Ancient Clay Deposits On mars Point To Potential For Past Life
The search for life beyond Earth has taken a significant leap forward. Recent findings indicate that vast clay deposits on Mars where formed in stable, water-rich environments. These conditions suggest that the red planet, billions of years ago, might have supported microbial life.
The implications of this discovery are profound. Such clay deposits could hold vital clues about Mars’s ancient past, transforming our understanding of planetary habitability.
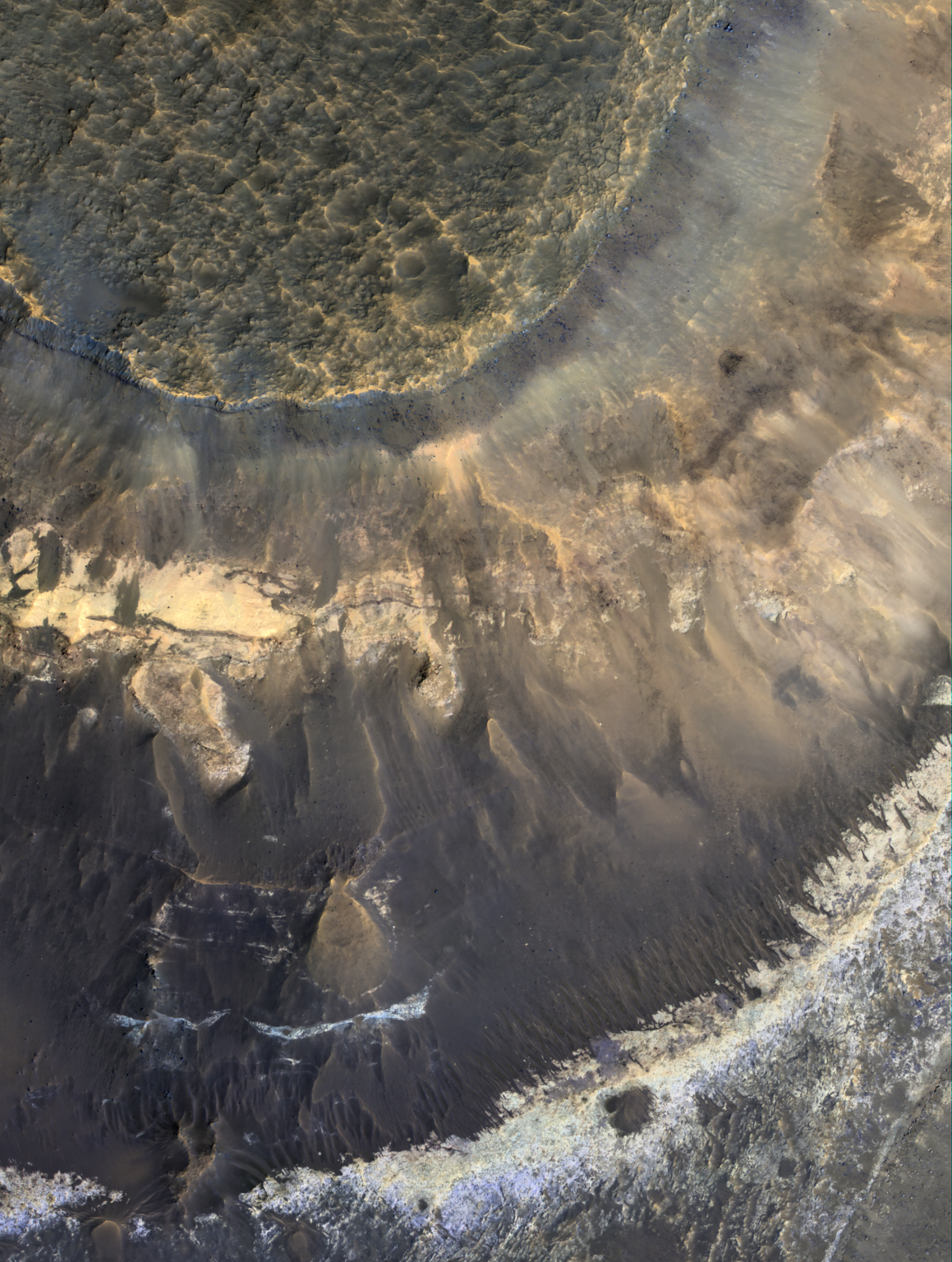
Vast Clay layers Suggest Habitable Conditions
Analysis of Martian landscapes reveals extensive clay deposits, some hundreds of feet thick, across the planet. These layers are similar to those found in tropical regions on Earth, where clay minerals are known for their ability to preserve traces of ancient life.
