins.
Geopolitical Risks: Global events, such as pandemics or political instability, can trigger large-scale claims and disrupt investment portfolios.
Demographic Shifts: Aging populations and changing mortality rates impact life insurance and health insurance demand.
Climate Change: Increased frequency and severity of natural disasters (hurricanes, wildfires, floods) are driving up property and casualty claims. Climate risk assessment is becoming a critical component of underwriting.
Case Study: The Response to Hurricane ian (2022)
Hurricane Ian, which devastated parts of Florida in 2022, provided a stark illustration of the challenges facing the insurance industry. The event resulted in an estimated $50-65 billion in insured losses. Major insurers faced significant claims volume, logistical hurdles in deploying adjusters, and scrutiny over coverage disputes.