Recent research has evaluated the potential of ipratropium bromide, an established bronchodilator, as a treatment option for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This investigation utilized advanced artificial intelligence to identify the drug’s efficacy when combined with remdesivir, an antiviral medication widely used for COVID-19 treatment. The study, conducted in South Korea, sheds light on innovative approaches to treating severe cases of COVID-19 and highlights the integration of AI in drug discovery.
The study, titled “A Randomized, Open-Label, Controlled Clinical Trial of Remdesivir Plus Ipratropium Bromide Versus Remdesivir Alone in Patients With Severe COVID-19,” was approved by the Institutional Review Board. It involved eight patients diagnosed with COVID-19, confirmed through molecular methods, including reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The trial aimed to assess the therapeutic effectiveness of ipratropium bromide alongside remdesivir in hospitalized patients.
Participants were stratified based on disease severity, with classifications aligned to World Health Organization (WHO) criteria. Severe cases exhibited clinical signs of pneumonia, while mild cases did not present with significant respiratory distress. The research team collected blood samples from patients at diagnosis and recovery stages, isolating human peripheral blood mononuclear cells for analysis.
Methodology and Data Collection
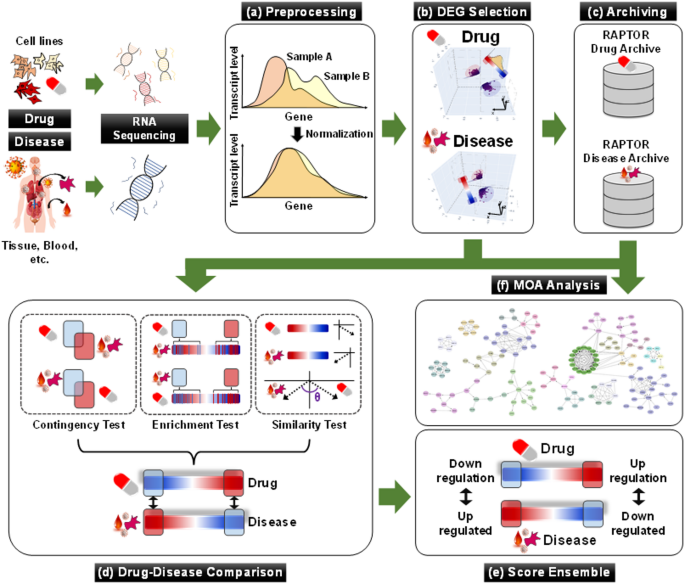
The research utilized a sophisticated AI drug-screening platform known as RAPTOR AI, which processes extensive transcriptome datasets to identify potential drug candidates. The platform evaluated gene expression profiles between normal and diseased states to determine the suitability of ipratropium bromide in treating COVID-19. This approach underscores the growing role of artificial intelligence in accelerating drug discovery and repurposing existing medications for new therapeutic uses.
In addition to the AI analysis, the study too employed traditional laboratory methods to assess the efficacy of the treatments. Vero cells, a type of cell line used for viral research, were infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus to evaluate the antiviral effects of both remdesivir and ipratropium bromide. The assessment included measuring cell viability and viral titers following treatment, providing a comprehensive view of the drugs’ impacts at the cellular level.
Results and Implications
Initial results from the trial indicated that the combination therapy of remdesivir and ipratropium bromide may provide enhanced benefits for patients with severe COVID-19. The study reported improvements in clinical outcomes, although detailed statistical analyses are expected to follow to validate these findings. The exploration of ipratropium bromide, typically used to manage chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), as an adjunct therapy in COVID-19 represents a promising avenue for treatment.
The study’s findings align with broader trends in healthcare, where repurposing existing medications can lead to rapid treatment options during urgent health crises. The integration of AI in this process not only expedites the identification of potential therapies but also optimizes treatment strategies based on real-world data.
Future Directions
As the clinical trial progresses, researchers will continue to monitor the efficacy and safety of the combination therapy in a larger patient population. The ongoing analysis will be crucial in determining the role of ipratropium bromide in COVID-19 management and whether it can be effectively incorporated into standard treatment protocols.
The implications of this research extend beyond COVID-19, as the methodologies employed could revolutionize how healthcare providers approach drug discovery and treatment optimization. The successful application of AI in identifying effective therapies could pave the way for new strategies in combating various infectious diseases.
Given the evolving nature of COVID-19 and its variants, continuous research is essential. Stakeholders in the healthcare sector are encouraged to stay informed about the latest developments in treatment options and the potential of AI-driven methodologies in enhancing patient care.
For those interested in the advancements in COVID-19 treatments and the role of artificial intelligence in medicine, engaging in discussions and sharing insights can foster a collaborative effort in improving health outcomes.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for medical concerns.