Published on June 16, 2025, in Nature Astronomy, the research highlights that these clay deposits likely formed in the presence of standing bodies of liquid water, such as lakes. This environment could have been conducive to the development and survival of microbial organisms.
The Formation of Martian Clays
The formation of clay deposits requires water, and their presence on Mars indicates a wetter, more Earth-like past. While the exact processes are still under investigation, scientists believe that these clay deposits resulted from the chemical weathering of rocks in the presence of water over extended periods.
This weathering process not only creates clay minerals but can also trap and preserve organic molecules, providing a potential record of past biological activity.
Did You Know? Clay minerals have a unique layered structure that allows them to absorb and protect organic molecules, making them excellent candidates for preserving biosignatures.
Comparison With Earth: key Differences
While Martian clays share similarities with those on Earth, there are notable differences. Unlike Earth, Mars lacks plate tectonics, which recycles the planet’s crust.This absence affects the chemical interactions between rocks, water, and gases like carbon dioxide.
One result of this difference is the “missing carbonates” puzzle. On Earth, carbon dioxide interacts with fresh rock to form carbonate minerals, effectively locking away the gas. The lack of fresh rock on Mars may explain why scientists have not found extensive carbonate clay deposits that you find on earth, despite the presence of carbon dioxide in its early atmosphere.
Could Martian Clays Harbor Life?
The discovery of extensive clay deposits significantly boosts the possibility of finding evidence of past life on Mars. These regions represent stable environments where liquid water was present for extended periods, a key requirement for life as we know it.
Future missions to Mars will likely target these clay-rich areas. They will search for biosignatures, such as organic molecules and microbial fossils, which could provide definitive proof of past life.
Pro Tip: Scientists use advanced techniques like mass spectrometry and X-ray diffraction to analyze the composition of clay minerals and identify potential biosignatures.
Implications for Future Mars Exploration
The most recent discovery has significant implications for future Mars exploration. Identifying areas with substantial clay deposits refines the search for potential landing sites and sample collection locations.
Future missions can prioritize these sites, increasing the likelihood of finding evidence related to life. This knowledge guides the development of specialized instruments and search strategies,thus,maximizing the chances of a groundbreaking discovery.
How do you think this discovery will influence the next Mars mission? What specific technologies should be prioritized for detecting potential biosignatures in these clay deposits?
the Broader Context: Mars and the Search for Extraterrestrial Life
The search for life on Mars is part of a broader effort to understand the potential for life beyond Earth. Mars, with its past evidence of water activity and potentially habitable environments, remains a primary target in this quest.
Discoveries on Mars not only shed light on the planet’s history but also provide valuable insights into the conditions that may support life elsewhere in the universe. Learning about the formation and composition of clay deposits on Mars helps scientists refine the search for habitable environments on other planets and moons.
Comparison Table: Earth vs. Mars
Here’s a table summarizing key differences and similarities between Earth and Mars, focusing on factors relevant to the formation and preservation of clay deposits:
| Feature | Earth | Mars |
|---|---|---|
| Presence of Liquid Water | Abundant | Evidence of past abundance, now limited |
| Plate Tectonics | Active | Absent |
| Atmospheric Density | High | Low |
| Carbonate Formation | Extensive | limited, “missing carbonates” puzzle |
| Clay Deposits | Widespread | Widespread |
| Potential for Life | Confirmed | Potential, under investigation |
Frequently Asked Questions About Clay deposits On Mars
-
Why are Clay Deposits on Mars critically important?
They suggest past water activity, a key ingredient for life.
-
Where are these Clay Deposits located?
Widespread across Mars, including the Hellas basin.
-
How do they compare to Earth’s clays?
Similar, but Mars lacks plate tectonics influencing formation.
-
Can Clay Deposits preserve life traces?
Yes, they can trap and protect organic molecules.
-
What’s next for Mars exploration?
Targeting Clay Deposits for biosignatures.
What are your thoughts on the prospect of discovering life on Mars? Share this article and join the conversation!
